Hike on a Graph
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 598 Accepted Submission(s): 249
Problem Description
"Hike
on a Graph" is a game that is played on a board on which an undirected
graph is drawn. The graph is complete and has all loops, i.e. for any
two locations there is exactly one arrow between them. The arrows are
coloured. There are three players, and each of them has a piece. At the
beginning of the game, the three pieces are in fixed locations on the
graph. In turn, the players may do a move. A move consists of moving
one's own piece along an arrow to a new location on the board. The
following constraint is imposed on this: the piece may only be moved
along arrows of the same colour as the arrow between the two opponents'
pieces.
In the sixties ("make love not war") a one-person variant of the game emerged. In this variant one person moves all the three pieces, not necessarily one after the other, but of course only one at a time. Goal of this game is to get all pieces onto the same location, using as few moves as possible. Find out the smallest number of moves that is necessary to get all three pieces onto the same location, for a given board layout and starting positions.
In the sixties ("make love not war") a one-person variant of the game emerged. In this variant one person moves all the three pieces, not necessarily one after the other, but of course only one at a time. Goal of this game is to get all pieces onto the same location, using as few moves as possible. Find out the smallest number of moves that is necessary to get all three pieces onto the same location, for a given board layout and starting positions.

Input
The
input file contains several test cases. Each test case starts with the
number n. Input is terminated by n=0. Otherwise, 1<=n<=50. Then
follow three integers p1, p2, p3 with 1<=pi<=n denoting the
starting locations of the game pieces. The colours of the arrows are
given next as a m×m matrix of whitespace-separated lower-case letters.
The element mij denotes the colour of the arrow between the locations i
and j. Since the graph is undirected, you can assume the matrix to be
symmetrical.
Output
For
each test case output on a single line the minimum number of moves
required to get all three pieces onto the same location, or the word
"impossible" if that is not possible for the given board and starting
locations.
Sample Input
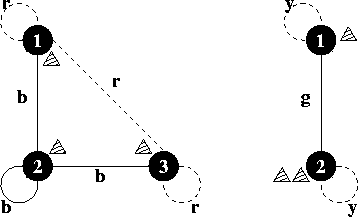
3 1 2 3
r b r
b b b
r b r
2 1 2 2
y g
g y
0
Sample Output
2
impossible
题解:看懂题意后根据题意进行广搜就OK。
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <iostream> #include <map> using namespace std; const int N=55; int n,a,b,c; bool vis[N][N][N]; map<string ,int> mp; char str[5]; int graph[N][N]; struct Node { int a,b,c; int step; }; int bfs() { memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis)); queue<Node> q; Node s; s.a = a,s.b = b,s.c = c,s.step = 0; vis[s.a][s.b][s.c] = true; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()) { Node now = q.front(); q.pop(); if(now.a==now.b&&now.b==now.c) return now.step; Node next; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { if(graph[now.a][i]==graph[now.b][now.c]) ///a->(b,c) { next = now; next.a = i; next.step+=1; if(!vis[next.a][next.b][next.c]) { vis[next.a][next.b][next.c] = true; q.push(next); } } if(graph[now.b][i]==graph[now.a][now.c]) ///b->(a,c) { next = now; next.b = i; next.step+=1; if(!vis[next.a][next.b][next.c]) { vis[next.a][next.b][next.c] = true; q.push(next); } } if(graph[now.c][i]==graph[now.a][now.b]) ///c->(a,b) { next = now; next.c = i; next.step+=1; if(!vis[next.a][next.b][next.c]) { vis[next.a][next.b][next.c] = true; q.push(next); } } } } return -1; } int main() { while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF,n) { mp.clear(); scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); int tot = 0; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { for(int j=1; j<=n; j++) { scanf("%s",str); if(mp[str]==0) { mp[str] = ++tot; graph[i][j] = tot; } else graph[i][j] = mp[str]; } } int ans = bfs(); if(ans==-1) { printf("impossible "); } else printf("%d ",ans); } }