1.代理模式
找个人将你原本想做的事情给做了。
三个部分组成:
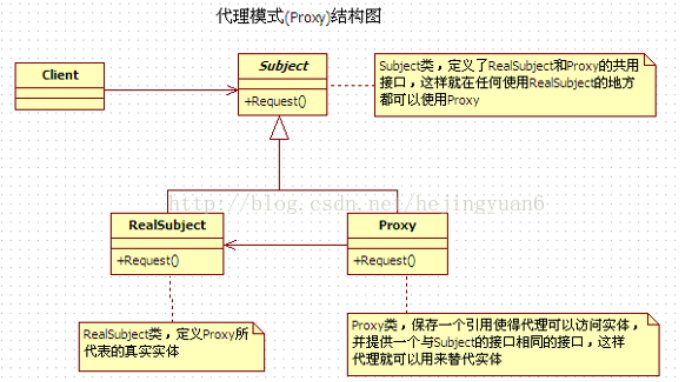
抽象主题角色:真实主题和代理主题的共同接口。
真实主题角色:定义了代理角色所代表的真实对象。
代理主题角色:含有对真实主题角色的引用。代理角色通常在将客户端调用传递给真实主题对象之前或者之后执行某些操作。
以收快递的案例:
收快递并签字,这个是抽象主题。
买家,货物的主人,这个是真实主题。
门卫代理收货并签字,这个是代理主题。
代理模式的类图:
实现步骤:
1).定义一个抽象的主题。
package com.jinglin.staticproxy; /** * 定义一个抽象的主题,这个主题就规定了方法 * @author sony * */ public interface IGetSomething { void getsomething(); }
2)实现的是真实主题的类,这个类继承自抽象主题:
public class RealGetSomething implements IGetSomething { @Override public void getsomething() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("主人亲自收货并签字了"); } }
3)实现的是代理主题的类,这个类继承自抽象主题,但是这个类关联了所代理的主题对象。
package com.jinglin.staticproxy; /** * 这是一个代理主题,也需要继承自抽象主题 * @author sony * */ public class ProxyGetSomething implements IGetSomething { private RealGetSomething realGetSomething;//依赖关系 public RealGetSomething getRealGetSomething() { return realGetSomething; } public void setRealGetSomething(RealGetSomething realGetSomething) { this.realGetSomething = realGetSomething; } public ProxyGetSomething(RealGetSomething _realGetSomething){ this.realGetSomething=_realGetSomething; } @Override public void getsomething() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub getbefore(); realGetSomething.getsomething(); getafter(); } private void getbefore(){ System.out.println("检查快递是否是本小区的"); } private void getafter(){ System.out.println("快递签收完毕"); } }
4)编写客户端调用的类(对外部开放的):
package com.jinglin.staticproxy; public class ClientDemo { private IGetSomething igetsomething; public IGetSomething getIgetsomething() { return igetsomething; } public void setIgetsomething(IGetSomething igetsomething) { this.igetsomething = igetsomething; } public ClientDemo(IGetSomething _igetsomething){ this.igetsomething=_igetsomething; } public void show(){ igetsomething.getsomething(); } }
5)最后编写测试类:
package com.jinglin.test; import org.junit.Test; import com.jinglin.staticproxy.ClientDemo; import com.jinglin.staticproxy.IGetSomething; import com.jinglin.staticproxy.ProxyGetSomething; import com.jinglin.staticproxy.RealGetSomething; public class ProxyStaticTest { @Test public void testit(){ RealGetSomething realGetSomething = new RealGetSomething(); IGetSomething igetsomething = new ProxyGetSomething(realGetSomething); ClientDemo client = new ClientDemo(igetsomething); client.show(); } }
2.分析刚才所实现的代理模式的问题
1)实现一个代理,必然要定义一个接口,要实现这个接口。如果一旦代理的内容很多,那么实现的接口就会很多。
2)代理平台,这个代理平台就帮我们实现根据传入的对象来实现代理。
动态代理,模拟mybatis的动态代理
a.首先定义了一个所有数据操作的接口层:
package com.jinglin.mybatis; /** * 定义一个接口,这个接口就规定了对数据库的操作 * @author sony * */ public interface ICommandData { void opdata(); }
b.定义一个继承自这个接口的真实主题对象:
public class DeleteData implements ICommandData { @Override public void opdata() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("这是对于数据库的删除方法"); }
}
另外一个:
public class SelectData implements ICommandData{ @Override public void opdata() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("这是对于数据库的查询的方法"); } }
c.定义一个动态代理的平台:模拟了一个getMapper方法:
package com.jinglin.mybatis; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; public class MybatisMapperHandler implements InvocationHandler { private Object obj; public void getconnection(){ System.out.println("获取连接对象,获取执行命令对象"); } public void closeconnection(){ System.out.println("执行完毕,关闭连接对象"); } public Object getMapper(Class<?> classz) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException { obj = classz.newInstance(); return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classz.getClassLoader(), classz.getInterfaces(), this); } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { getconnection(); Object ret = method.invoke(obj, args); closeconnection(); return ret; } }
最后在测试的时候调用:
public class TestIt { @Test public void testit() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException{ MybatisMapperHandler mybatisMapperHandler = new MybatisMapperHandler(); ICommandData icommandData = new SelectData(); ICommandData selectdatamapper=(ICommandData) mybatisMapperHandler.getMapper(icommandData.getClass()); selectdatamapper.opdata(); ICommandData icommandData2 = new DeleteData(); icommandData2 = (ICommandData) mybatisMapperHandler.getMapper(icommandData2.getClass()); icommandData2.opdata(); } }
4.AOP编程
1)程序代码的构成部分?
通用代码+业务代码
2)开发一个销售记录和进货的功能,每次销售和每次进货都要有日志记录。

业务代码和通用代码的分离的思想,AOP思想,在实际开发的时候将通用代码植入到所需的业务代码中。AOP减少模块间的耦合,低侵入
3)AOP的开发,可以借助于Spring。
Aspect(切面):
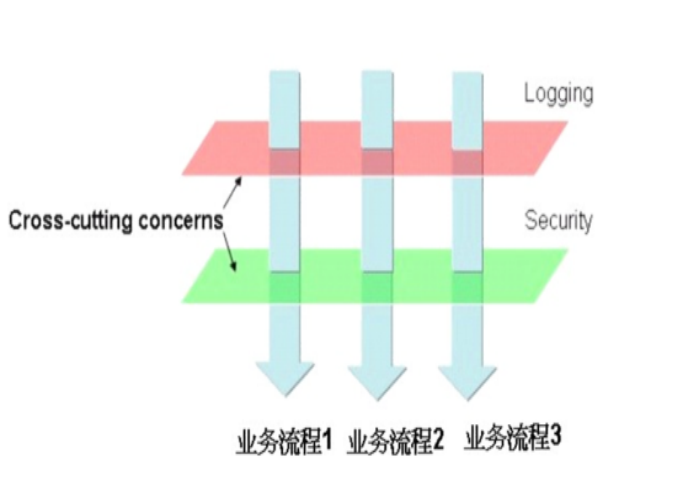
将散落于各个业务逻辑之中的Cross-cutting concerns收集起来,设计成各个独立可重用的对象,这些对象称为Aspect
例:动态代理中的LogHandler就是一个Aspect
Advice(增强):在特定的连接点上执行的动作,执行的这个动作就相当于对原始对象的功能做了增强。
Aspect对Cross-cutting concerns(横切关注点)的具体实现称为Advice。
Advice中包括了Cross-cutting concerns的行为或所要提供的服务
例:在动态代理的示例中代理类的invoke()就是Advice的具体实例
Joinpoint(连接点):
Advice在应用程序执行时加入业务流程的点或时机称为Joinpoint,具体来说就是Advice在应用程序中被执行的时机
Spring只支持方法的Joinpoint,执行时机可能是某个方法被执行之前或之后
Pointcut(切入点):切入点就是一系列连接点的集合。
Pointcut定义了感兴趣的Joinpoint,当调用的方法符合Pointcut表示式时,将Advice织入应用程序上提供服务
在Spring中,您可以在定义文件或Annotation中编写Pointcut,说明哪些Advice要应用至方法的前后
Target(目标对象):真正执行业务逻辑的对象
一个Advice被应用的对象或目标对象,也就是被代理的类
例:在动态代理的示例中HelloSpeaker就是LogHandler中Advice的Target
Weave(织入):将切面整合到程序的执行流程中
Advice被应用至对象之上的过程称为织入,在AOP中织入的方式有几个时间点:
编译时期
类加载时期
执行时期
案例:
开发一个商业信息管理系统,这个商业信息管理系统主要的功能就是销售,就是进货。通用功能就是日志记录,权限检查,事务处理等。
1)开发业务类或者通用代码的类。

注意,类与类之间无任何关联。
2)将开发的类加入到spring中,作为bean。
首先修改beans的声明
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd">
<!-- 将bean对象加入到容器中 --> <!-- 配置业务类的bean--> <bean id="purchaseservice" class="com.jinglin.aop.service.PurchaseService"></bean> <bean id="sellservice" class="com.jinglin.aop.service.SellService"></bean> <!-- 配置切面类的 --> <bean id="logcommon" class="com.jinglin.aop.common.LogCommon"></bean> <bean id="rolecommon" class="com.jinglin.aop.common.RoleCommon"></bean>
3)配置AOP的切面:
<!--对于AOP的配置 --> <aop:config> <!-- 配置程序执行前的切面类 --> <aop:aspect id="roleaspect" ref="rolecommon"> <!-- 配置连接点的集合 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com..*.*Service.*(..))" id="mypointcut"/> <!--业务方法执行之前的配置增强 --> <aop:before method="beforeexecution" pointcut-ref="mypointcut"/> </aop:aspect> <!-- 配置程序执行后的切面类 --> <aop:aspect id="logaspect" ref="logcommon"> <!-- 配置连接点的集合 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com..*.*Service.*(..))" id="mypointcut2"/> <!--业务方法执行之后的配置增强 --> <aop:after method="afterexecution" pointcut-ref="mypointcut2"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
4)编写测试类:
public class AopTest { static ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac=null; static{ ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); } @Test public void aoptest(){ //进货 PurchaseService purchaseService=(PurchaseService) ac.getBean("purchaseservice"); purchaseService.stockit(); //销售 SellService sellService=(SellService) ac.getBean("sellservice"); sellService.sellit(); } }