当KestrelServer启动时,会绑定相应的IP地址,同时在绑定时将加入HttpConnectionMiddleware作为终端连接的中间件。

1 public async Task StartAsync<TContext>(IHttpApplication<TContext> application, CancellationToken cancellationToken) 2 { 3 try 4 { 5 ... 6 7 async Task OnBind(ListenOptions endpoint) 8 { 9 // Add the HTTP middleware as the terminal connection middleware 10 endpoint.UseHttpServer(endpoint.ConnectionAdapters, ServiceContext, application, endpoint.Protocols); 11 12 var connectionDelegate = endpoint.Build(); 13 14 // Add the connection limit middleware 15 if (Options.Limits.MaxConcurrentConnections.HasValue) 16 { 17 connectionDelegate = new ConnectionLimitMiddleware(connectionDelegate, Options.Limits.MaxConcurrentConnections.Value, Trace).OnConnectionAsync; 18 } 19 20 var connectionDispatcher = new ConnectionDispatcher(ServiceContext, connectionDelegate); 21 var transport = _transportFactory.Create(endpoint, connectionDispatcher); 22 _transports.Add(transport); 23 24 await transport.BindAsync().ConfigureAwait(false); 25 } 26 27 await AddressBinder.BindAsync(_serverAddresses, Options, Trace, OnBind).ConfigureAwait(false); 28 } 29 30 ... 31 }

1 public static IConnectionBuilder UseHttpServer<TContext>(this IConnectionBuilder builder, IList<IConnectionAdapter> adapters, ServiceContext serviceContext, IHttpApplication<TContext> application, HttpProtocols protocols) 2 { 3 var middleware = new HttpConnectionMiddleware<TContext>(adapters, serviceContext, application, protocols); 4 return builder.Use(next => 5 { 6 return middleware.OnConnectionAsync; 7 }); 8 }
当请求抵达此中间件时,在其OnConnectionAsync方法里会创建HttpConnection对象,并通过该对象处理请求

1 public async Task OnConnectionAsync(ConnectionContext connectionContext) 2 { 3 ... 4 5 var connection = new HttpConnection(httpConnectionContext); 6 _serviceContext.ConnectionManager.AddConnection(httpConnectionId, connection); 7 8 try 9 { 10 var processingTask = connection.ProcessRequestsAsync(_application); 11 12 ... 13 } 14 ... 15 }
ProcessRequestsAsync方法内部会根据HTTP协议的不同创建Http1Connection或者Http2Connection对象,一般为Http1Connection。

1 public async Task ProcessRequestsAsync<TContext>(IHttpApplication<TContext> httpApplication) 2 { 3 try 4 { 5 ... 6 7 lock (_protocolSelectionLock) 8 { 9 // Ensure that the connection hasn't already been stopped. 10 if (_protocolSelectionState == ProtocolSelectionState.Initializing) 11 { 12 switch (SelectProtocol()) 13 { 14 case HttpProtocols.Http1: 15 // _http1Connection must be initialized before adding the connection to the connection manager 16 requestProcessor = _http1Connection = CreateHttp1Connection(_adaptedTransport, application); 17 _protocolSelectionState = ProtocolSelectionState.Selected; 18 break; 19 case HttpProtocols.Http2: 20 // _http2Connection must be initialized before yielding control to the transport thread, 21 // to prevent a race condition where _http2Connection.Abort() is called just as 22 // _http2Connection is about to be initialized. 23 requestProcessor = CreateHttp2Connection(_adaptedTransport, application); 24 _protocolSelectionState = ProtocolSelectionState.Selected; 25 break; 26 case HttpProtocols.None: 27 // An error was already logged in SelectProtocol(), but we should close the connection. 28 Abort(ex: null); 29 break; 30 default: 31 // SelectProtocol() only returns Http1, Http2 or None. 32 throw new NotSupportedException($"{nameof(SelectProtocol)} returned something other than Http1, Http2 or None."); 33 } 34 35 _requestProcessor = requestProcessor; 36 } 37 } 38 39 if (requestProcessor != null) 40 { 41 await requestProcessor.ProcessRequestsAsync(httpApplication); 42 } 43 44 await adaptedPipelineTask; 45 await _socketClosedTcs.Task; 46 } 47 ... 48 }
Http1Connection父类HttpProtocol里的ProcessRequests方法会创建一个Context对象,但这还不是最终要找到的HttpContext。

1 private async Task ProcessRequests<TContext>(IHttpApplication<TContext> application) 2 { 3 // Keep-alive is default for HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2; parsing and errors will change its value 4 _keepAlive = true; 5 6 while (_keepAlive) 7 { 8 ... 9 10 var httpContext = application.CreateContext(this); 11 12 try 13 { 14 KestrelEventSource.Log.RequestStart(this); 15 16 // Run the application code for this request 17 await application.ProcessRequestAsync(httpContext); 18 19 if (_ioCompleted == 0) 20 { 21 VerifyResponseContentLength(); 22 } 23 } 24 ... 25 } 26 }
在HostingApplication类中会看到HttpContext原来是由HttpContextFactory工厂类生成的。

1 public Context CreateContext(IFeatureCollection contextFeatures) 2 { 3 var context = new Context(); 4 var httpContext = _httpContextFactory.Create(contextFeatures); 5 6 _diagnostics.BeginRequest(httpContext, ref context); 7 8 context.HttpContext = httpContext; 9 return context; 10 }
HttpContextFactory类才是最后的一站。

1 public HttpContext Create(IFeatureCollection featureCollection) 2 { 3 if (featureCollection == null) 4 { 5 throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(featureCollection)); 6 } 7 8 var httpContext = new DefaultHttpContext(featureCollection); 9 if (_httpContextAccessor != null) 10 { 11 _httpContextAccessor.HttpContext = httpContext; 12 } 13 14 var formFeature = new FormFeature(httpContext.Request, _formOptions); 15 featureCollection.Set<IFormFeature>(formFeature); 16 17 return httpContext; 18 }
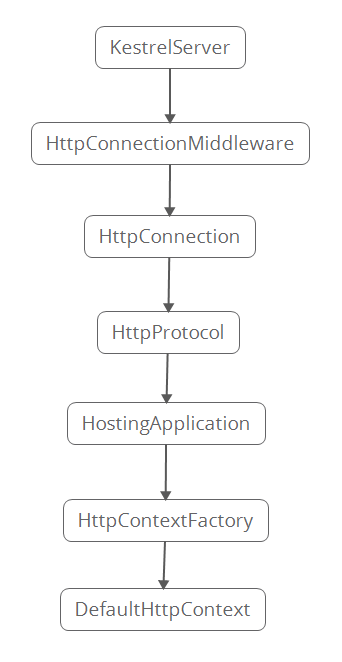
生成的HttpContext对象最终传递到IHttpApplication的ProcessRequestAsync方法。之后的事情便是WebHost与HostingApplication的工作了。
请求(Request),响应(Response),会话(Session)这些与HTTP接触时最常见到的名词,都出现在HttpContext对象中。说明在处理HTTP请求时,若是需要获取这些相关信息,完全可以通过调用其属性而得到。
通过传递一个上下文环境参数,以协助获取各环节处理过程中所需的信息,在各种框架中是十分常见的作法。ASP.NET Core里的用法并无特别的创新,但其实用性还是毋庸置疑的。如果想要构建自己的框架时,不妨多参考下ASP.NET Core里的代码,毕竟它已是一个较成熟的产品,其中有许多值得借鉴的地方。
