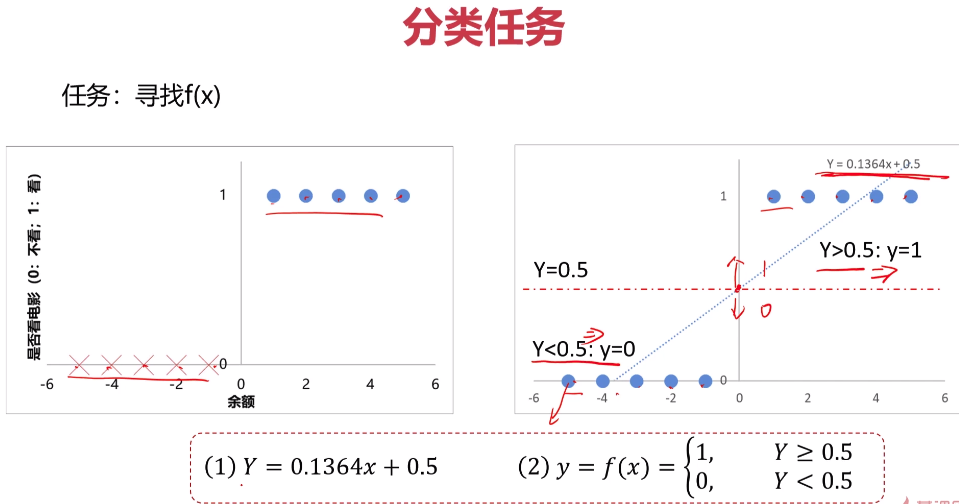
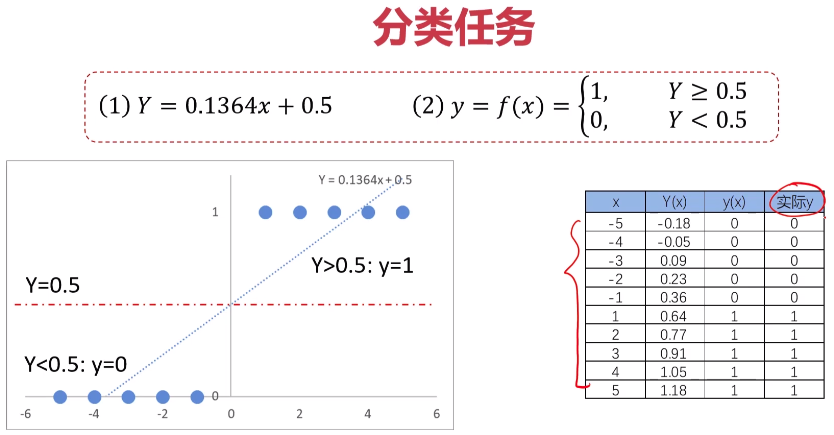
- 分类问题介绍






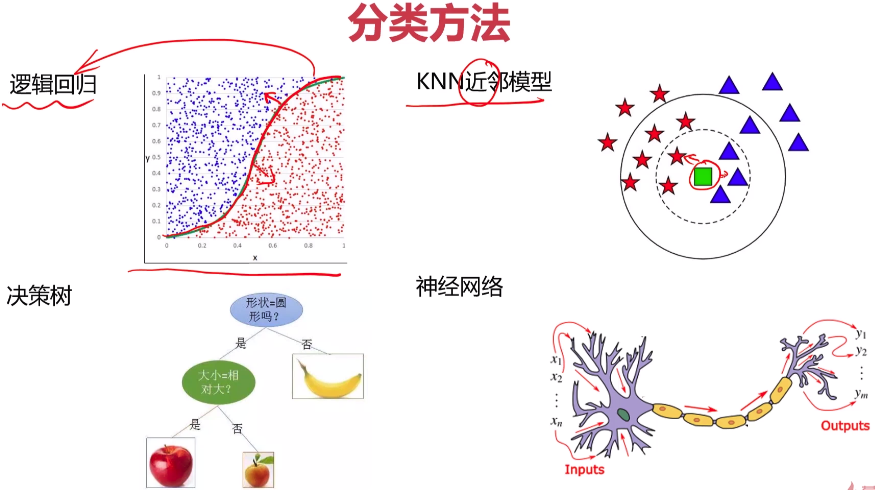


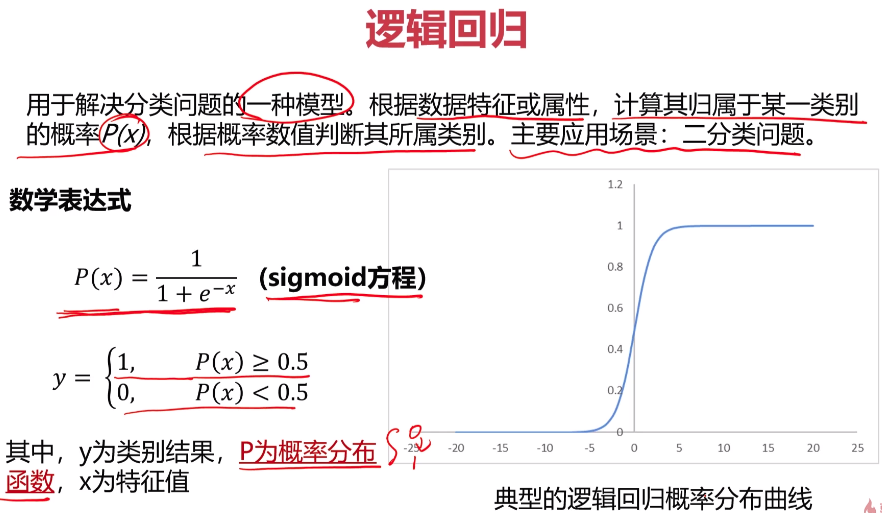
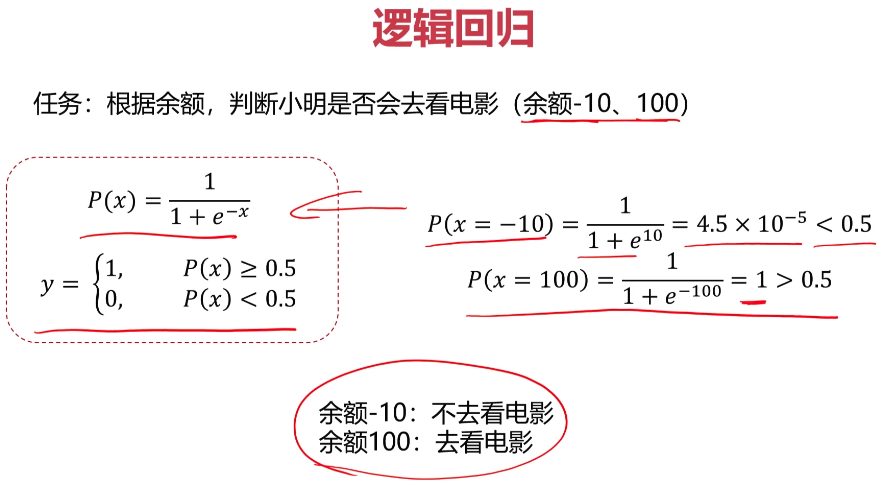
- 逻辑回归



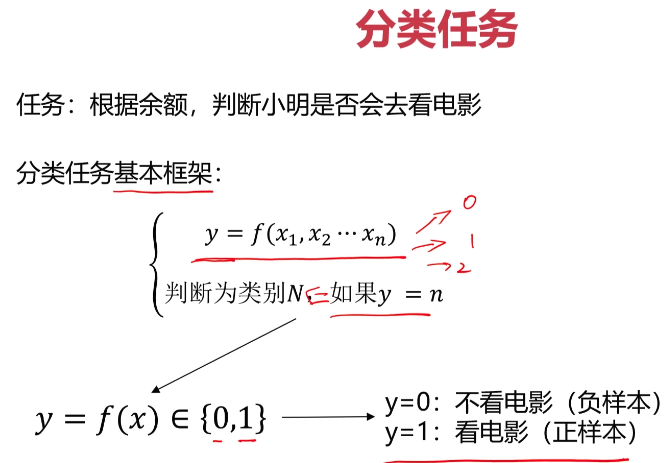


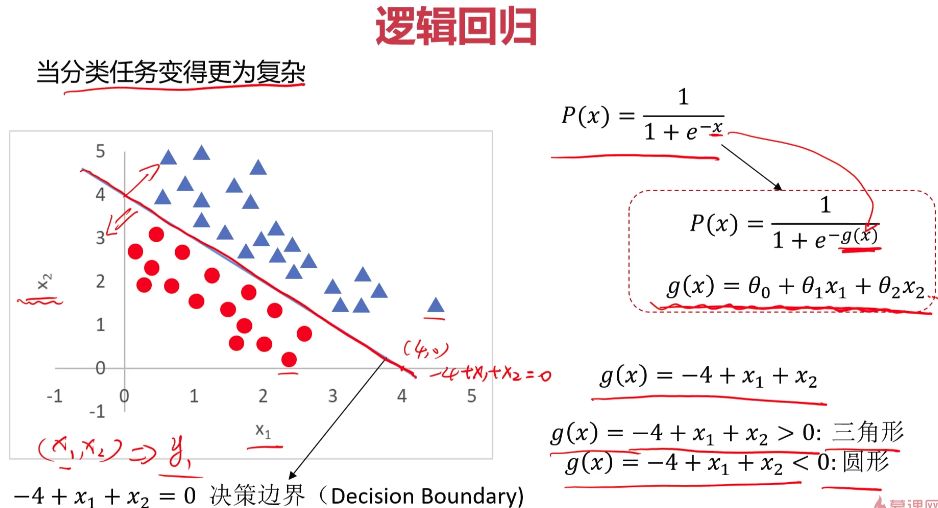
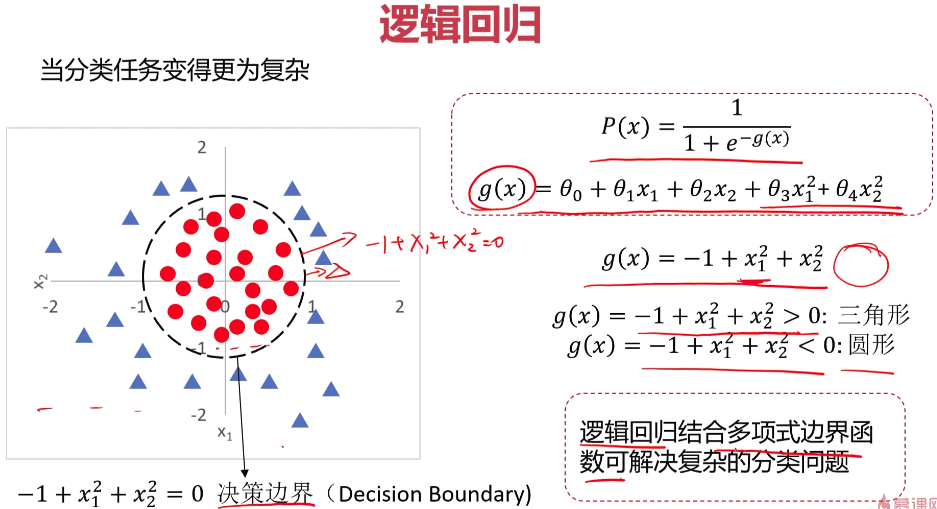

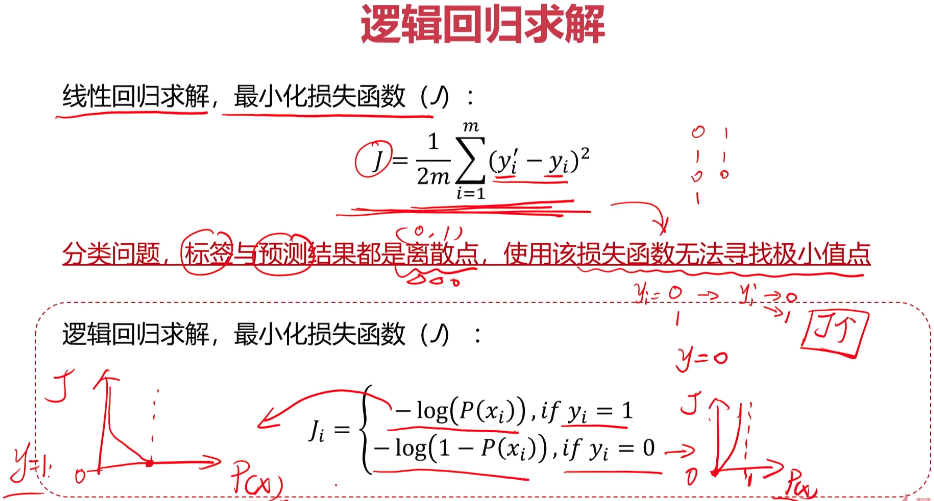

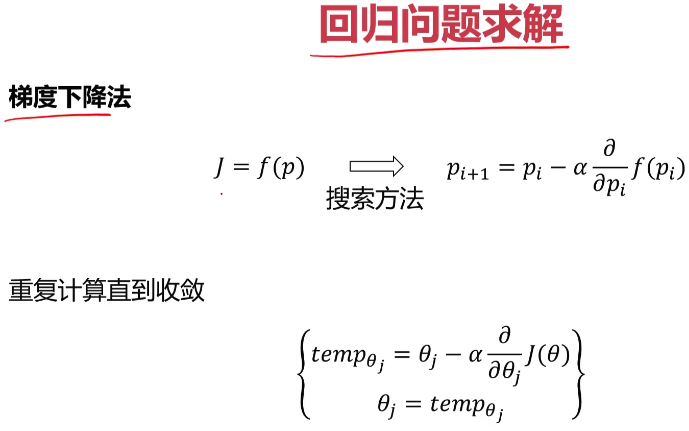

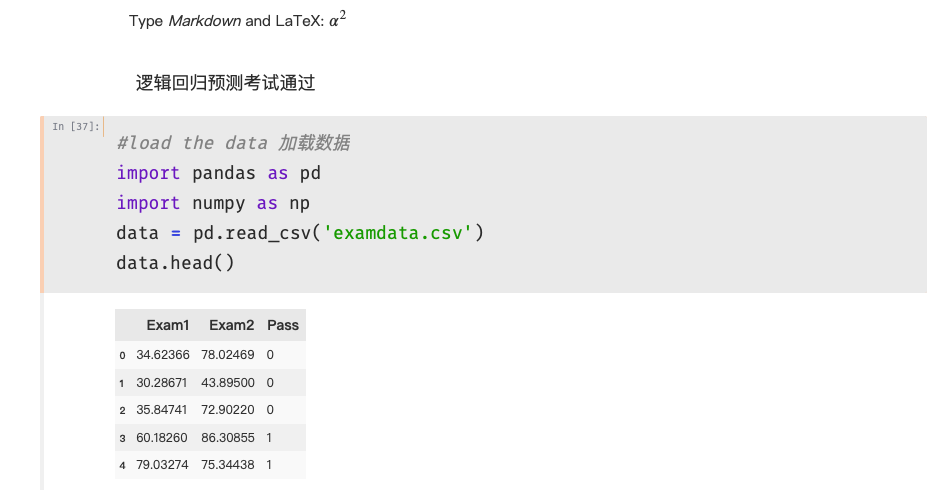
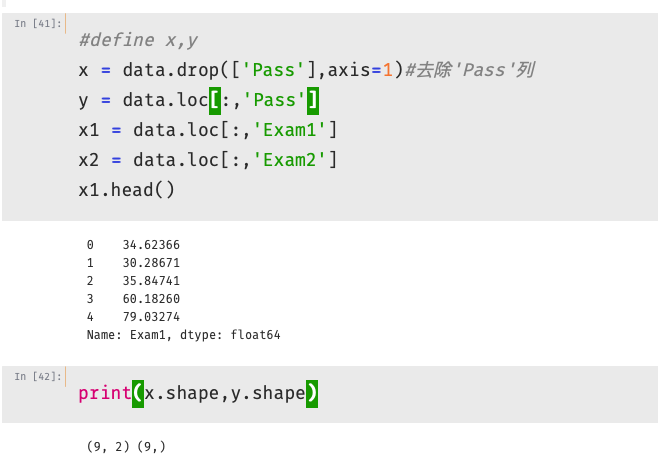
- 实战准备



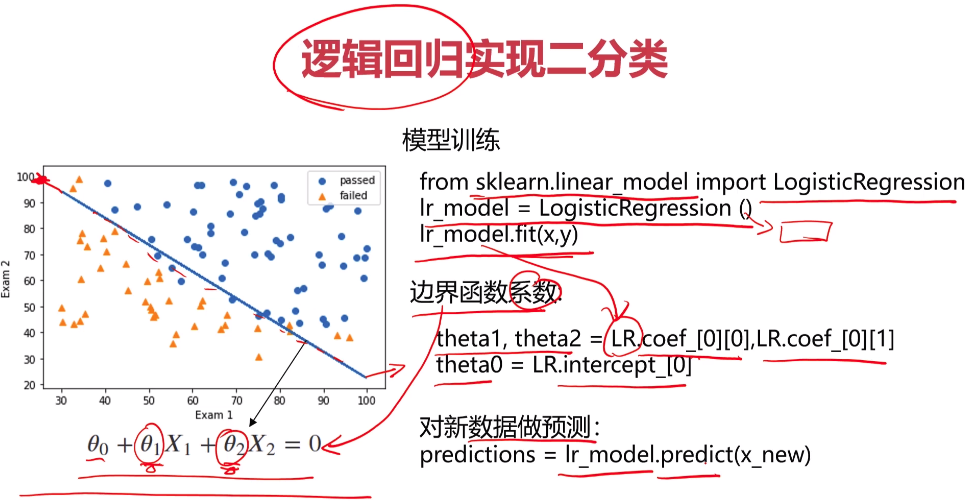
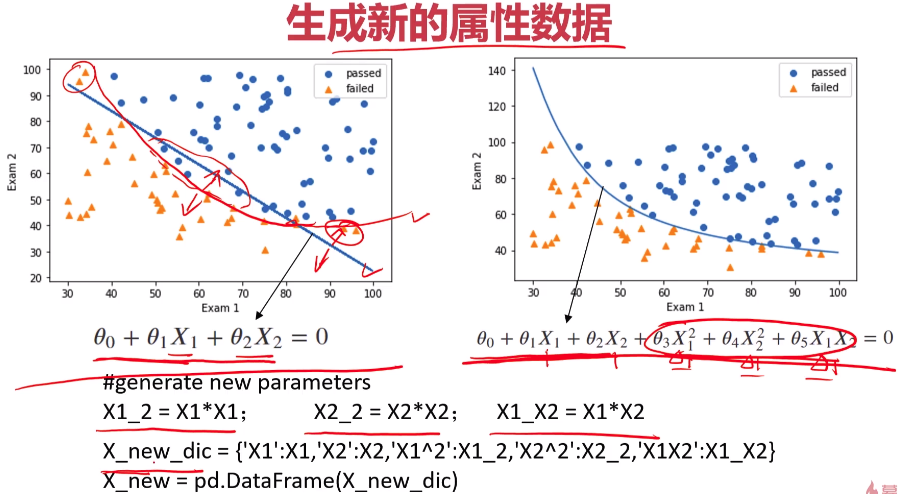

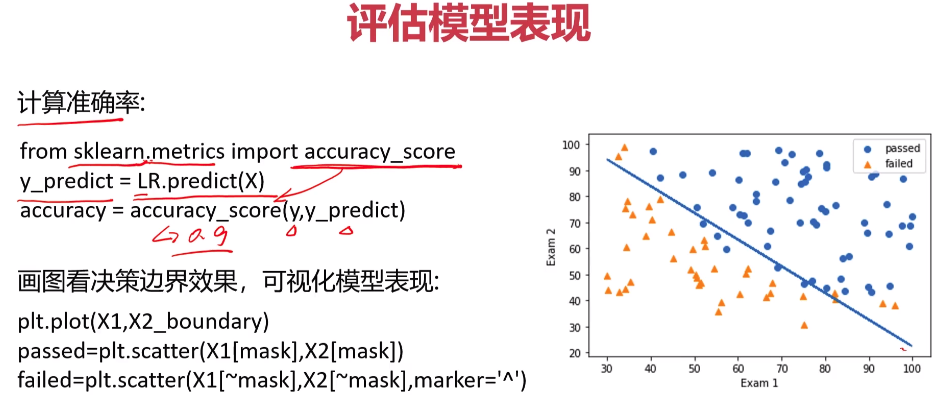
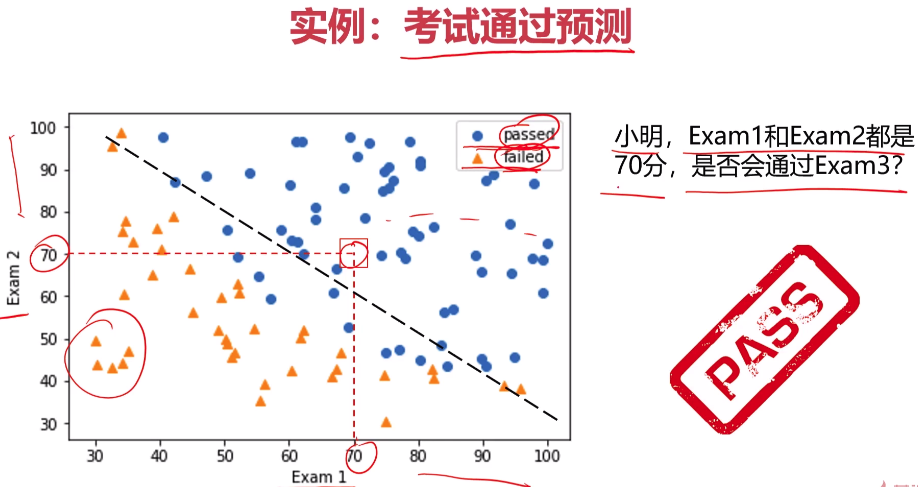
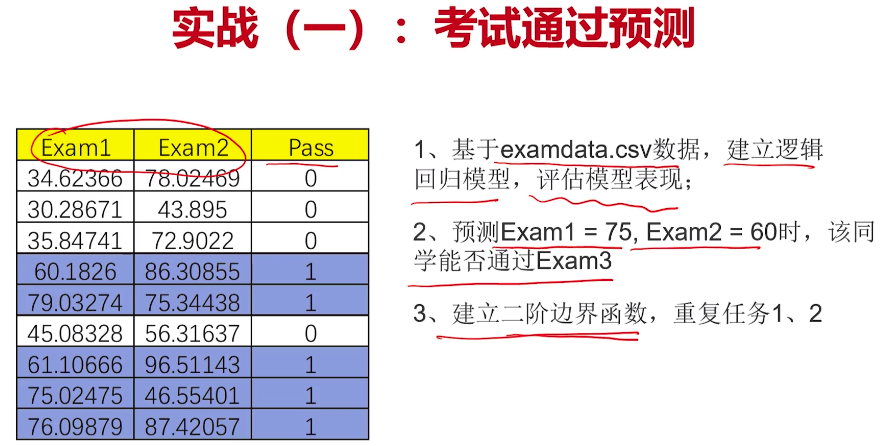
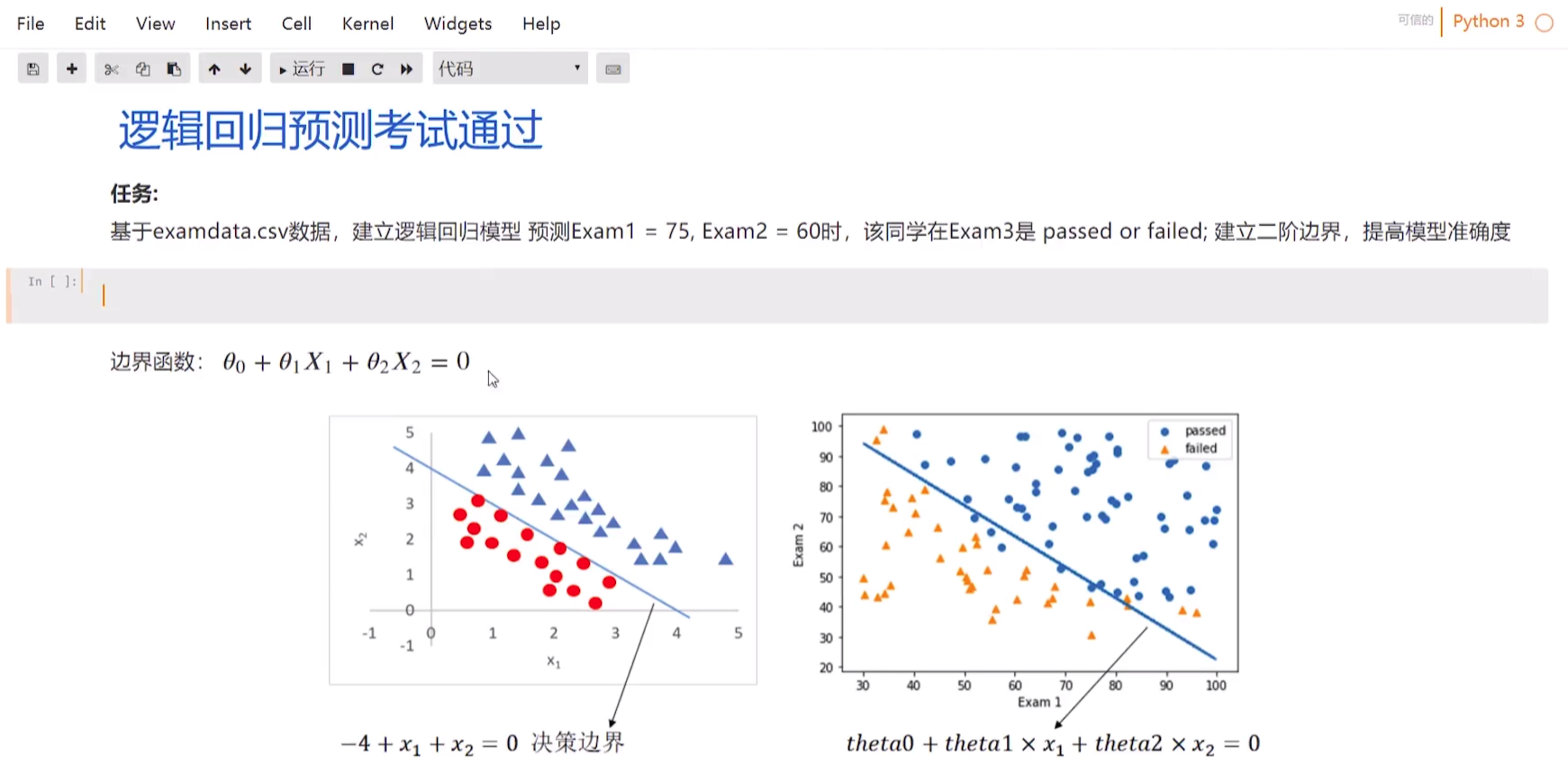
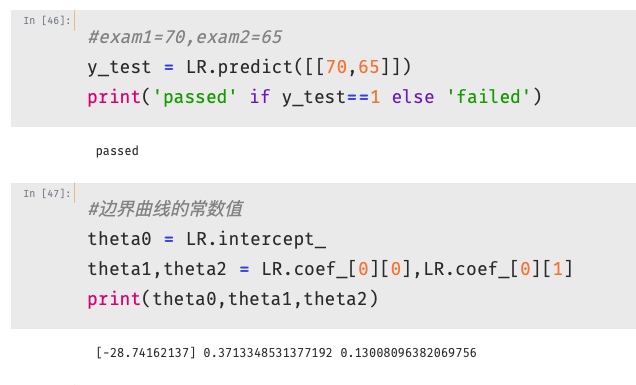
- 考试通过实战


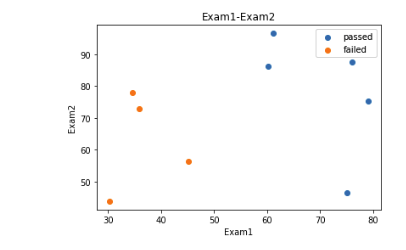
1 fig2 = plt.figure() #新建图形 2 passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][mask])#绘制散点图:展示通过考生的成绩 3 failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][~mask])#绘制散点图:展示通过考生的成绩 4 plt.title('Exam1-Exam2')#标题 5 plt.xlabel('Exam1')#x轴 6 plt.ylabel('Exam2')#y轴 7 plt.legend((passed,failed),('passed','failed'))#题注 8 plt.show()#展示

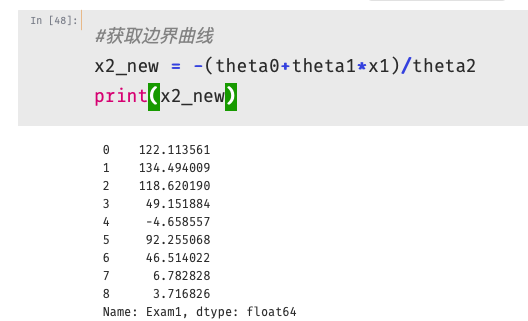
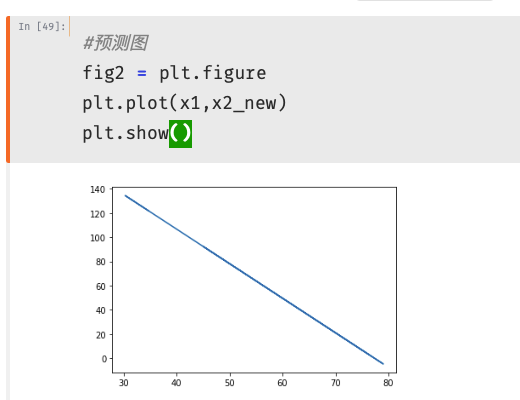
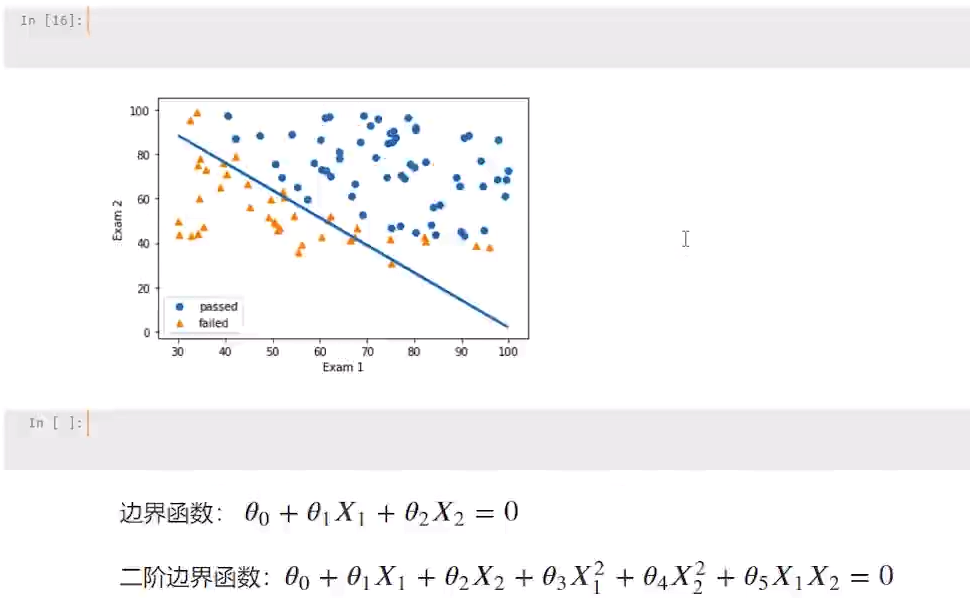
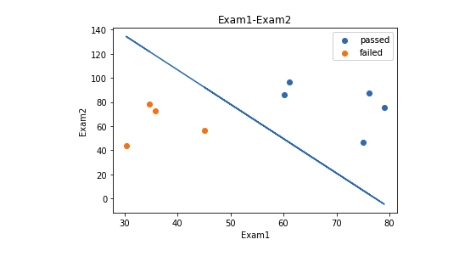
1 #原始数据图 2 fig3 = plt.figure() #新建图形 3 passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][mask])#绘制散点图:展示通过考生的成绩 4 failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][~mask])#绘制散点图:展示通过考生的成绩 5 plt.plot(x1,x2_new)#预测曲线 6 plt.title('Exam1-Exam2')#标题 7 plt.xlabel('Exam1')#x轴 8 plt.ylabel('Exam2')#y轴 9 plt.legend((passed,failed),('passed','failed'))#题注 10 plt.show()#展示

1 #绘制边界图形 2 theta0 = LR2.intercept_ 3 theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,theta5 = LR2.coef_[0][0],LR2.coef_[0][1],LR2.coef_[0][2],LR2.coef_[0][3],LR2.coef_[0][4] 4 a = theta4 5 b = theta5*x1_new+theta2 6 c = theta0+theta1*x1_new+theta3*x1_new*x1_new 7 x2_new_boundary = (-b+np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a) # abs():取绝对值 8 print(x2_new_boundary)
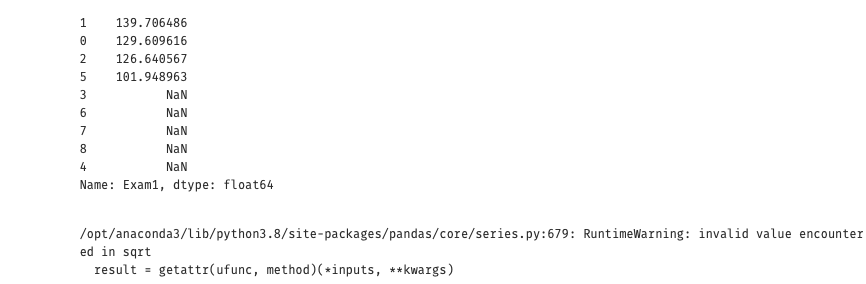
1 #将原始数据与多阶函数进行混合 2 fig5 = plt.figure() #新建图形 3 passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][mask])#绘制散点图:展示通过考生的成绩 4 failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][~mask])#绘制散点图:展示通过考生的成绩 5 plt.plot(x1_new,x2_new_boundary)#预测曲线 6 plt.title('Exam1-Exam2')#标题 7 plt.xlabel('Exam1')#x轴 8 plt.ylabel('Exam2')#y轴 9 plt.legend((passed,failed),('passed','failed'))#题注 10 plt.show() 11 12 plt.plot(x1_new,x2_new_boundary) 13 plt.show()
- 实战:芯片质量预测



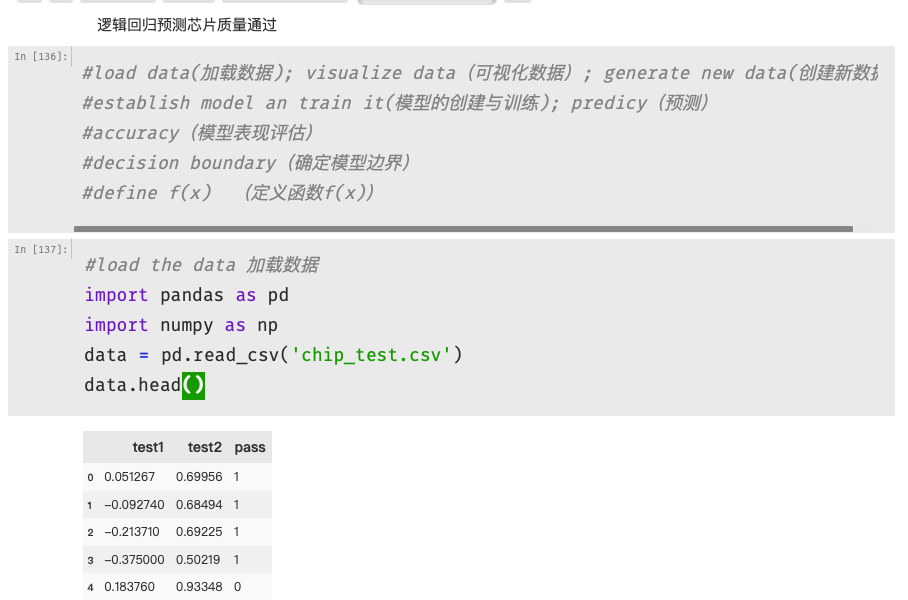

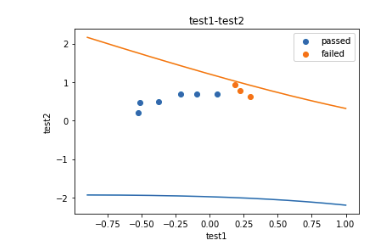
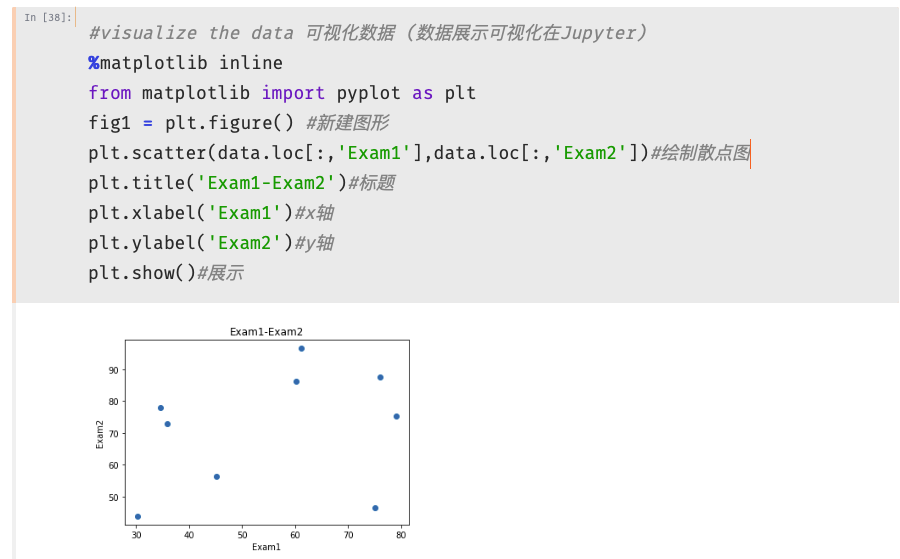
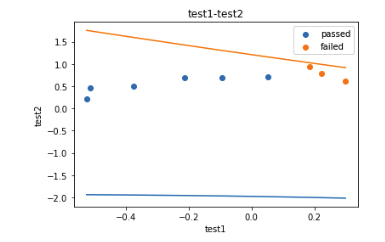
1 #visualize the data 可视化数据 (数据展示可视化在Jupyter) 2 %matplotlib inline 3 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 4 fig1 = plt.figure() #新建图形 5 passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][mask])#绘制散点图 6 failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][~mask])#绘制散点图 7 plt.title('test1-test2')#标题 8 plt.xlabel('test1')#x轴 9 plt.ylabel('test2')#y轴 10 plt.legend((passed,failed),('passed','failed'))#题注 11 plt.show()#展示

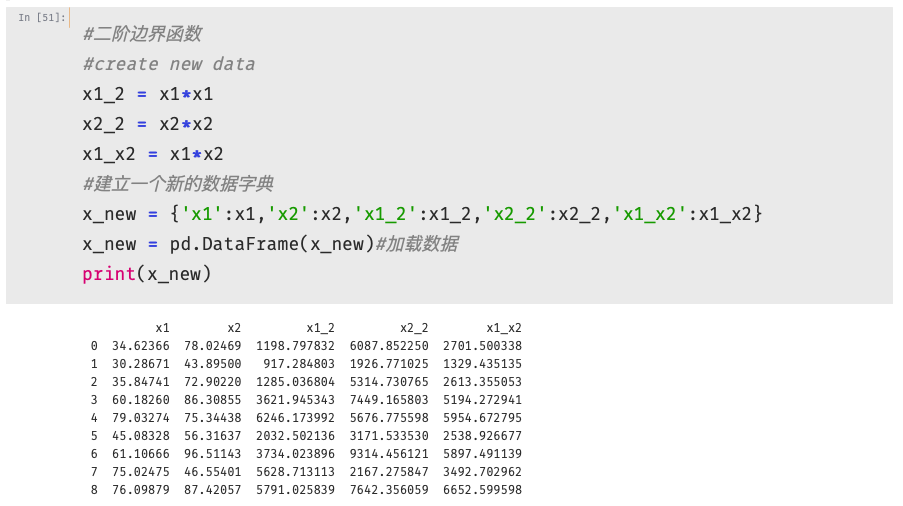
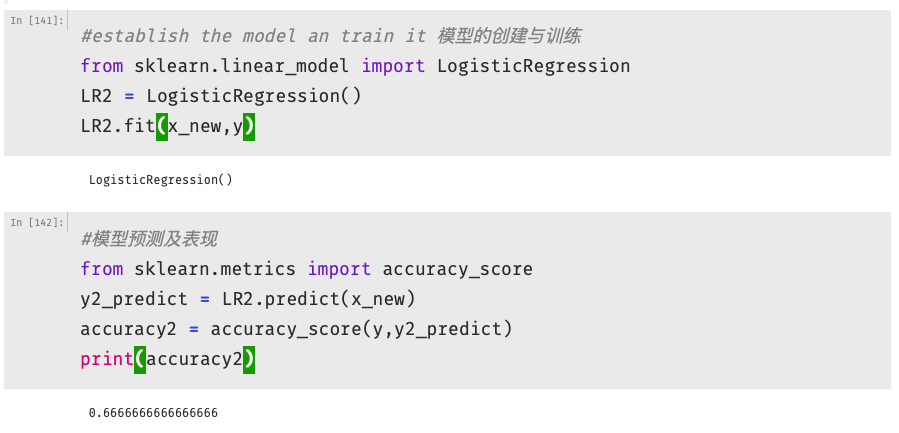
1 #define x,y 2 x = data.drop(['pass'],axis=1)#去除'pass'列 3 y = data.loc[:,'pass'] 4 x1 = data.loc[:,'test1'] 5 x2 = data.loc[:,'test2'] 6 x1.head() 7 8 #二阶边界函数 9 #create new data 10 x1_2 = x1*x1 11 x2_2 = x2*x2 12 x1_x2 = x1*x2 13 #建立一个新的数据字典 14 x_new = {'x1':x1,'x2':x2,'x1_2':x1_2,'x2_2':x2_2,'x1_x2':x1_x2} 15 x_new = pd.DataFrame(x_new)#加载数据 16 print(x_new)

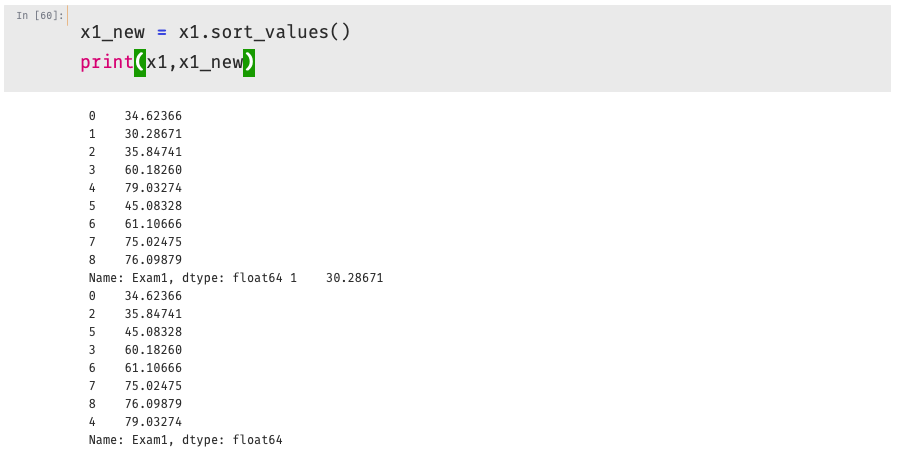
1 x1_new = x1.sort_values() 2 theta0 = LR2.intercept_ 3 theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,theta5 = LR2.coef_[0][0],LR2.coef_[0][1],LR2.coef_[0][2],LR2.coef_[0][3],LR2.coef_[0][4] 4 a = theta4 5 b = theta5*x1_new+theta2 6 c = theta0+theta1*x1_new+theta3*x1_new*x1_new 7 x2_new_boundary = (-b+np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a) # abs():取绝对值 8 9 #将原始数据与多阶函数进行混合 10 fig2 = plt.figure() #新建图形 11 passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][mask])#绘制散点图 12 failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][~mask])#绘制散点图 13 plt.plot(x1_new,x2_new_boundary)#预测曲线 14 plt.title('test1-test2')#标题 15 plt.xlabel('test1')#x轴 16 plt.ylabel('test2')#y轴 17 plt.legend((passed,failed),('passed','failed'))#题注 18 plt.show()



1 #将原始数据与多阶函数进行混合 2 fig3 = plt.figure() #新建图形 3 passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][mask])#绘制散点图 4 failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][~mask])#绘制散点图 5 plt.plot(x1_new,x2_new_boundary1)#预测曲线 6 plt.plot(x1_new,x2_new_boundary2)#预测曲线 7 plt.title('test1-test2')#标题 8 plt.xlabel('test1')#x轴 9 plt.ylabel('test2')#y轴 10 plt.legend((passed,failed),('passed','failed'))#题注 11 plt.show()
1 x1_range = [-0.9 + x/10000 for x in range(0,19000)] 2 x1_range = np.array(x1_range) 3 x2_new_boundary1 = [] 4 x2_new_boundary2 = [] 5 for x in x1_range: 6 x2_new_boundary1.append(f(x)[0]) 7 x2_new_boundary2.append(f(x)[1])
1 #将原始数据与多阶函数进行混合 2 fig4 = plt.figure() #新建图形 3 passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][mask])#绘制散点图 4 failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][~mask])#绘制散点图 5 plt.plot(x1_range,x2_new_boundary1)#预测曲线 6 plt.plot(x1_range,x2_new_boundary2)#预测曲线 7 plt.title('test1-test2')#标题 8 plt.xlabel('test1')#x轴 9 plt.ylabel('test2')#y轴 10 plt.legend((passed,failed),('passed','failed'))#题注 11 plt.show()