Description
Little Victor adores the sets theory. Let us remind you that a set is a group of numbers where all numbers are pairwise distinct. Today Victor wants to find a set of integers S that has the following properties:
- for all x
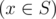 the following inequality holds l ≤ x ≤ r;
the following inequality holds l ≤ x ≤ r; - 1 ≤ |S| ≤ k;
- lets denote the i-th element of the set S as si; value
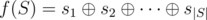 must be as small as possible.
must be as small as possible.
Help Victor find the described set.
The first line contains three space-separated integers l, r, k (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ 1012; 1 ≤ k ≤ min(106, r - l + 1)).
Print the minimum possible value of f(S). Then print the cardinality of set |S|. Then print the elements of the set in any order.
If there are multiple optimal sets, you can print any of them.
8 15 3
1
2
10 11
8 30 7
0
5
14 9 28 11 16
Operation 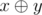 represents the operation of bitwise exclusive OR. In other words, it is the XOR operation.
represents the operation of bitwise exclusive OR. In other words, it is the XOR operation.
正解:分类讨论
解题报告:
今天考试原题,直接上题解:
分类讨论。
首先注意到(2x) ⊕ (2x + 1) = 1。一个直接推论就是(2x) ⊕ (2x + 1) ⊕ (2x + 2) ⊕(2x + 3) = 0。而k ≥ 5的时候一定可以选出四个数其异或和为0(例如,如果l是偶数,那么选l, l + 1, l + 2, l + 3,否则选l + 1, l + 2, l + 3, l + 4。这样总是合法的,因为r ≥ l + 4)。
然后按照k的值分类讨论。
k = 1。答案就是l。
k = 2。如果r = l + 1,那么答案是min(l ⊕ r, l),其中l表示只选一个数,l ⊕ r表示选两个数。否则答案一定为1。当r > l + 1的时候,如果l是偶数,那么答案是l ⊕ (l + 1),否则答案是(l + 1) ⊕ (l + 2)。
k = 3。答案不会超过1,因为从[l, r]中选两个数一定可以使得答案为1。我们关心的是三个数的异或和为0的情况。这3个数的最高位不可能相同(否则异或起来的最高位为1)。设这三个数为x, y, z(x < y <z),且y = 2 ^k + b, z = 2^ k + c, b < c。那么x ⊕ b ⊕ c = 0。为了让l ≤ x, y, z ≤ r,我们需要使得x尽量大而c尽量小。假设x ≥ 2 ^(k−1) ,那么可以推出z ≥ 2^( k−1) + 2^ k 。我们需要使x尽量大而c尽量小,那么令x = 2 ^(k − 1), z = 2 ^(k−1) + 2^ k ,可以得到y = z − 1。满足要求。那么如果x < 2^( k−1) 呢?我们会发现:此时z没必要≥ 2^ k ,因为取y = 2^( k−1 + b), z = 2 ^(k−1 )+ c依然满足条件。
所以枚举k并检查x = 2 ^k − 1, z = 2^ k + 2^( k−1) , y = z − 1这三个数是否在[l, r]内,如果在的话,就找到了一组解。
k = 4。如果r − l ≥ 4,那么答案一定为0。否则,枚举{x|x ∈ Z ∧ l ≤ x ≤ r}的所有子集,求异或和的最小值。
我的代码后面分类讨论部分写丑了。
1 //It is made by jump~ 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <cstdio> 6 #include <cmath> 7 #include <algorithm> 8 #include <ctime> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <queue> 11 #include <map> 12 #include <set> 13 using namespace std; 14 typedef long long LL; 15 LL l,r,len; 16 int k; 17 LL jilu1,jilu2,jilu3,num; 18 19 inline int getint() 20 { 21 int w=0,q=0; 22 char c=getchar(); 23 while((c<'0' || c>'9') && c!='-') c=getchar(); 24 if (c=='-') q=1, c=getchar(); 25 while (c>='0' && c<='9') w=w*10+c-'0', c=getchar(); 26 return q ? -w : w; 27 } 28 29 inline LL getlong() 30 { 31 LL w=0,q=0; 32 char c=getchar(); 33 while((c<'0' || c>'9') && c!='-') c=getchar(); 34 if (c=='-') q=1, c=getchar(); 35 while (c>='0' && c<='9') w=w*10+c-'0', c=getchar(); 36 return q ? -w : w; 37 } 38 39 inline LL check(){ 40 LL t=0; 41 while( ((1LL<<t)-1LL) < l) t++; 42 if(( (1LL<<t)+(1LL<<(t-1LL)) )<=r) return t; 43 return -1; 44 } 45 46 inline void work(){ 47 LL now; 48 l=getlong(); r=getlong(); k=getint(); len=r-l+1; 49 if(k==1) printf("%I64d 1 %I64d",l,l); 50 else if(k==2) { 51 if(l&1) { 52 if(r-l+1==2){ 53 if((l^r)<l) printf("%I64d 2 %I64d %I64d",l^r,l,r); 54 else printf("%I64d 1 %I64d",l,l); 55 } 56 else printf("1 2 %I64d %I64d",l+1,l+2); 57 } 58 else printf("1 2 %I64d %I64d",l,l+1); 59 } 60 else if(k==3) { 61 if((now=check())!=-1) { 62 printf("0 3 "); printf("%I64d ",(1LL<<now)-1LL); 63 printf("%I64d %I64d",(1LL<<now)+(1LL<<(now-1LL))-1LL, (1LL<<now)+(1LL<<(now-1LL) ) ); 64 } 65 else { printf("1 2 "); if(l&1) printf("%I64d %I64d",l+1,l+2); else printf("%I64d %I64d",l,l+1); } 66 } 67 else{ 68 if(l&1) { 69 if(r-l+1>4) printf("0 4 %I64d %I64d %I64d %I64d",l+1,l+2,l+3,l+4); 70 else{ 71 now=l; num=1; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) for(int j=i+1;j<4;j++) if( ((l+i)^(l+j)) < now) now=((l+i)^(l+j)),num=2,jilu1=l+i,jilu2=l+j; 72 if( (l^(l+1)^(l+2) ) < now) now=(l^(l+1)^(l+2) ),num=3,jilu1=l,jilu2=l+1,jilu3=l+2; if( (l^(l+1)^(l+3) ) < now) now=(l^(l+1)^(l+3) ),num=3,jilu1=l,jilu2=l+1,jilu3=l+3; 73 if( (l^(l+2)^(l+3) ) < now) now=(l^(l+2)^(l+3) ),num=3,jilu1=l,jilu2=l+2,jilu3=l+3; if( ((l+1)^(l+2)^(l+3) ) < now) now=((l+1)^(l+2)^(l+3)),num=3,jilu1=l+1,jilu2=l+2,jilu3=l+3; 74 if( (l^(l+1)^(l+2)^(l+3) ) < now) now=(l^(l+1)^(l+2)^(l+3) ),num=4; 75 printf("%I64d %I64d ",now,num); if(num==1) printf("%I64d",now); else if(num==2) printf("%I64d %I64d",jilu1,jilu2); else if(num==3) printf("%I64d %I64d %I64d",jilu1,jilu2,jilu3); else printf("%I64d %I64d %I64d %I64d",l,l+1,l+2,l+3); 76 } 77 } 78 else printf("0 4 %I64d %I64d %I64d %I64d",l,l+1,l+2,l+3); 79 } 80 } 81 82 int main() 83 { 84 work(); 85 return 0; 86 }