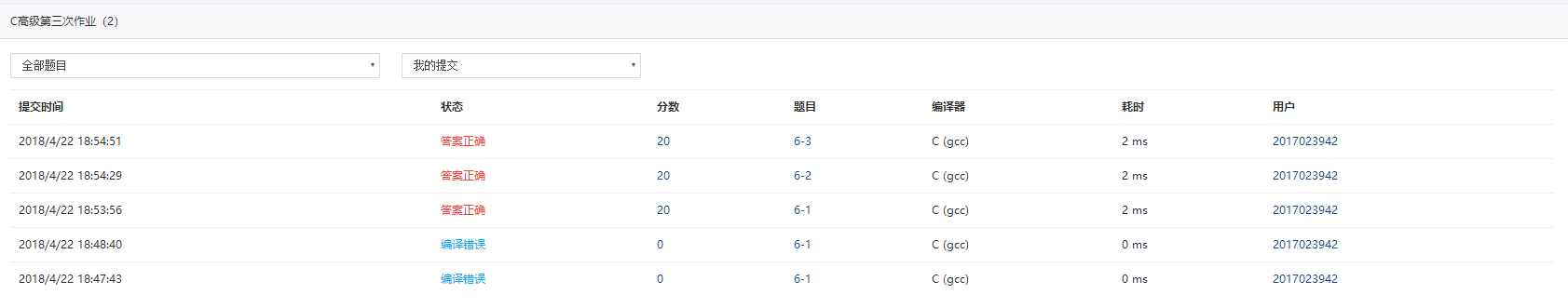
第一题
代码:
char *getmonth( int n )
{
switch(n)
{
case 1:return"January";
case 2:return "February";
case 3:return "March";
case 4:return "April";
case 5:return "May";
case 6:return "June";
case 7:return "July";
case 8:return "August";
case 9:return "September";
case 10:return "October";
case 11:return "November";
case 12:return "December";
default:return NULL;
}
}
思路:在子函数中利用switch进行选择输出不同的月份
流程图:
错误:
无
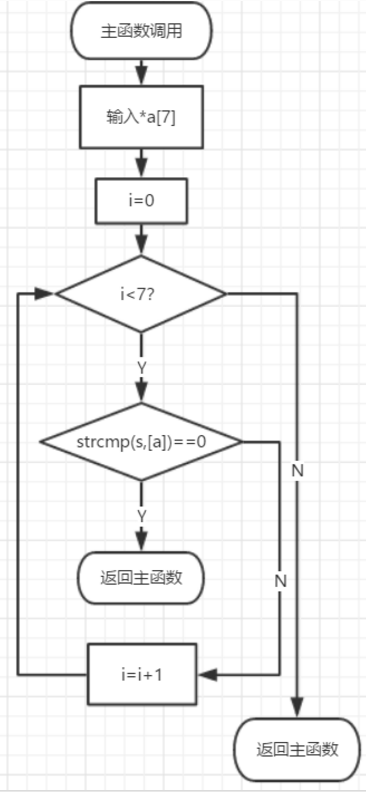
第二题
代码:
int getindex( char *s )
{
int i;
char *day[7]= { "Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday" };
for (i = 0; i <= 6; i ++)
{
if (strcmp(s,day[i]) == 0)
break;
}
if(i>6)
{
i=-1;
}
return i;
}
思路:
创建子函数,在子函数中建立数列利用对比将输入数所对应的数字输出
错误:
无
第三题:
代码:
int max_len( char *s[], int n )
{
int i,a=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(a<strlen(s[i]))
{
a=strlen(s[i]);
}
}
return a;
}
思路:
建立子函数,通过指针的指针可以计算每一位的字符长度的特性,记录并比较出最长字符
错误:
无
第四题:
代码
#include<string.h>
char *match(char *s, char ch1, char ch2 )
{
int i=0,j=0,len=0;
char *a;
len = strlen(s);
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(s[i]==ch1)
{
a=&s[i];
for(j=i;j<len;j++)
{
if(s[j]==ch2)
{
printf("%c
", s[j]);
return a;
}
else
{
printf("%c", s[j]);
}
}
printf("
");
return a;
}
}
printf("
");
*s='�';
return s;
}
思路:
1.读入s,ch1,ch2;
2.用for循环确定ch1在s中的位置,若查找不到则跳出;
3.再次用for循环,输出单个字符,并确定ch2位置,若不存在则跳出;
4.返回s;
错误:
无
第五题;
代码:
struct ListNode *readlist()
{
struct ListNode *p,*head,*n;
head=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
n=head;
while(1)
{
p=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&p->data);
if(p->data==(-1))
break;
n->next=p;
n=p;
}
n->next=NULL;
return head->next;
}
struct ListNode *getodd( struct ListNode **L )
{
struct ListNode *i,*j,*k,*h1,*h2;
j=h1=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
h1->next=NULL;
k=h2=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
h2->next=NULL;
i=*L;
int n=0;
for(;i;i=i->next)
{
if((i->data)%2==1)
{
j->next=i;
j=i;
}
else
{
k->next=i;
k=i;
}
}
j->next=NULL;
k->next=NULL;
*L=h2->next;
return h1->next;
}
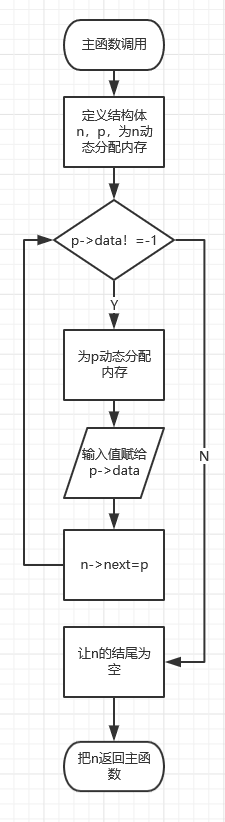
思路:
1.在readlist中,要求用输入的值建立链表,用p->data==-1判链表结束;
2.定义head作为链表头文件,并且定义链表n放置输入元素;
3.在getodd中,要求将建立的链表拆分为两个链表,将单数和双数分配;
4.定义h1,h2作为两新链表头文件;
5.历遍链表,将单数放置入j链表,指向h1,将双数放置入k链表,指向h2;
6.将k链表赋给原链表,并返回h1链表;
流程图:

错误:
无
第六题:
struct stud_node *createlist()
{
struct stud_node *p,*head,*n;
head=(struct stud_node*)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node));
n=head;
while(1)
{
p=(struct stud_node*)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node));
scanf("%d ",&p->num);
if(p->num==0)
break;
scanf("%s %d",&p->name,&p->score);
n->next=p;
n=p;
}
n->next=NULL;
return head->next;
}
struct stud_node *deletelist( struct stud_node *head, int min_score )
{
struct stud_node *p,*k;
p=(struct stud_node*)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node));
k=p;
for(;head;head=head->next)
{
if((head->score)>=min_score)
{
k->next=head;
k=head;
}
}
k->next=NULL;
return p->next;
}
思路:
1.在createlist中,将输入的数建立一个新链表,并将其返回;
2.定义head作为链表头文件,并定义链表p作储存用,当输入0时终结链表;
3.返回链表头文件;
4.在deletelist中,将读入的链表删除低于读入数字int min_score的链表;
5.对链表进行历遍,当p->score小于min_score时将链表向前推进,挤掉要删除项;
6.返回链表头文件
错误:
无
第七题:
程序:
struct ListNode *mergelists(struct ListNode *list1, struct ListNode *list2)
{
struct ListNode *h,*p,*i,*k;
h=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
p=h;
i=list1;
k=list2;
while(i!=NULL&&k!=NULL)
{
if(i->data<k->data)
{
p->next=i;
i=i->next;
}
else
{
p->next=k;
k=k->next;
}
p=p->next;
}
while(i)
{
p->next=i;
i=i->next;
p=p->next;
}
while(k)
{
p->next=k;
k=k->next;
p=p->next;
}
p->next=NULL;
return h->next;
}
思路:
1.在mergelists中,要求将读入的链表list1,list2拼接为一个链表;
2.定义h作为新链表头文件,并定义p用于储存新链表数值;
3.使用while结构用于排列当两链表同时没结束时,可利用链表原为升序链表这一特点进行排序
4.同第3点逻辑可实现对其中一链表未结束而另一链表以结束的两种情况的循环;
5.返回链表p;
错误:
无