一,队列的定义
♦和栈相反,队列是一种先进先出的线性表。它只允许在表的一端进行插入,而在另一端进行删除元素。
♦在队列中,允许插入的一端叫队尾。允许删除的一端叫队头。
♦队列中的元素按a0,a1.....an这个顺序入队,退队时也必须按这个顺序出队。即a0出队后,a1才可以出队。
二,顺序队列的表示和实现
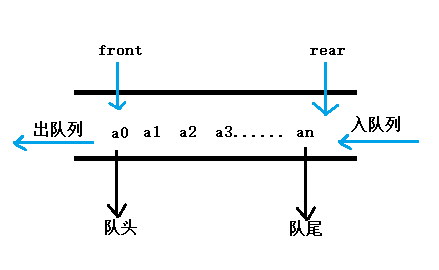
在队列的顺序存储结构中,除了用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储从队头到队尾的元素外,
还需附设两个指针front和rear分别指向队列头元素及队尾元素的下一个位置。
初始化建立空队列时,令front=rear=0;每当插入新的队列尾元素时,“尾指针增1”,每当删除
队列头元素时,“头指针增1”。
因此,在非空队列中,头指针始终指向队列头元素,而尾指针始终指向队列尾元素的下一个位置。
代码展示:
1 import java.util.*; 2 class Queue{ 3 // 存储队列的元素 4 private int[] queue; 5 // 队头 6 private int front; 7 // 队尾 8 private int rear; 9 10 public Queue() { // 初始化一个长度为15的队列 11 /*this.queue=new int[15]; 12 this.front=0; 13 this.rear=0;*/ 14 this(15); 15 } 16 17 // 自定义队列大小 18 public Queue(int size) { 19 this.queue=new int[size]; 20 this.front=0; 21 this.rear=0; 22 } 23 24 // 入队操作 25 public void offer(int val){ 26 if(full()) //入队前对队空间进行检测 27 { //队满,则扩容 28 this.queue=Arrays.copyOf(this.queue,this.queue.length+1); 29 } 30 this.queue[this.rear]=val; //放一个元素,rear下标后移一位,所以rear指向的是最后一个元素的下一位 31 this.rear++; 32 } 33 34 // 出队,并把队头元素返回 35 public int poll(){ 36 if(empty()) //出队前判断是否队空 37 { 38 return -1; 39 } 40 return this.queue[front++]; // 41 } 42 43 // 查看队头元素 44 public int peek(){ 45 return this.queue[front]; 46 } 47 48 // 判断队满 49 public boolean full(){ 50 return this.queue.length==this.rear; 51 } 52 53 // 判断队空 54 public boolean empty(){ 55 return this.rear==this.front; 56 } 57 } 58 59 public class Queuetext { 60 public static void main(String[] args) { 61 Queue qq=new Queue(5); 62 for(int i=0;i<5;i++) 63 { 64 qq.offer(i); //入队 65 } 66 67 if(qq.full()) //查看队满 68 { 69 System.out.println("队满!"); 70 } 71 System.out.println(qq.peek()); //打印队头 72 System.out.println(qq.poll()); //出队 73 System.out.println(qq.poll()); 74 System.out.println(qq.poll()); 75 System.out.println(qq.poll()); 76 System.out.println(qq.poll()); 77 if(qq.empty()) //查看队空 78 { 79 System.out.println("队空!"); 80 } 81 } 82 }
代码实现:

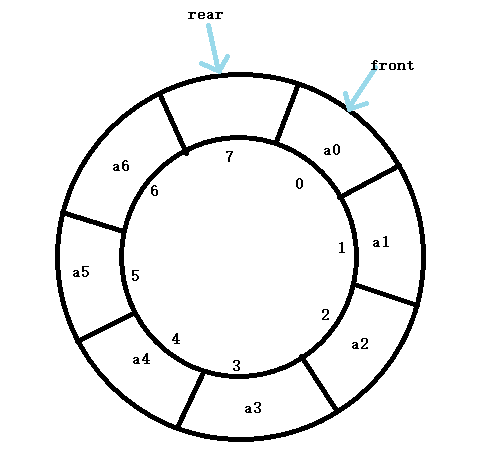
三,循环队列的表示和实现
因为采用顺序栈存储数据时,当头指针和尾指针都指向队列的末尾时,即使队列前面
是空的,也会因为被判断队满而无法继续存储。为了充分利用向量空间,克服“假溢出”的现象
因此人们便想出了循环队列的存储方式。
循环队列中是把顺序队列首尾相连,把存储队列元素的表从逻辑上看成一个环。当存储
空间的最后一个位置已被占用,而在要进入队列时,只需第一个位置空闲,便可将元素加入
到第一个位置中,即将存空间的第一个位置作为队尾。
循环队列可以更简便防止“假溢出”的情况发生,但队列的大小却是固定的。
在循环队列中,指针和队列元素之间的关系不变。
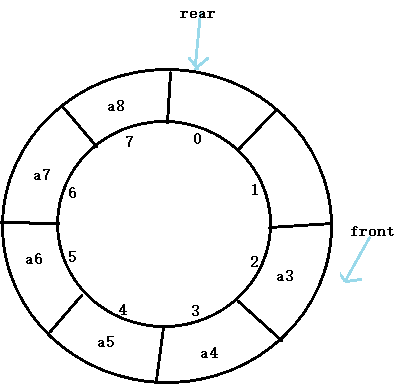
在顺序队列中,采用q.front=q.rear来判断队空。用q.stack.length=q.rear来判断队满。
但在循环队列中,去不适用。
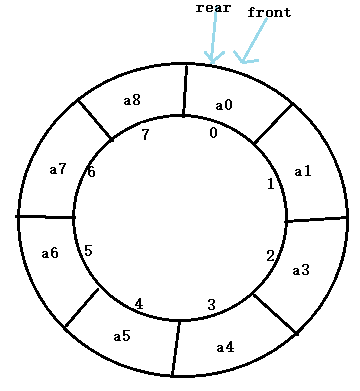
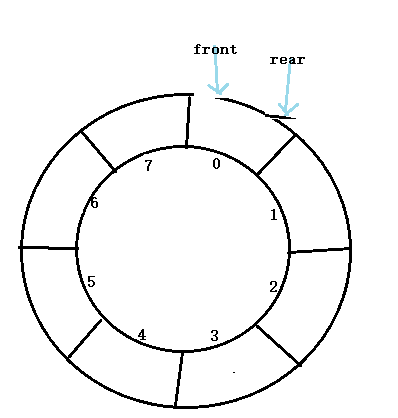
此时队满,q.front=q.rear 此时队空,q.front=q.rear
所以在循环队列中,为区别两种情况,规定循环队列最多只能存放MaxSize-1个元素,当循环队列
中只剩下一个元素时,队列就已经满了。
并且用 队空:q.front=q.rear 队满:q.front=(q.rear+1)%n 来判断队列情况。
1 import java.util.*; 2 class Queue{ 3 // 存储队列的元素 4 private int[] queue; 5 // 队头 6 private int front; 7 // 队尾 8 private int rear; 9 10 public Queue() { // 初始化一个长度为15的队列 11 /*this.queue=new int[15]; 12 this.front=0; 13 this.rear=0;*/ 14 this(15); 15 } 16 17 // 自定义队列大小 18 public Queue(int size) { 19 this.queue=new int[size]; 20 this.front=0; 21 this.rear=0; 22 } 23 24 // 入队操作 25 public void offer(int val){ 26 if(full()) //入队前对队空间进行检测 27 { //队满,则扩容 28 this.queue=Arrays.copyOf(this.queue,this.queue.length+1); 29 } 30 this.queue[this.rear]=val; //放一个元素,rear下标后移一位,所以rear指向的是最后一个元素的下一位 31 this.rear=(this.rear+1)%this.queue.length; //这样写是为了将队列环起来 32 } 33 34 // 出队,并把队头元素返回 35 public int poll(){ 36 if(empty()) //出队前判断是否队空 37 { 38 return -1; 39 } 40 return this.queue[front++]; // 41 } 42 43 // 查看队头元素 44 public int peek(){ 45 return this.queue[front]; 46 } 47 48 // 判断队满 49 public boolean full(){ 50 51 return this.front==(this.rear+1)%this.queue.length; 52 } 53 54 // 判断队空 55 public boolean empty(){ 56 return this.rear==this.front; 57 } 58 } 59 60 public class Queuetext { 61 public static void main(String[] args) { 62 Queue qq=new Queue(5); 63 for(int i=0;i<5;i++) 64 { 65 qq.offer(i); //入队 66 } 67 68 if(qq.full()) //查看队满 69 { 70 System.out.println("队满!"); 71 } 72 System.out.println(qq.peek()); //打印队头 73 System.out.println(qq.poll()); //出队 74 System.out.println(qq.poll()); 75 System.out.println(qq.poll()); 76 System.out.println(qq.poll()); 77 System.out.println(qq.poll()); 78 if(qq.empty()) //查看队空 79 { 80 System.out.println("队空!"); 81 } 82 } 83 }