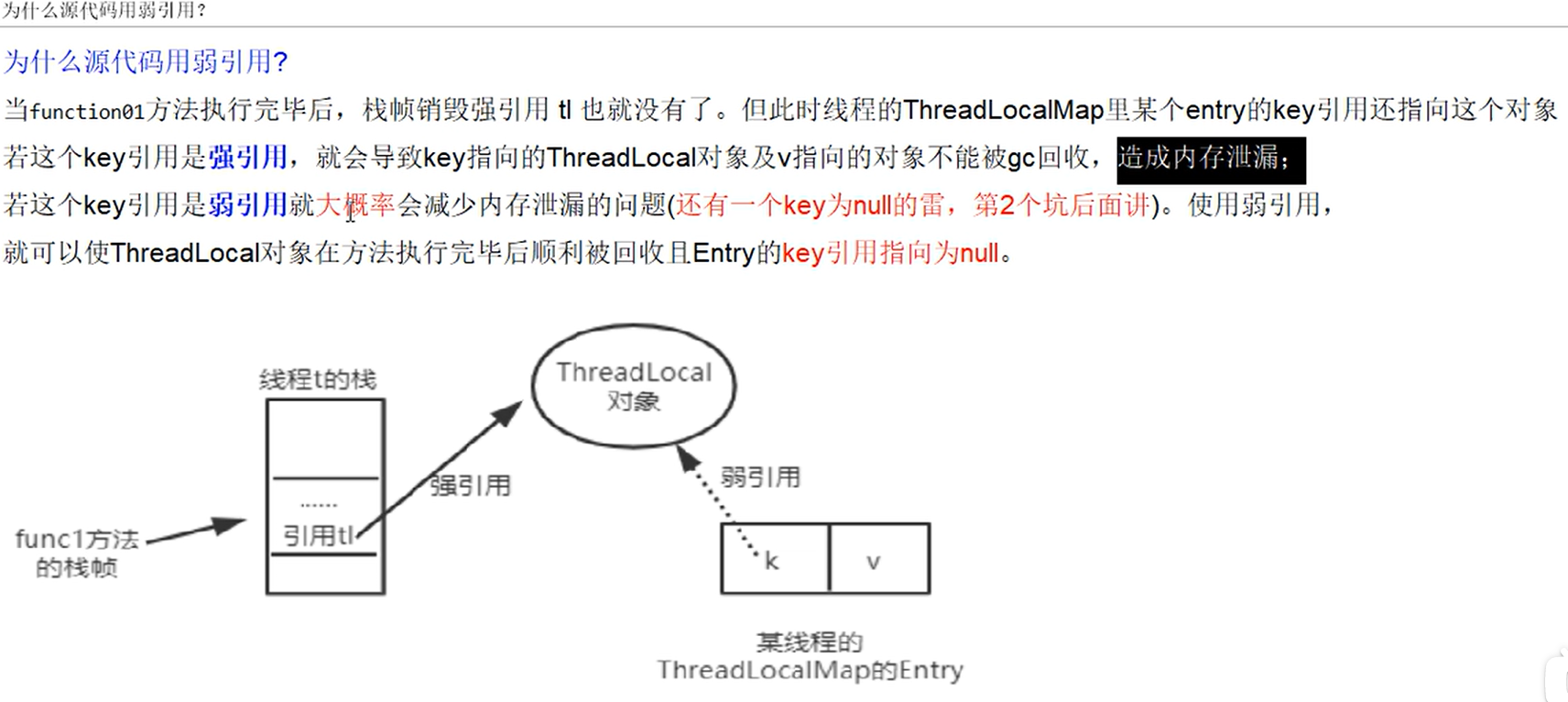
1代码1
class House { int saleCount = 0; public synchronized void saleHouse() { saleCount++; } // ThreadLocal<Integer> saleVolume = new ThreadLocal<Integer>() { // @Override // protected Integer initialValue() { // return 0; // } // }; ThreadLocal<Integer> saleVolume = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> 0); public void saleVolumeByThreadLocal() { saleVolume.set(1 + saleVolume.get()); } } public class ThreadLocalDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { House house = new House(); for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { try { new Thread(() -> { int size = new Random().nextInt(5) + 1; // System.out.println(size); for (int j = 1; j <= size; j++) { house.saleHouse(); house.saleVolumeByThreadLocal(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "卖出多少套" + house.saleVolume.get()); }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); }catch (Exception e) { }finally { house.saleVolume.remove(); } } try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "共卖出多少套:" + house.saleCount); } }
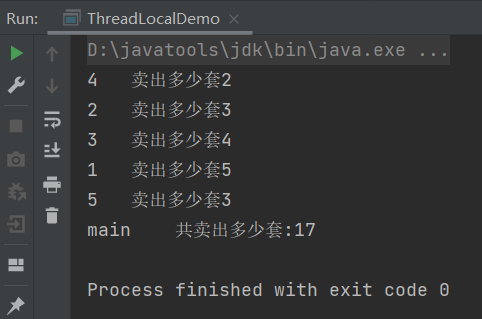
2.代码2
class MyData { ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocalField = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> 0); public void add() { threadLocalField.set(1 + threadLocalField.get()); } } public class ThreadLocalDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); MyData myData = new MyData(); try { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { threadPool.submit(() -> { try { Integer beforeInt = myData.threadLocalField.get(); myData.add(); Integer afterInt = myData.threadLocalField.get(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "beforeInt " + beforeInt + "\t" + " afterInt " + afterInt); } finally { myData.threadLocalField.remove(); } }); } } finally { threadPool.shutdown(); } try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
3.强软弱虚四大应用代码:
class MyObject { //这个方法一般不用复写 @Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable { System.out.println("-----invoke finalize method---"); } } public class ReferenceDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { MyObject myObject = new MyObject(); ReferenceQueue<MyObject> referenceQueue = new ReferenceQueue<>(); PhantomReference<MyObject> phantomReference = new PhantomReference<>(myObject, referenceQueue); List<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<>(); new Thread(() ->{ while (true) { list.add(new byte[10 * 1024 * 1024]); try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(phantomReference.get()+"\t" +"list add ok"); } },"t1").start(); new Thread(() -> { while (true) { Reference<? extends MyObject> reference = referenceQueue.poll(); if(reference != null) { System.out.println("有虚对象回收加入了队列"); break; } } },"t2").start(); } private static void strongReference() { MyObject myObject = new MyObject(); System.out.println("gc beore: " +myObject); myObject = null; System.gc(); //人工开启gc,一般不用 try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("gc after: " + myObject); } private static void softReference() { SoftReference<MyObject> softReference = new SoftReference<>(new MyObject()); System.gc(); //人工开启gc,一般不用 System.out.println("gc after 内存够用: " + softReference.get()); try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { byte[] bytes = new byte[50 * 1024 * 1024]; }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("gc after 内存不够: " + softReference.get()); } } private static void weakReference() { WeakReference<MyObject> weakReference = new WeakReference<>(new MyObject()); System.out.println("gc beore: " +weakReference.get()); System.gc(); //人工开启gc,一般不用 try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("gc after: " + weakReference.get()); } }




5.为什么要用弱引用?不用会怎么样