Java NIO(New IO或 Non Blocking IO)是从java 1.4版本开始引入的一个新的IO
API,可以替代标准的Java IO API。NIO支持面向缓冲区的、基于通道的IO操作。NIO将以更加高效的方式进行文件的读写操作。
java IO 与 java NIO 的区别

一、通道(Channel)与缓冲区(Buffer)
若需要使用 NIO 系统,需要获取用于连接 IO 设备的通道以及用于容纳数据的缓冲区。然后操作缓冲区,对数据进行处理。简而言之,Channel 负责传输, Buffer 负责存储。
1、缓冲区(Buffer)
缓冲区(Buffer) :一个用于特定基本数据类型的容器。由 java.nio 包定义的,所有缓冲区都是 Buffer 抽象类的子类。
Java NIO 中的 Buffer 主要用于与 NIO 通道进行交互,数据是从通道读入缓冲区,从缓冲区写入通道中的。
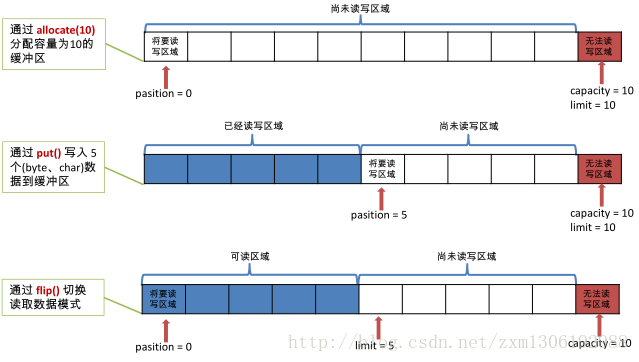
Buffer 的常用方法
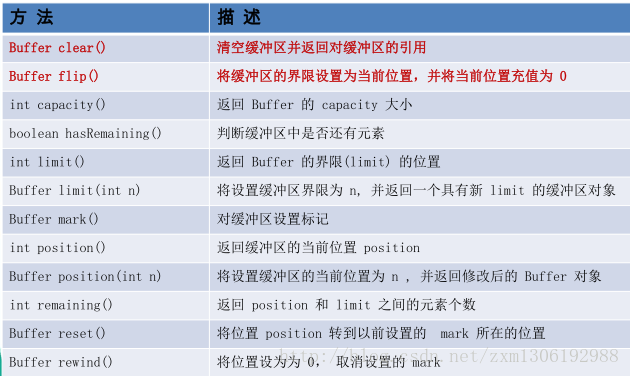
非直接缓冲区
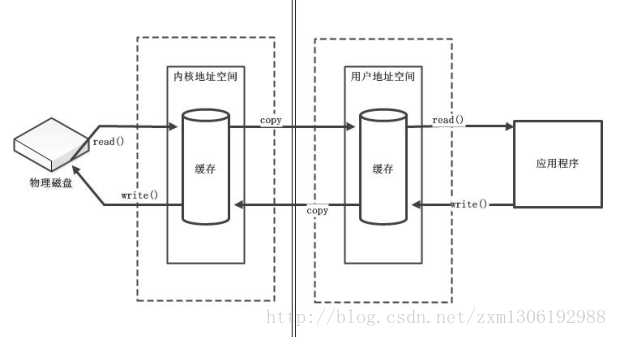
直接缓冲区
public class TestBuffer {
@Test
public void test1(){
String str="abcde";
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
System.out.println("--------------allocate()----------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
buf.put(str.getBytes());
System.out.println("-------------put()-------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
buf.flip();
System.out.println("--------------flip()------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
byte[] dst=new byte[buf.limit()];
buf.get(dst);
System.out.println(new String(dst,0,dst.length));
System.out.println("--------------get()------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
buf.rewind();
System.out.println("--------------rewind()------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
buf.clear();
System.out.println("--------------clear()------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
System.out.println((char)buf.get());
}
@Test
public void test2(){
String str="abcde";
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buf.put(str.getBytes());
buf.flip();
byte[] dst=new byte[buf.limit()];
buf.get(dst,0,2);
System.out.println(new String(dst,0,2));
System.out.println(buf.position());
buf.mark();
buf.get(dst,2,2);
System.out.println(new String(dst, 2, 2));
System.out.println(buf.position());
buf.reset();
System.out.println(buf.position());
if(buf.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(buf.remaining());
}
}
@Test
public void test3(){
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
System.out.println(buf.isDirect());
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
2、通道(Channel)
通道:由java.nio.channels包定义。
Channel表示IO源与目标打开的连接。
Channel类似于传统的“流”。但其自身不能直接访问数据,Channel只能与Buffer进行交互。
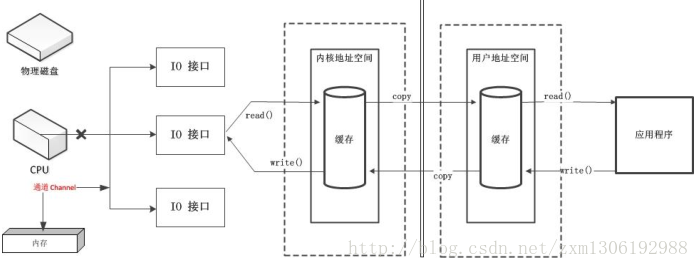
操作系统中:通道是一种通过执行通道程序管理I/O操作的控制器,它使主机(CPU和内存)与I/O操作之间达到更高的并行程度。需要进行I/O操作时,CPU只需启动通道,然后可以继续执行自身程序,通道则执行通道程序,管理与实现I/O操作。
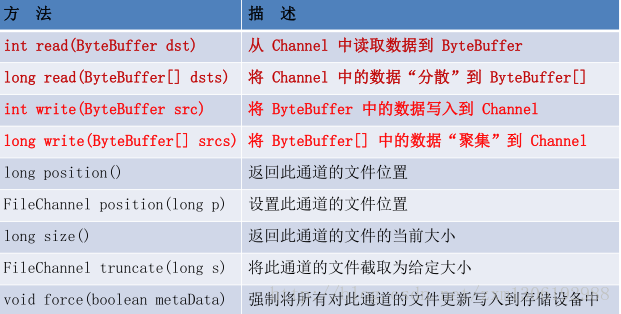
FileChannel 的常用方法
public class TestChannel {
@Test
public void test1(){
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
FileInputStream fis=null;
FileOutputStream fos=null;
FileChannel inChannel=null;
FileChannel outChannel=null;
try{
fis=new FileInputStream("d:/1.avi");
fos=new FileOutputStream("d:/2.avi");
inChannel=fis.getChannel();
outChannel=fos.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(inChannel.read(buf)!=-1){
buf.flip();
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(outChannel!=null){
try {
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(inChannel!=null){
try {
inChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos!=null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fis!=null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时间:"+(end-start));
}
@Test
public void test2() {
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
FileChannel inChannel=null;
FileChannel outChannel=null;
try {
inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/1.avi"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
outChannel=FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/2.avi"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
MappedByteBuffer inMappedBuf=inChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outMappedBuf=outChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size());
byte[] dst=new byte[inMappedBuf.limit()];
inMappedBuf.get(dst);
outMappedBuf.put(dst);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(outChannel!=null){
try {
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(inChannel!=null){
try {
inChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费的时间为:"+(end-start));
}
@Test
public void test3(){
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
FileChannel inChannel=null;
FileChannel outChannel=null;
try {
inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/1.avi"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
outChannel=FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/2.avi"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
inChannel.transferTo(0, inChannel.size(), outChannel);
outChannel.transferFrom(inChannel, 0, inChannel.size());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(outChannel!=null){
try {
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(inChannel!=null){
try {
inChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费的时间为:"+(end-start));
}
@Test
public void test4(){
RandomAccessFile raf1=null;
FileChannel channel1=null;
RandomAccessFile raf2=null;
FileChannel channel2=null;
try {
raf1=new RandomAccessFile("1.txt","rw");
channel1=raf1.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buf1=ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
ByteBuffer buf2=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
ByteBuffer[] bufs={buf1,buf2};
channel1.read(bufs);
for(ByteBuffer byteBuffer : bufs){
byteBuffer.flip();
}
System.out.println(new String(bufs[0].array(),0,bufs[0].limit()));
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(new String(bufs[1].array(),0,bufs[1].limit()));
raf2=new RandomAccessFile("2.txt", "rw");
channel2=raf2.getChannel();
channel2.write(bufs);
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(channel2!=null){
try {
channel2.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(channel1!=null){
try {
channel1.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(raf2!=null){
try {
raf2.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(raf1!=null){
try {
raf1.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void test5(){
Map<String,Charset> map=Charset.availableCharsets();
Set<Entry<String,Charset>> set=map.entrySet();
for(Entry<String,Charset> entry:set){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"="+entry.getValue());
}
}
@Test
public void test6(){
Charset cs1=Charset.forName("GBK");
CharsetEncoder ce=cs1.newEncoder();
CharsetDecoder cd=cs1.newDecoder();
CharBuffer cBuf=CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
cBuf.put("啦啦哈哈吧吧");
cBuf.flip();
ByteBuffer bBuf=null;
try {
bBuf = ce.encode(cBuf);
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int i=0;i<12;i++){
System.out.println(bBuf.get());
}
bBuf.flip();
CharBuffer cBuf2=null;
try {
cBuf2 = cd.decode(bBuf);
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(cBuf2.toString());
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
二、NIO 的非阻塞式网络通信
传统的 IO 流都是阻塞式的。也就是说,当一个线程调用 read() 或 write()时,该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取或写入,该线程在此期间不能执行其他任务。因此,在完成网络通信进行 IO 操作时,由于线程会阻塞,所以服务器端必须为每个客户端都提供一个独立的线程进行处理,当服务器端需要处理大量客户端时,性能急剧下降。
Java NIO 是非阻塞模式的。当线程从某通道进行读写数据时,若没有数据可用时,该线程可以进行其他任务。线程通常将非阻塞 IO 的空闲时间用于在其他通道上执行 IO 操作,所以单独的线程可以管理多个输入和输出通道。因此,NIO 可以让服务器端使用一个或有限几个线程来同时处理连接到服务器端的所有客户端。
选择器(Selector)
选择器(Selector) 是 SelectableChannle 对象的多路复用器,Selector 可以同时监控多个 SelectableChannel 的 IO 状况,也就是说,利用 Selector可使一个单独的线程管理多个 Channel。Selector 是非阻塞 IO 的核心。
public class TestBlockingNIO {
@Test
public void client() throws IOException{
SocketChannel sChannel=SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9898));
FileChannel inChannel=FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(inChannel.read(buf)!=-1){
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
sChannel.shutdownOutput();
int len=0;
while((len=sChannel.read(buf))!=-1){
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len));
buf.clear();
}
inChannel.close();
sChannel.close();
}
@Test
public void server() throws IOException{
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
FileChannel outChannel=FileChannel.open(Paths.get("2.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
SocketChannel sChannel=ssChannel.accept();
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(sChannel.read(buf)!=-1){
buf.flip();
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
buf.put("服务端接收数据成功".getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
sChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
ssChannel.close();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
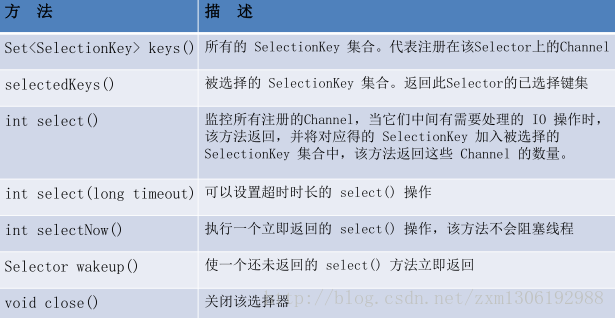
SelectionKey
当调用 register(Selector sel, int ops) 将通道注册选择器时,选择器对通道的监听事件,需要通过第二个参数 ops 指定。
可以监听的事件类型(用 可使用 SelectionKey 的四个常量 表示):
读 : SelectionKey.OP_READ (1)
写 : SelectionKey.OP_WRITE (4)
连接 : SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT (8)
接收 : SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT (16)
若注册时不止监听一个事件,则可以使用“位或”操作符连接。
SelectionKey:表示 SelectableChannel 和 Selector 之间的注册关系。每次向选择器注册通道时就会选择一个事件(选择键)。选择键包含两个表示为整数值的操作集。操作集的每一位都表示该键的通道所支持的一类可选择操作。
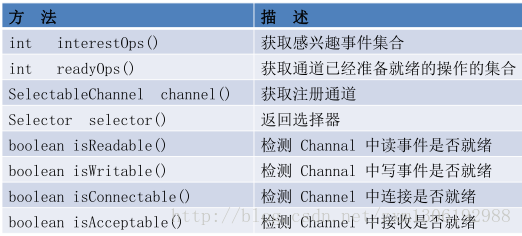
Selector 的常用方法
public class TestNonBlockingNIO {
@Test
public void client()throws IOException{
SocketChannel sChannel=SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNext()){
String str=scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString()+"
"+str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
sChannel.close();
}
@Test
public void server() throws IOException{
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
Selector selector=Selector.open();
ssChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while(selector.select()>0){
Iterator<SelectionKey> it=selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey sk=it.next();
if(sk.isAcceptable()){
SocketChannel sChannel=ssChannel.accept();
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else if(sk.isReadable()){
SocketChannel sChannel=(SocketChannel)sk.channel();
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len=0;
while((len=sChannel.read(buf))>0){
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len));
buf.clear();
}
}
it.remove();
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
DatagramChannel
Java NIO中的DatagramChannel是一个能收发UDP包的通道。
public class TestNonBlockNIO2 {
@Test
public void send() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel dc=DatagramChannel.open();
dc.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNext()){
String str=scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString()+"
"+str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
dc.send(buf, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
buf.clear();
}
dc.close();
}
@Test
public void receive() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel dc=DatagramChannel.open();
dc.configureBlocking(false);
dc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
Selector selector=Selector.open();
dc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
while(selector.select()>0){
Iterator<SelectionKey> it=selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey sk=it.next();
if(sk.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
dc.receive(buf)
;
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,buf.limit()));
buf.clear();
}
}
it.remove();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
管道 (Pipe)
Java NIO 管道是2个线程之间的单向数据连接。Pipe有一个source通道和一个sink通道。数据会被写到sink通道,从source通道读取。

public class TestPipe {
@Test
public void test1()throws IOException{
Pipe pipe=Pipe.open();
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel=pipe.sink();
buf.put("通过单向管道发送数据".getBytes());
buf.flip();
sinkChannel.write(buf);
Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel=pipe.source();
buf.flip();
int len=sourceChannel.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len));
sourceChannel.close();
sinkChannel.close();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
三、NIO.2 – Path 、Paths 、Files
Path 与 Paths
- java.nio.file.Path 接口代表一个平台无关的平台路径,描述了目录结构中文件的位置。
- Paths 提供的 get() 方法用来获取 Path 对象:Path get(String first, String … more) : 用于将多个字符串串连成路径。
- Path 常用方法:
- boolean endsWith(String path) : 判断是否以 path 路径结束
- boolean startsWith(String path) : 判断是否以 path 路径开始
- boolean isAbsolute() : 判断是否是绝对路径
- Path getFileName() : 返回与调用 Path 对象关联的文件名
- Path getName(int idx) : 返回的指定索引位置 idx 的路径名称
- int getNameCount() : 返回Path 根目录后面元素的数量
- Path getParent() :返回Path对象包含整个路径,不包含Path 对象指定的文件路径
- Path getRoot() :返回调用 Path 对象的根路径
- Path resolve(Path p) :将相对路径解析为绝对路径
- Path toAbsolutePath() : 作为绝对路径返回调用 Path 对象
- String toString() : 返回调用 Path 对象的字符串表示形式
Files 类
java.nio.file.Files 用于操作文件或目录的工具类。
- Files常用方法:
- Path copy(Path src, Path dest, CopyOption … how) : 文件的复制
- Path createDirectory(Path path, FileAttribute< ? > … attr) : 创建一个目录
- Path createFile(Path path, FileAttribute< ? > … arr) : 创建一个文件
- void delete(Path path) : 删除一个文件
- Path move(Path src, Path dest, CopyOption…how) : 将 src 移动到 dest 位置
- long size(Path path) : 返回 path 指定文件的大小
-
Files常用方法:用于判断
- boolean exists(Path path, LinkOption … opts) : 判断文件是否存在
- boolean isDirectory(Path path, LinkOption … opts) : 判断是否是目录
- boolean isExecutable(Path path) : 判断是否是可执行文件
- boolean isHidden(Path path) : 判断是否是隐藏文件
- boolean isReadable(Path path) : 判断文件是否可读
- boolean isWritable(Path path) : 判断文件是否可写
- boolean notExists(Path path, LinkOption … opts) : 判断文件是否不存在
- public static < A extends BasicFileAttributes> A readAttributes(Path path,Class< A > type,LinkOption…options) : 获取与 path 指定的文件相关联的属性。
-
Files常用方法:用于操作内容
- SeekableByteChannel newByteChannel(Path path, OpenOption…how) : 获取与指定文件的连接,how 指定打开方式。
- DirectoryStream newDirectoryStream(Path path) : 打开 path 指定的目录
- InputStream newInputStream(Path path, OpenOption…how):获取 InputStream 对象
- OutputStream newOutputStream(Path path, OpenOption…how) : 获取 OutputStream 对象









