一、定义
IntentService是Android里面的一个封装类,继承自四大组件之一的Service
二、作用
处理异步请求,实现多线程
三、工作流程
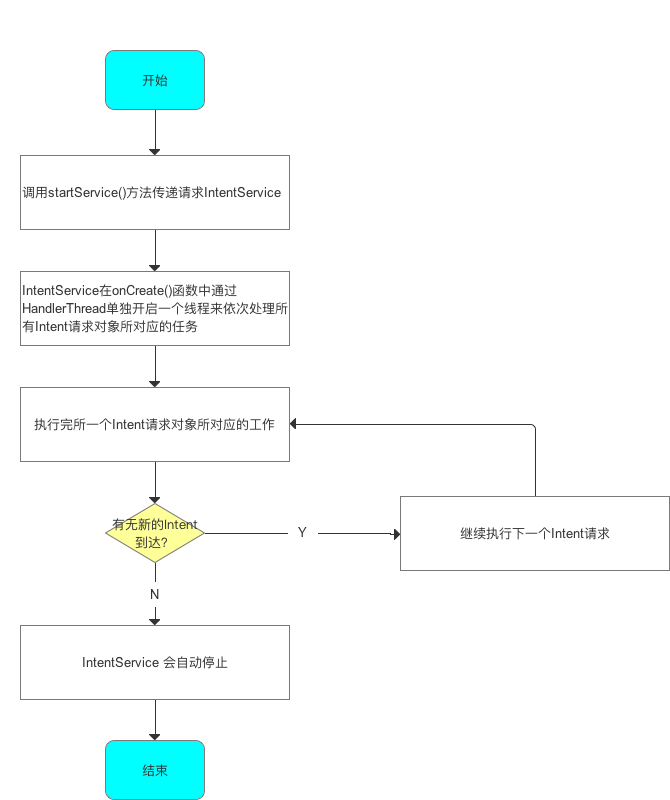
注意:若启动IntentService多次,那么每个耗时操作则以队列的方式在IntentService的onHandleIntent回调方法中依次执行,执行完自动结束。
四、实现步骤
- 步骤1:定义IntentService的子类:传入线程名称、复写onHandleIntent()方法
- 步骤2:在Manifest.xml中注册服务
- 步骤3:在Activity中开启Service服务
五、具体实例
- 步骤1:定义IntentService的子类:传入线程名称、复写onHandleIntent()方法
public class myIntentService extends IntentService { /*构造函数*/ public myIntentService() { //调用父类的构造函数 //构造函数参数=工作线程的名字 super("myIntentService"); } /*复写onHandleIntent()方法*/ //实现耗时任务的操作 @Override protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) { //根据Intent的不同进行不同的事务处理 String taskName = intent.getExtras().getString("taskName"); switch (taskName) { case "task1": Log.i("myIntentService", "do task1"); break; case "task2": Log.i("myIntentService", "do task2"); break; default: break; } } @Override public void onCreate() { Log.i("myIntentService", "onCreate"); super.onCreate(); } /*复写onStartCommand()方法*/ //默认实现将请求的Intent添加到工作队列里 @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { Log.i("myIntentService", "onStartCommand"); return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); } @Override public void onDestroy() { Log.i("myIntentService", "onDestroy"); super.onDestroy(); } }
- 步骤2:在Manifest.xml中注册服务
<service android:name=".myIntentService"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="cn.scu.finch"/> </intent-filter> </service>
- 步骤3:在Activity中开启Service服务
Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//同一服务只会开启一个工作线程
//在onHandleIntent函数里依次处理intent请求。
Intent i = new Intent("cn.scu.finch");
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("taskName", "task1");
i.putExtras(bundle);
startService(i);
Intent i2 = new Intent("cn.scu.finch");
Bundle bundle2 = new Bundle();
bundle2.putString("taskName", "task2");
i2.putExtras(bundle2);
startService(i2);
startService(i); //多次启动
}
}
- 结果
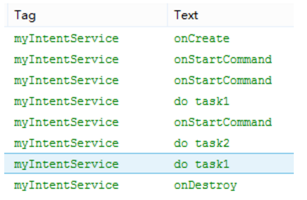
六、源码分析
七、使用场景
-
线程任务需要按顺序、在后台执行的使用场景
最常见的场景:离线下载
-
由于所有的任务都在同一个Thread looper里面来做,所以不符合多个数据同时请求的场景。
八、对比
8.1 IntentService与Service的区别
-
从属性 & 作用上来说 Service:依赖于应用程序的主线程(不是独立的进程 or 线程)
不建议在Service中编写耗时的逻辑和操作,否则会引起ANR;
IntentService:创建一个工作线程来处理多线程任务
-
Service需要主动调用stopSelft()来结束服务,而IntentService不需要(在所有intent被处理完后,系统会自动关闭服务)
8.2 IntentService与其他线程的区别
-
IntentService内部采用了HandlerThread实现,作用类似于后台线程;
-
与后台线程相比,IntentService是一种后台服务,优势是:优先级高(不容易被系统杀死),从而保证任务的执行。
对于后台线程,若进程中没有活动的四大组件,则该线程的优先级非常低,容易被系统杀死,无法保证任务的执行
转载自:https://lrh1993.gitbooks.io/android_interview_guide/content/android/basis/IntentService.html