一、职能简介
Activity
Activity并不负责视图控制,它只是控制生命周期和处理事件。真正控制视图的是Window。一个Activity包含了一个Window,Window才是真正代表一个窗口。Activity就像一个控制器,统筹视图的添加与显示,以及通过其他回调方法,来与Window、以及View进行交互。
Window
Window是视图的承载器,内部持有一个 DecorView,而这个DecorView才是 view 的根布局。Window是一个抽象类,实际在Activity中持有的是其子类PhoneWindow。PhoneWindow中有个内部类DecorView,通过创建DecorView来加载Activity中设置的布局R.layout.activity_main。Window 通过WindowManager将DecorView加载其中,并将DecorView交给ViewRoot,进行视图绘制以及其他交互。
DocorView
DecorView是FrameLayout的子类,它可以被认为是Android视图树的根节点视图。DecorView作为顶级View,一般情况下它内部包含一个竖直方向的LinearLayout,在这个LinearLayout里面有上下三个部分,上面是个ViewStub,延迟加载的视图(应该是设置ActionBar,根据Theme设置),中间的是标题栏(根据Theme设置,有的布局没有),下面的是内容栏。
具体情况和Android版本及主体有关,以其中一个布局为例,如下所示:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:fitsSystemWindows="true" android:orientation="vertical"> <!-- Popout bar for action modes --> <ViewStub android:id="@+id/action_mode_bar_stub" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:inflatedId="@+id/action_mode_bar" android:layout="@layout/action_mode_bar" android:theme="?attr/actionBarTheme" /> <FrameLayout style="?android:attr/windowTitleBackgroundStyle" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="?android:attr/windowTitleSize"> <TextView android:id="@android:id/title" style="?android:attr/windowTitleStyle" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="@null" android:fadingEdge="horizontal" android:gravity="center_vertical" /> </FrameLayout> <FrameLayout android:id="@android:id/content" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dip" android:layout_weight="1" android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top" /> </LinearLayout>
在Activity中通过setContentView所设置的布局文件其实就是被加到内容栏之中的,成为其唯一子View,就是上面的id为content的FrameLayout中,在代码中可以通过content来得到对应加载的布局。
ViewGroup content = (ViewGroup)findViewById(android.R.id.content);
ViewGroup rootView = (ViewGroup) content.getChildAt(0);
ViewRoot
ViewRoot可能比较陌生,但是其作用非常重大。所有View的绘制以及事件分发等交互都是通过它来执行或传递的。
ViewRoot对应ViewRootImpl类,它是连接WindowManagerService和DecorView的纽带,View的三大流程(测量(measure),布局(layout),绘制(draw))均通过ViewRoot来完成。
ViewRoot并不属于View树的一份子。从源码实现上来看,它既非View的子类,也非View的父类,但是,它实现了ViewParent接口,这让它可以作为View的名义上的父视图。RootView继承了Handler类,可以接收事件并分发,Android的所有触屏事件、按键事件、界面刷新等事件都是通过ViewRoot进行分发的。
下面结构图可以清晰的揭示四者之间的关系:
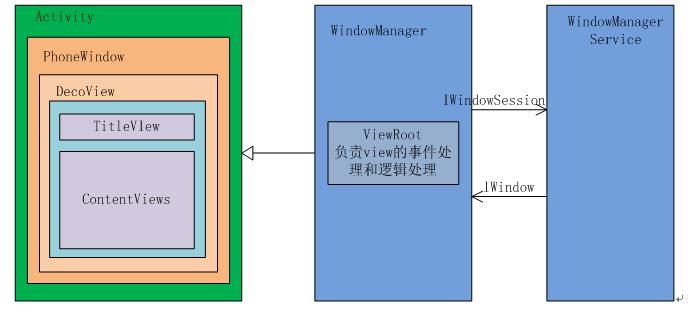
二、DecorView的创建
三、DecorView的显示
四、总结
以上通过源码形式介绍了Window、Activity、DecorView以及ViewRoot之间的错综关系,以及如何创建并显示DecorView。
通过以上了解可以知道,Activity就像个控制器,不负责视图部分。Window像个承载器,装着内部视图。DecorView就是个顶层视图,是所有View的最外层布局。ViewRoot像个连接器,负责沟通,通过硬件的感知来通知视图,进行用户之间的交互。
转载自:https://lrh1993.gitbooks.io/android_interview_guide/content/android/basis/decorview.html