视频版B站地址:从零开始写代码 Python 遗传算法实例2 调度车间问题_哔哩哔哩_bilibili






代码
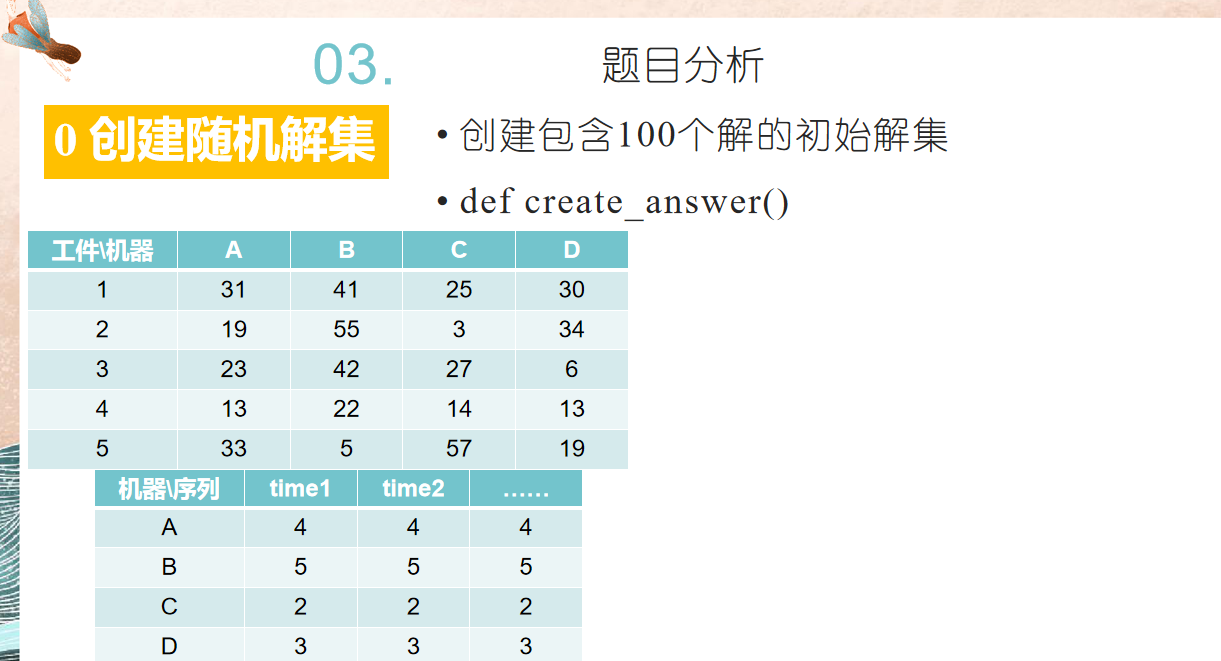
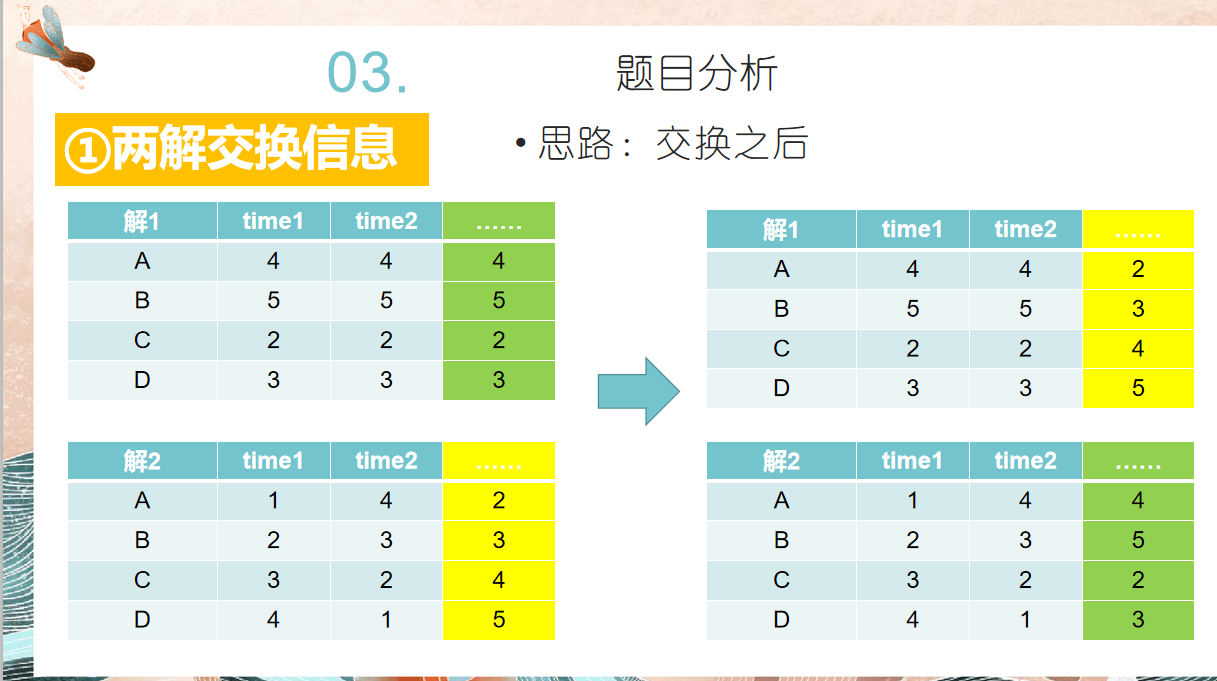
# author:会武术之白猫 # date:2021-10-20 # 调度算法的遗传实现 import random def test_008(nums): def random_answer(nums): fact_n = len(nums) fact = [1 for i in range(fact_n)] machine_n = len(nums[0]) result = [[]for i in range(machine_n)] while(True): if sum(fact) == 0: break choice = [i for i in range(fact_n)] for i in range(machine_n): val = random.choices(choice)[0] choice.remove(val) if fact[val] == 0: result[i].append('') continue result[i].append(val) fact[val] -= 1/nums[val][i] if fact[val] < 0: fact[val] = 0 # for item in result: # print(item) # print(fact) # print(len(result[0])) return result def start(answer, n, nums): res = [1 for i in range(len(nums))] for i in range(len(answer)): for j in range(n): if answer[i][j] == '': continue res[answer[i][j]] -= 1/nums[answer[i][j]][i] if res[answer[i][j]] < 0: res[answer[i][j]] = 0 return res def end(answer, res, nums): n = -1 while(True): if sum(res) == 0 or n == len(answer[0]) - 1: break n += 1 for i in range(len(answer)): if answer[i][n] == '': continue res[answer[i][n]] -= 1/nums[answer[i][n]][i] if res[answer[i][n]] < 0: res[answer[i][n]] = 0 return n + 2 def change(x, y): length = len(x[0]) x_left = [] x_right = [] y_left = [] y_right = [] for i in range(len(x)): x_left.append(x[i][:length // 2]) x_right.append(x[i][length //2:]) y_left.append(y[i][:length // 2]) y_right.append(y[i][length //2:]) res_x = start(x_left, length // 2, nums) n_x = end(y_right, res_x, nums) res_y = start(y_left, length // 2, nums) n_y = end(x_right, res_y, nums) x, y = [], [] for i in range(len(x_left)): mid_x = x_left[i] + y_right[i][:n_x] mid_y = y_left[i] + x_right[i][:n_y] x.append(mid_x) y.append(mid_y) return [x, y] def variate(new_group): return new_group group_num = 1000 times = 100 group = [] choice = [] res_group = [] for i in range(group_num): answer = random_answer(nums) group.append(answer) choice.append(1/len(answer[0])) choice = [item/sum(choice) for item in choice] for i in range(1, len(choice)): choice[i] += choice[i - 1] for i in range(times): new_group = [] for j in range(group_num//2): team = [] for t in range(2): y = random.random() if choice[0] >= y: team.append(group[0]) continue for tt in range(1, len(choice)): if choice[tt - 1] < y and y <= choice[tt]: team.append(group[tt]) break new_group.extend(change(team[0], team[1])) new_group = variate(new_group) group = new_group mid_group = [len(item[0]) for item in new_group] min_index = mid_group.index(min(mid_group)) res_group.append([new_group[min_index], min(mid_group)]) res_group.sort(key = lambda x:x[1], reverse = False) for item in res_group: print(item[1]) for item in res_group[0][0]: print(item) return nums = [[31,41,25,30], [19,55,3,34], [23,42,27,6], [13,22,14,13], [33,5,57,19]] test_008(nums)