Cycling
Time Limit: 5000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1247 Accepted Submission(s): 411
Problem Description
You
want to cycle to a programming contest. The shortest route to the
contest might be over the tops of some mountains and through some
valleys. From past experience you know that you perform badly in
programming contests after experiencing large differences in altitude.
Therefore you decide to take the route that minimizes the altitude
difference, where the altitude difference of a route is the difference
between the maximum and the minimum height on the route. Your job is to
write a program that finds this route.
You are given:
the number of crossings and their altitudes, and
the roads by which these crossings are connected.
Your program must find the route that minimizes the altitude difference between the highest and the lowest point on the route. If there are multiple possibilities, choose the shortest one.
For example:
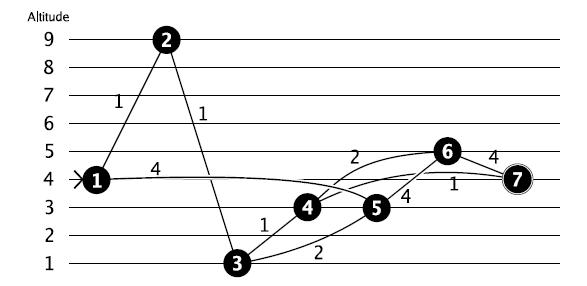
In this case the shortest path from 1 to 7 would be through 2, 3 and 4, but the altitude difference of that path is 8. So, you prefer to go through 5, 6 and 4 for an altitude difference of 2. (Note that going from 6 directly to 7 directly would have the same difference in altitude, but the path would be longer!)
You are given:
the number of crossings and their altitudes, and
the roads by which these crossings are connected.
Your program must find the route that minimizes the altitude difference between the highest and the lowest point on the route. If there are multiple possibilities, choose the shortest one.
For example:

In this case the shortest path from 1 to 7 would be through 2, 3 and 4, but the altitude difference of that path is 8. So, you prefer to go through 5, 6 and 4 for an altitude difference of 2. (Note that going from 6 directly to 7 directly would have the same difference in altitude, but the path would be longer!)
Input
On the first line an integer t (1 <= t <= 100): the number of test cases. Then for each test case:
One line with two integers n (1 <= n <= 100) and m (0 <= m <= 5000): the number of crossings and the number of roads. The crossings are numbered 1..n.
n lines with one integer hi (0 <= hi <= 1 000 000 000): the altitude of the i-th crossing.
m lines with three integers aj , bj (1 <= aj , bj <= n) and cj (1 <= cj <= 1 000 000): this indicates that there is a two-way road between crossings aj and bj of length cj . You may assume that the altitude on a road between two crossings changes linearly.
You start at crossing 1 and the contest is at crossing n. It is guaranteed that it is possible to reach the programming contest from your home.
One line with two integers n (1 <= n <= 100) and m (0 <= m <= 5000): the number of crossings and the number of roads. The crossings are numbered 1..n.
n lines with one integer hi (0 <= hi <= 1 000 000 000): the altitude of the i-th crossing.
m lines with three integers aj , bj (1 <= aj , bj <= n) and cj (1 <= cj <= 1 000 000): this indicates that there is a two-way road between crossings aj and bj of length cj . You may assume that the altitude on a road between two crossings changes linearly.
You start at crossing 1 and the contest is at crossing n. It is guaranteed that it is possible to reach the programming contest from your home.
Output
For each testcase, output one line with two integers separated by a single space:
the minimum altitude difference, and
the length of shortest path with this altitude difference.
the minimum altitude difference, and
the length of shortest path with this altitude difference.
Sample Input
1
7 9
4
9
1
3
3
5
4
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 4 1
4 7 1
1 5 4
5 6 4
6 7 4
5 3 2
6 4 2
Sample Output
2 11
题解:这题做的时候完全没思路,一直在想两点之间的高度问题,怎样才能从子问题递推到父亲问题找到最优的解,后面还是不会,,,然后看了题解发现自己的思维太死板了。。这个题只要枚举所有的高度差,然后按照高度差排序,当在某个高度差的限制下我们能够达到第n点(当然这个时候路径上每个点都应该在low和high之间),那么这个结果就是我们要的结果。
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <math.h> #include <queue> #include <string.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int N = 105; const int INF = 999999999; struct Node { ///枚举高度差所需要用到的结构体 int low,high; }node[N*N]; struct Edge{ int v,w,next; }edge[N*N]; int head[N]; ll h[N]; int graph[N][N]; int n,m; int cmp(Node a,Node b){ return (a.high-a.low)<(b.high-b.low); } bool vis[N]; int d[N]; void addEdge(int u,int v,int w,int &k){ edge[k].v = v,edge[k].w = w; edge[k].next = head[u],head[u]=k++; } void spfa(int s,int low,int high){ queue<int > q; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ d[i] = INF; vis[i] = false; } d[s] = 0; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()){ int u = q.front(); q.pop(); vis[u] = false; if(h[u]>high||h[u]<low) continue; for(int k = head[u];k!=-1;k=edge[k].next){ int v = edge[k].v,w = edge[k].w; if(h[v]>high||h[v]<low) continue; if(d[v]>d[u]+w){ d[v] = d[u]+w; if(!vis[v]){ vis[v]=true; q.push(v); } } } } } int main() { int tcase; scanf("%d",&tcase); while(tcase--){ memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%lld",&h[i]); } int tot = 0; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int a,b,c; scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); addEdge(a,b,c,tot); addEdge(b,a,c,tot); } int k = 0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=i;j<=n;j++){ if(h[i]<h[j]){ node[k].low = h[i]; node[k++].high = h[j]; } else { node[k].low = h[j]; node[k++].high = h[i]; } } } sort(node,node+k,cmp); for(int i=0;i<k;i++){ spfa(1,node[i].low,node[i].high); if(d[n]<INF){ printf("%d %d ",node[i].high-node[i].low,d[n]); break; } } } }