属性集【Properties】
java.util.Properties类继承于Hashtable,用来表示一个持久的属性集。它使用键值结构存储数据,每个键及其对应的值都是一个字符串。
-
public Properties():创建一个空的属性集列表
共性的api方法
-
public Object setProperty(String key,String value): 保存一对属性。
-
public String getProperty(String key):使用此属性列表中的指定的键搜索对应的值。
-
public Set<String> stringPropertyNames():获取所有键的名称并封装到Set集合中。
与流相关的方法
-
public void load(InputStream input):从字节输入流中读取键值对
参数中使用了字节输入流,通过流对象,可以关联到某个文件上,这样就可以加载文件中的数据。文件中的数据格式:
格式:key = value
例如: date=小孙 size=12000 name=abc.txt
代码演示:
1 //0.构建一个流对象
2 FileReader fr = new FileReader("day29_IO\abc.txt");
3 //1.创建Properties集合
4 Properties properties = new Properties();
5 //2.使用Properties集合中的各方法load读取保存在输入流中的数据
6 properties.load(fr);
7 //遍历Properties集合
8 final Set<String> set = properties.stringPropertyNames();
9 for (String key : set) {
10 //通过key获取value值
11 final String value = properties.getProperty(key);
12 System.out.println(key + " = "+ value);
13 }
14 fr.close();
15 /*
16 age = 18
17 date = 小孙
18 name = abc.txt
19 size = 120000
20 目的地 = D:abc.txt
21 */
-
public void store(OutputStream out,String comments):从集合当中的数据写入到字节输出流中
1 //1.创建Properties集合对象,添加数据
2 final Properties properties = new Properties();
3 properties.setProperty("四大名著1", "红楼梦");
4 properties.setProperty("四大名著2", "水浒传");
5 properties.setProperty("四大名著3", "三国演义");
6 properties.setProperty("四大名著4", "西游记");
7 //2.创建字节输出流/字符输出流对象,构造方法中绑定需要写入数据的目的地
8 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("day29_IO\abcd.txt", true);
9 //3.使用Properties集合中的方法store,把集合当中的临时数据,持久化写入硬盘当中存储
10 properties.store(fw, "si da ming zhu");
11 //4.释放资源
12 fw.close();
缓冲流【Buffered】
按照类型分为:
-
字符缓冲流:BufferedReader,BufferedWriter
-
字节缓冲流:BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream
缓冲流的基本原理,是在创建流对象的时候,会先创建一个内置的默认大小的缓冲区数组,通过缓冲区读写数据,减少系统IO操作的彩虹色,减少开销,提高程序的读写的效率。
字节缓冲流
构造方法:
-
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream input) 创建一个新的缓冲输入流
-
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream output)创建一个新的缓冲输出流
代码示例:
1 /*
2 BufferedInputStream extends InputStream
3 它里面含有从父类继承过来的api方法“close()、read(int b)、read(byte[] bytes)...
4
5 字节缓冲输出流
6 构造方法
7 - public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)创建一个 BufferedInputStream 并保存其参数,即输入流 in,以便将来使用。
8 - public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in,int size) 创建具有指定缓冲区大小的 BufferedInputStream
9 并保存其参数,即输入流 in,以便将来使用。
10 使用步骤
11 1.创建一个FileInputStream流对象,构造方法中绑定需要读取数据的数据源
12 2.创建BufferedInputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileInputStream流对象
13 3.使用BufferedInputStream对象中的方法read,把数据读取到内存中。
14 4.释放资源。
15 */
16 import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
17 import java.io.FileInputStream;
18 import java.io.IOException;
19
20 public class Demo01BufferedInputStream {
21 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
22 //1.创建一个FileInputStream流对象,构造方法中绑定需要读取数据的数据源
23 final FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("day29_IO\one.txt");
24 //2.创建BufferedInputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileInputStream流对象
25 final BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
26 //3.使用BufferedInputStream对象中的方法read,把数据读取到内存中。
27 /*int len = 0;
28 while ((len = bis.read()) != -1){
29 System.out.println((char)len);
30 }*/
31 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
32 int len = 0;//记录读到有效字节个数
33 while ((len = bis.read(bytes))!= -1){
34 System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));//HelloWorld_Java
35 }
36 //4. 释放资源。
37 bis.close();
38 fis.close();
39 }
40 }
1 /*
2 BufferedOutputStream extends OutputStream
3 它里面含有从父类继承过来的api方法“close()、flush()、write(int b)、write(byte[] bytes)...
4
5 字节缓冲输出流
6 构造方法
7 - public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream output)创建一个新的缓冲输出流,将数据写入到字节输出流中。
8 - public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream output,int size)
9 创建一个新的缓冲输出流,将具有指定缓冲区大小的数据写入字节输出流中
10 使用步骤
11 1.创建一个FileOutputStream流对象,构造方法中绑定需要写入数据的目的地
12 2.创建BufferedOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileOutputStream流对象
13 3.使用BufferedOutputStream对象中的方法write,把数据写入到内部缓冲区中。
14 4.使用BufferedOutputStream对象中的方法flush,把内存缓冲区中的数据刷新到目的地中。
15 5.释放资源。
16 */
17
18 import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
19 import java.io.FileOutputStream;
20 import java.io.IOException;
21
22 public class Demo02BufferedOutputStream {
23 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
24
25 // 1.创建一个FileOutputStream流对象,构造方法中绑定需要写入数据的目的地
26 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("day29_IO\one.txt");
27 //2.创建BufferedOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileOutputStream流对象
28 final BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
29 //3.使用BufferedOutputStream对象中的方法write,把数据写入到内部缓冲区中。
30 bos.write("HelloWorld_Java".getBytes());
31 //4.使用BufferedOutputStream对象中的方法flush,把内存缓冲区中的数据刷新到目的地中。
32 bos.flush();
33 //5.释放资源。
34 bos.close();
35 fos.close();
36 }
37 }
字符缓冲流
构造方法
-
public BufferedWriter(Writer out):创建一个新的字符缓冲输出流
-
public BuffererReader(Reader in):创建一个新的字符缓冲输入流
特有方法
-
BufferedReader:public String readLine():读取整行的文本信息。
-
BufferedWriter:public void newLine():写入一行的行分隔符,由系统属性定义换行符号。
字符缓冲输入流代码演示:
1 //1.创建一个字符缓冲输入流对象,构造方法中传递一个字符输入流
2 final BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("day29_IO\abc.txt"));
3 //2.使用字符缓冲输入流对象中的read/readLine
4 /*String str = br.readLine();
5 System.out.println(str);*/
6 //循环的结束条件 readLine()返回值是null
7 String str = null;
8 while ((str = br.readLine()) != null){
9 System.out.println(str);
10 }
11 //3.释放资源。
12 br.close();
字符缓冲输出流代码演示:
1 //1.创建一个字符缓冲输出流对象,构造方法中传递一个字符输出流
2 final BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("day29_IO\two.txt"));
3 //2.调用字符缓冲输出流对象中的write,把数据写入到内存缓冲区中
4 bw.write("我今天中午吃的面太辣了,我学习了PS");
5 bw.newLine();
6 bw.write("MikuMikudance软件");
7 bw.newLine();
8 bw.write("c4d");
9 //3.调用字符缓冲输出流对象中的flush方法,把内存缓冲区中的数据刷新到文件中。
10 bw.flush();
11 //4.释放资源。
12 bw.close();
练习:文件复制
代码演示:
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
2 show01();
3 show02();
4 }
5 //不使用缓冲流的操作
6 public static void show01() throws IOException {
7 final long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
8 //1.构建字节输入流对象
9 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\dongtu.gif");
10 //2.构建一个字节输出流对象
11 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("day29_IO\doutu.gif");
12 //3.调用字节输入流对象中的方法read()
13 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
14 int len = 0;
15 while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
16 //4.把读取到的字节内容写入到目的地文件中,调用write(byte[] b,int off,int len)
17 fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
18 }
19 //5.释放资源 先开后关
20 fos.close();
21 fis.close();
22 final long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
23 System.out.println("文件复制耗费的时间为:" + (end - start));//1720
24 }
25 public static void show02() throws IOException {
26 //获取开始的时间
27 final long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
28 //1.构建一个字节缓冲输入流
29 final BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\dongtu" +
30 ".gif"));
31 //2.构建一个字节缓冲输出流
32 final BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\code\doutu.gif"));
33 //3.调用字节缓冲输入流对象中的方法read(byte[] b)读取文件
34 final byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
35 //确定while循环结束条件 read() == -1
36 int len = 0;//记录读取到的有效字节个数
37 while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
38 //4.把读取到的字节内容写入到目的地文件中,调用write
39 bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
40 }
41 //5.释放资源
42 bos.close();
43 bis.close();
44 final long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
45 System.out.println("文件复制耗费的时间为:" + (end - start)); //582
46 }
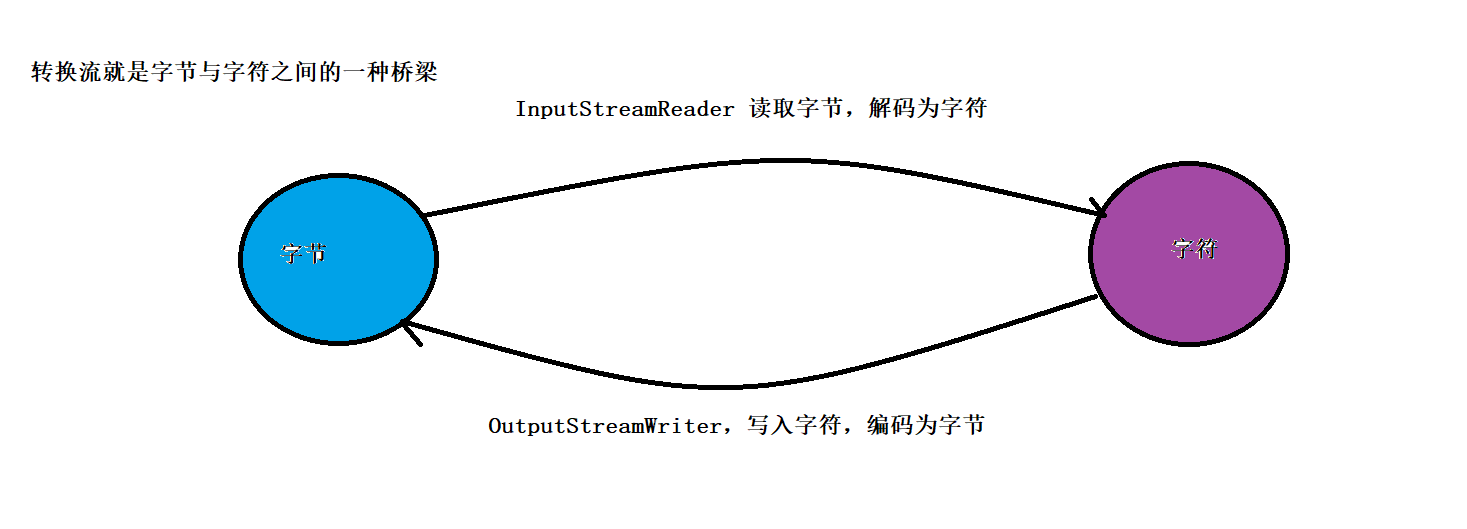
转换流【字节流< – – >字符流】
字符编码:
按照某种规则,将字符存储到计算机中,称为编码;反之,将存储在计算机中的二进制数按照某种规则解析显示出来,称为解码。在进行编码和解码过程中,我们必须采用同一种规则,才能保证数据正常,否则,会导致乱码现象
-
字符编码:就是一套自然语言中的字符与二进制数之间的对应规则。
字符集:
-
字符集:是一个系统可支持的所有字符的集合,包括各国文字,标点符号,图形符号,数字等,也叫编码表。
计算机中要准确的存储和识别各种文字的字符符号,需要进行字符编码,一套字符即至少有一套字符编码。
常见的字符编码集有ASCII字符集、GBK字符集、Unicode字符集。
ASCII字符集:
-
ASCII是基于拉丁字母的一套电脑编码系统,用于显示现代英语
-
基本的ASCII字符集,使用7位(bit)表示一个字符,共128个字符。ASCII的扩展字符集使用8位(bit)表示一个字符,共256个字符
ISO-8859-1字符集:
-
拉丁码表,别名– – Lantin-1,用于显示欧洲使用的语言,包括荷兰、丹麦、德语、意大利语、西班牙语等。
-
ISO-8859-1使用单字节码表,兼容ASCII码表。
GB字符集
-
GB2312:称为简体中文码表,里面大概含有7000多个简体汉字,此外数学符号,罗马希腊的字母、日本的假名都编进去了,连在ASCII里的原来就有的数字、标点、字母都统统重新用的两个字节编写进去了。
-
GBK:最常用的中文码表。是在原来的GB2312码表基础上进行扩展。使用双字节编码。共收录了21000多个汉字,完全兼容GB2312标准,同时支持繁体汉字以及日韩汉字等。
-
GB18030:最新的中文码表,共收录了7万多汉字,采用多字节编码,每个字可以有1个字节,2个字节或者4个字节组成,支持国内少数民族的文字,同时支持繁体字以及日韩汉字等。
Unicode字符集:
-
Unicode编码系统为表达任意语言的任意字符而设计的,是业界的标准,也成为了同一编码,标准万国码表。
-
它最多使用4个字节的数字来表示每个字母、符号、或者文字,有三种常见的编码方案:UTF-8,UTF-16,UTF-32.
-
UTF-8编码表,用来表示Unicode标准中的任意字符,编码规则:
1.128个US-ASCII字符,使用的是一个字节编码
2.拉丁字的字母,需要两个字节编码
3.大部分常见的汉字,使用的是三个字节编码
4.其他极少数的辅助字符,采用的四个字节编码
编码会引发的问题
由于编码规则不一致,导致引发乱码现象。
那么如何读取GBK编码的文件呢?
InputStreamReader类
转换流java.io.InputStreamreader是Reader的子类,它是从字节流到字符流的桥梁。它读取字节,并使用指定的字符集将其解码为字符。它的字符集可以由名称指定,或者可以使用平台默认的字符集。
构造方法
-
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in):创建一个使用默认的字符集的字符流。】
-
public InpuStreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName):创建一个指定字符集的字符流。
代码演示:
1 //读取使用GBK编码的文件 2 public static void show01() throws IOException { 3 //1.创建InputStreamReader对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流和指定的编码表名称 4 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("E:\文档\正课文档\day29\新建文本文档.txt"), "GBK"); 5 //2.使用InputStreamReader对象中的方法read来读取文件中的信息 6 int len = 0; 7 while ((len = isr.read())!= -1){ 8 System.out.print((char)len ); 9 } 10 //3.释放资源 11 isr.close(); 12 }
OutputStream类
转换流java.io.OutputStreamWriter是Writer的子类,它是字符流到字节流的桥梁。使用指定的字符集将字符编码为字节。它的字符集可以手动指定,也可以使用平台默认的字符集。
构造方法
-
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out):创建一个使用平台默认的字符集的字符流
-
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out,String charsetName):创建一个指定的字符集的字符流。