概述
递归(recursion) 又称递回,在数学与计算机科学中,是指在函数的定义中使用函数自身的方法。
一般来说,递归需要有边界条件、递归前进段和递归返回段。当边界条件不满足时,递归前进;当边界条件满足时,递归返回。
构成递归需具备的条件:
1. 子问题须与原始问题为同样的事,且更为简单;
2. 不能无限制地调用本身,须有个出口,化简为非递归状况处理。
代码取自美国课本 "Java How to Program "(Deitel & Detel)的练习: 20.25。 以中序遍历递归方法为例,这里显示的图解,仅诠释开始一小部分递归前进段与递归返回段的交叉过程。通过这一小段的繁琐解释,希望读者可见到二叉树递归遍历的端倪。
private void inorderHelper( TreeNode node ){ if ( node == null ) //若节点为空 return; //无任何操作 inorderHelper( node.leftNode ); //有序遍历下一级左子树 System.out.print( node.data + " " ); //输出节点数据 inorderHelper( node.rightNode );//有序遍历下一级右子树 }
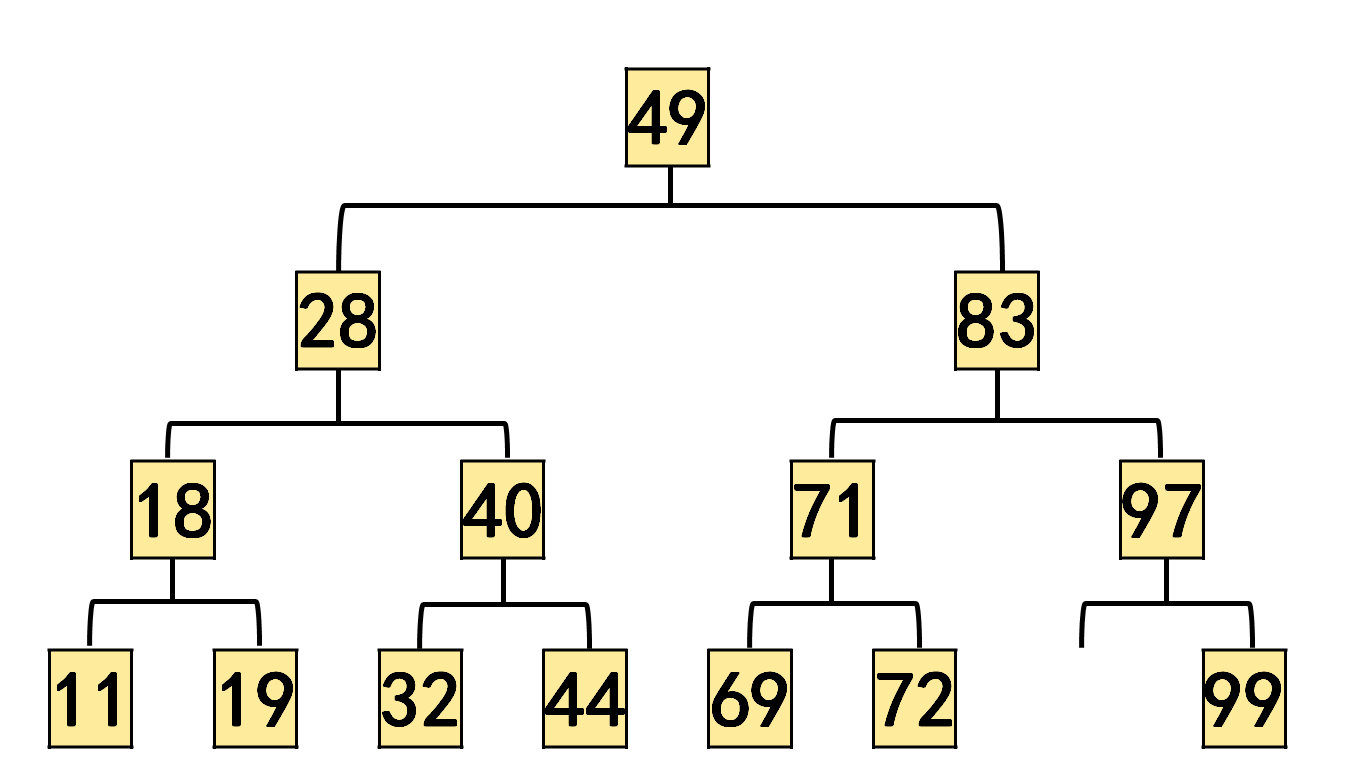
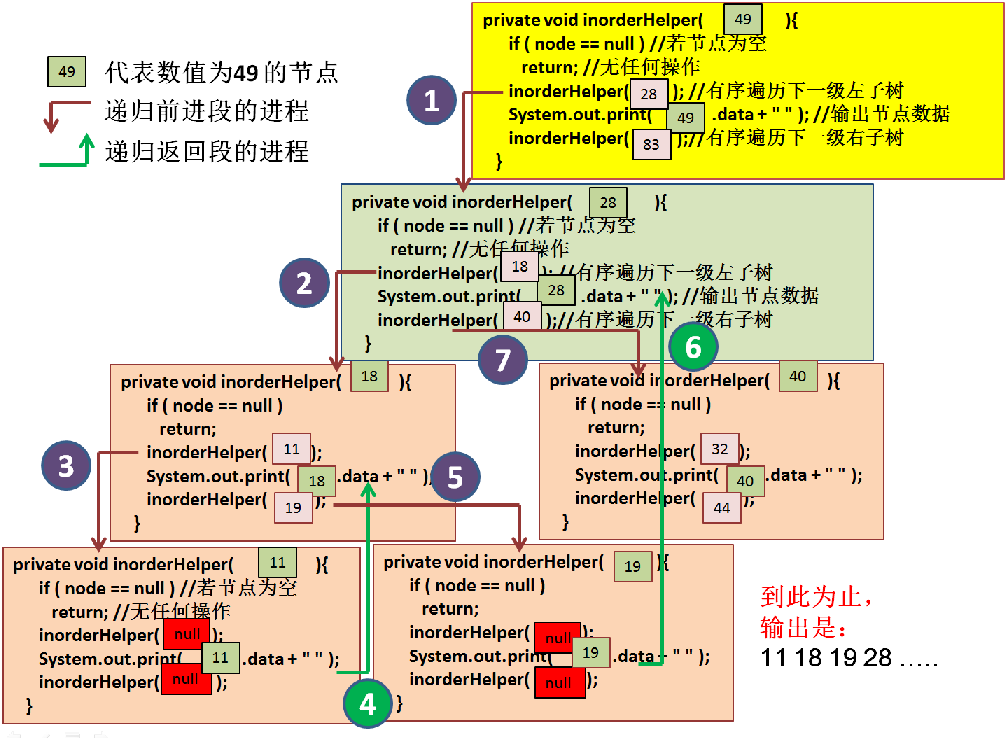
插图说明:
前进段的进程 1 :鉴于以树根 节点 "49" 为参数,调用 inorderHelper(...),开始调用以下一级树根 节点 "28" 为参数 的inorderHelper(...) 方法。
前进段的进程 2 :鉴于以树根 节点 "28" 为参数,调用 inorderHelper(...),开始调用以下一级树根 节点 "18" 为参数 的 inorderHelper(...) 方法。
前进段的进程 3 :鉴于以树根 节点 "18" 为参数,调用 inorderHelper(...),开始调用以下一级树根 节点 "11" 为参数 的 inorderHelper(...) 方法。
节点 "11" 为叶节点,递归前进到终点。开始启动返回操作, 输出其数值 11。
至此,参数为 节点 "11" 的 方法 inorderHelper(...) 执行完毕。返回进程 4 启动下一个 输出:18。
输出 18 的代码行执行完毕,进入前进段进程 5, 执行接下来一行的代码:调用参数为 节点 "19" 的节点的方法 inorderHelper(...)
节点 "19" 为叶节点,递归前进到终点。开始启动返回操作, 输出其数值 19。
至此,参数为 节点 "19" 的 方法 inorderHelper(...) 执行完毕。返回进程 6 启动下一个 输出:28。
实现方法:
package test; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; //把一个数组的值存入二叉树中,然后进行3种方式的遍历 public class BinaryTree { private int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }; private static List<Node> nodeList = null; //内部类结点 private static class Node { Node leftChild; Node rightChild; int data; //构造方法初始化 Node(int newData) { leftChild = null; rightChild = null; data = newData; } } public void createBinTree() { nodeList = new LinkedList<Node>(); // 将一个数组的值依次转换为Node节点 for (int nodeIndex = 0; nodeIndex < array.length; nodeIndex++) { nodeList.add(new Node(array[nodeIndex])); } // 对前lastParentIndex-1个父节点按照父节点与孩子节点的数学关系建立二叉树 for (int parentIndex = 0; parentIndex < array.length / 2 - 1; parentIndex++) { // 左孩子 nodeList.get(parentIndex).leftChild = nodeList.get(parentIndex * 2 + 1); // 右孩子 nodeList.get(parentIndex).rightChild = nodeList.get(parentIndex * 2 + 2); } // 最后一个父节点:因为最后一个父节点可能没有右孩子,所以单独拿出来处理 int lastParentIndex = array.length / 2 - 1; // 左孩子 nodeList.get(lastParentIndex).leftChild = nodeList.get(lastParentIndex * 2 + 1); // 右孩子,如果数组的长度为奇数才建立右孩子 if (array.length % 2 == 1) { nodeList.get(lastParentIndex).rightChild = nodeList.get(lastParentIndex * 2 + 2); } } /** * 先序遍历 * * 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已 * * @param node * 遍历的节点 */ public static void preOrderTraverse(Node node) { if (node == null) return; System.out.print(node.data + " "); preOrderTraverse(node.leftChild); preOrderTraverse(node.rightChild); } /** * 中序遍历 * * 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已 * * @param node * 遍历的节点 */ public static void inOrderTraverse(Node node) { if (node == null) return; inOrderTraverse(node.leftChild); System.out.print(node.data + " "); inOrderTraverse(node.rightChild); } /** * 后序遍历 * * 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已 * * @param node * 遍历的节点 */ public static void postOrderTraverse(Node node) { if (node == null) return; postOrderTraverse(node.leftChild); postOrderTraverse(node.rightChild); System.out.print(node.data + " "); } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree binTree = new BinaryTree(); binTree.createBinTree(); // nodeList中第0个索引处的值即为根节点 Node root = nodeList.get(0); System.out.println("先序遍历:"); preOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println("中序遍历:"); inOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println("后序遍历:"); postOrderTraverse(root); } }
输出结果:
先序遍历:
2 4 8 9 5 3 6 7
中序遍历:
4 9 2 5 1 6 3 7
后序遍历:
9 4 5 2 6 7 3 1