线程创建
继承Thread类
public class TestThread1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { // run 方法线程体 System.out.println("我在看视频"); } public static void main(String[] args) { // main 主线程体 // 创建一个线程对象 TestThread1 testThread1 = new TestThread1(); // 调用start()方法开启线程 testThread1.start(); } }
实现Runnable接口
public class TestThread2 implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("我在学习"); } public static void main(String[] args) { TestThread2 testThread2 = new TestThread2(); // 开启子线程 (这里采用代理模式) new Thread(testThread2).start(); } }
实现Callable接口(了解)
public class TestThread3 implements Callable<Integer> { // 这里需要返回类型 @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { System.out.println("法外狂徒张三在作案"); return 100; } public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(new TestThread3()); new Thread(futureTask).start(); Integer integer = futureTask.get(); // 这里获取返回值 System.out.println(integer); } }
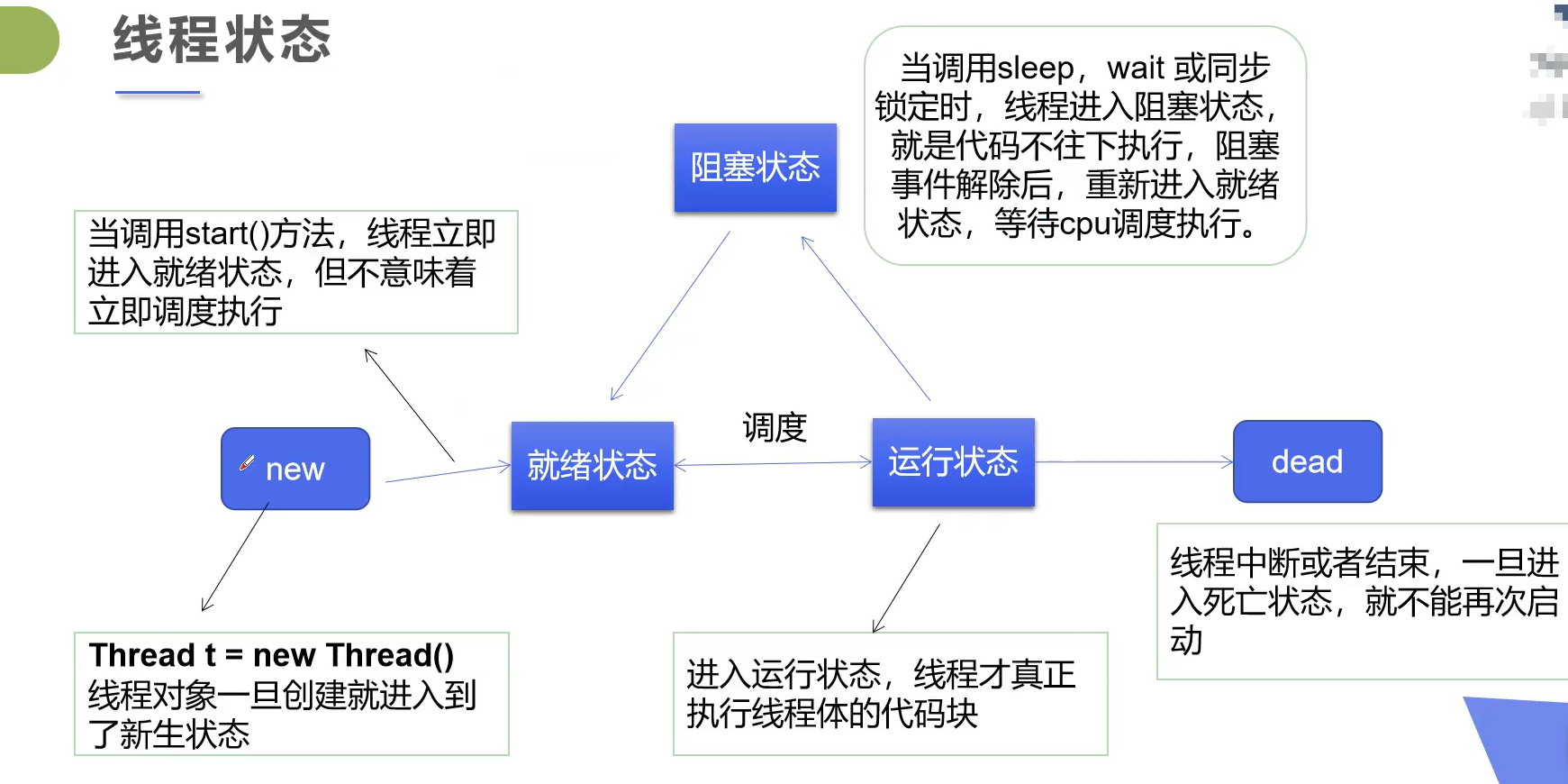
线程状态
查看线程的状态通过getState()方法。
线程休眠
Thread.sleep(1000); // 单位是毫秒
- sleep指定当前线程阻塞的毫秒数
- sleep时间到达后线程进入就绪状态
- 每一个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁
线程礼让
Thread.yield(); // 礼让
- 礼让线程,让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞
- 将线程从运行状态转为就绪状态
- 礼让是让cpu重新调度,所以礼让不一定成功!
线程插入
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 自定义线程 Thread t = new Thread(()-> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println("我来插入执行"); } }); // 主线程 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { if (i == 10) { t.join(); // 强制插入t线程,待t线程执行完,再继续执行main线程 } System.out.println("我是主线程"); } }
线程优先级
- 线程调度器按照优先级决定应该调度哪个线程来执行
- 线程的优先级用数字表示,范围从1~10
- getPriority() 获取优先级
- setPriority(int xx) 设置优先级
- 注意:若设置优先级,一定先设置优先级,后启动
守护线程
- 线程分为用户线程和守护线程
- 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
- 通过setDaemon(true)来设置该线程为守护线程
锁问题
初步了解多线程在并发问题中,采取的简单措施。
- synchronized 关键字,锁的是this,用于同步方法,或者代码块
- 可重入锁Lock,ReentrantLock类实现了Lock,它拥有与synchronized 相同的并发性和内存语义,在实现线程安全的控制中,比较常用的是ReentrantLock,可以显示加锁,释放锁。
生产消费者模式
生产消费者模式问题可以有两种解决方法:管道法(用缓冲区)、信号灯法(标识变量)
示例:缓冲区方式
public class TestPC { public static void main(String[] args) { SynContainer container = new SynContainer(); new Productor(container).start(); new Consumer(container).start(); } } // 生产者 线程 class Productor extends Thread{ SynContainer container; public Productor(SynContainer container) { this.container = container; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { try { container.product(new Chicken(i)); System.out.println("生产-->" + i/10 + "-" + i%10 + "只鸡"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } // 消费者 线程 class Consumer extends Thread { SynContainer container; public Consumer(SynContainer container) { this.container = container; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { try { Chicken chicken = container.pop(); System.out.println("消费了-->" + chicken.getId()/10 + "-" + chicken.getId()%10 + "只鸡"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } // 产品 class Chicken { int id; // 编号 public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public Chicken(int id) { this.id = id; } } class SynContainer { // 声明缓冲区的数量 Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10]; // 存在的数量 int count = 0; // 生产一只鸡 public synchronized void product(Chicken chicken) throws InterruptedException { while (count >= 9) { this.wait(); } chickens[count++] = chicken; this.notifyAll(); // 唤醒消费进程 } // 消费鸡 public synchronized Chicken pop() throws InterruptedException { while (count <= 0) { this.wait(); } count--; this.notifyAll(); // 唤醒生产者 return chickens[count]; } }