● 导航:去任意陌生的地方
● 周边:找餐馆、找酒店、找银行、找电影院
● 在上述应用中,都用到了地图和定位功能,在iOS开发中,要想加入这2 大功 能,必须基于2个框架进行开发
● Map Kit :用于地图展示
● Core Location :用于地理定位
● 2个热门专业术语
● LBS :Location Based Service
● SoLoMo :Social Local Mobile(索罗门)
CoreLocation框架的使用
#import <CoreLocation/CoreLocation.h>
● CoreLocation框架使用须知
● CoreLocation框架中所有数据类型的前缀都是CL
● CoreLocation中使用CLLocationManager对象来做用户定位
CLLocationManager
● 开始用户定位
• - (void)startUpdatingLocation;
● 停止用户定位
• - (void) stopUpdatingLocation;
● 当调用了startUpdatingLocation方法后,就开始不断地定位用户的位 置,中途会频繁地调用代理的下面方法
● - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateLocations:(NSArray *)locations;
• locations参数里面装着CLLocation对象
CLLocation
● @property(readonly,nonatomic)CLLocationCoordinate2Dcoordinate;
• 经纬度
● @property(readonly,nonatomic)CLLocationDistancealtitude;
• 海拔
● @property(readonly,nonatomic)CLLocationDirectioncourse;
• 路线,航向(取值范围是0.0°~359.9°,0.0°代表真北方向)
● @property(readonly,nonatomic)CLLocationSpeedspeed;
• 行走速度(单位是m/s)
● 用- (CLLocationDistance)distanceFromLocation:(const CLLocation*)location
方法可以计算2个位置之间的距离
CLLocationManager
● 每隔多少米定位一次
● @property(assign, nonatomic) CLLocationAccuracy desiredAccuracy;
● 定位精确度(越精确就越耗电)
CLLocationCoordinate2D
CLLocationDegrees latitude; // 纬度
CLLocationDegrees longitude; // 经度
}CLLocationCoordinate2D;
● 一般用CLLocationCoordinate2DMake函数来创建CLLocationCoordinate2D
用户隐私的保护
● 从iOS 6开始,苹果在保护用户隐私方面做了很大的加强,以下操作都必须经 过用户批准授权
● 要想获得用户的位置
● 想访问用户的通讯录、日历、相机、相册等等
● 当想访问用户的隐私信息时,系统会自动弹出一个对话框让用户授权
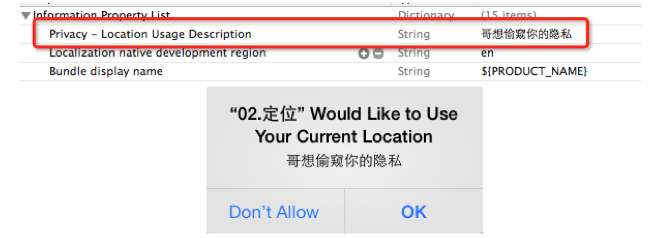
● 为了严谨起见,最好在使用定位功能之前判断当前应用的定位功能是否可用
• + (BOOL)locationServicesEnabled;
CLGeocoder
● 地理编码:根据给定的地名,获得具体的位置信息(比如经纬度、地址的全称等) ● 反地理编码:根据给定的经纬度,获得具体的位置信息
● 地理编码方法
● -(void)geocodeAddressString:(NSString*)addressString completionHandler: (CLGeocodeCompletionHandler)completionHandler;
● 反地理编码方法
● -(void)reverseGeocodeLocation:(CLLocation*)location completionHandler: (CLGeocodeCompletionHandler)completionHandler;
CLGeocodeCompletionHandler
● 这个block传递2个参数
• error :当编码出错时(比如编码不出具体的信息)有值
• placemarks :里面装着CLPlacemark对象
CLPlacemark
● @property(nonatomic,readonly)CLLocation*location;
• 地理位置
● @property(nonatomic,readonly)CLRegion*region;
• 区域
● @property(nonatomic,readonly)NSDictionary*addressDictionary;
• 详细的地址信息
● @property(nonatomic,readonly)NSString*name;
• 地址名称
● @property(nonatomic,readonly)NSString*locality;
• 城市
实例:Core Location :用于地理定位

#import "HMViewController.h" #import <CoreLocation/CoreLocation.h> @interface HMViewController () <CLLocationManagerDelegate> @property (nonatomic, strong) CLLocationManager *locMgr; @end @implementation HMViewController - (CLLocationManager *)locMgr { if (!_locMgr) { // 1.创建位置管理器(定位用户的位置) self.locMgr = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init]; // 2.设置代理 self.locMgr.delegate = self; } return _locMgr; } - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; if ([CLLocationManager locationServicesEnabled]) { // 开始定位用户的位置 [self.locMgr startUpdatingLocation]; // [self.locMgr startMonitoringForRegion:<#(CLRegion *)#>]; // self.locMgr.purpose // self.locMgr.distanceFilter = kCLDistanceFilterNone; // self.locMgr.desiredAccuracy = kcllocationac } else { // 不能定位用户的位置 // 1.告诉用户检查网络状况 // 2.提醒用户打开定位开关 } [self countDistance]; } - (void)countDistance { CLLocation *loc1 = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:40 longitude:116]; CLLocation *loc2 = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:41 longitude:116]; CLLocationDistance distance = [loc1 distanceFromLocation:loc2]; NSLog(@"(%@)和(%@)的距离:%f", loc1, loc2, distance); } #pragma mark - CLLocationManagerDelegate /** * 当定位到用户的位置时,就会调用(调用比较频繁) */ - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateLocations:(NSArray *)locations { // 数组里面存放的是CLLocation对象, 一个CLLocation就代表一个位置 CLLocation *loc = [locations lastObject]; // 纬度:loc.coordinate.latitude // 经度:loc.coordinate.longitude NSLog(@"纬度=%f, 经度=%f", loc.coordinate.latitude, loc.coordinate.longitude); // 停止更新位置(不用定位服务,应当马上停止定位,非常耗电) [manager stopUpdatingLocation]; } //- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didEnterRegion:(CLRegion *)region //{ // //} // //- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didExitRegion:(CLRegion *)region //{ // //} @end
实例:地理编码 and 反地理编码

#import "HMViewController.h" #import <CoreLocation/CoreLocation.h> @interface HMViewController () @property (nonatomic, strong) CLGeocoder *geocoder; #pragma mark - 地理编码 - (IBAction)geocode; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *addressField; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UILabel *longitudeLabel; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UILabel *latitudeLabel; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UILabel *detailAddressLabel; #pragma mark - 反地理编码 - (IBAction)reverseGeocode; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *longtitudeField; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *latitudeField; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UILabel *reverseDetailAddressLabel; @end @implementation HMViewController - (CLGeocoder *)geocoder { if (!_geocoder) { self.geocoder = [[CLGeocoder alloc] init]; } return _geocoder; } - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; } /** * 地理编码:地名 -> 经纬度 */ - (void)geocode { // 1.获得输入的地址 NSString *address = self.addressField.text; if (address.length == 0) return; // 2.开始编码 [self.geocoder geocodeAddressString:address completionHandler:^(NSArray *placemarks, NSError *error) { if (error || placemarks.count == 0) { self.detailAddressLabel.text = @"你输入的地址找不到,可能在火星上"; } else { // 编码成功(找到了具体的位置信息) // 输出查询到的所有地标信息 for (CLPlacemark *placemark in placemarks) { NSLog(@"name=%@ locality=%@ country=%@ postalCode=%@", placemark.name, placemark.locality, placemark.country, placemark.postalCode); } // 显示最前面的地标信息 CLPlacemark *firstPlacemark = [placemarks firstObject]; self.detailAddressLabel.text = firstPlacemark.name; CLLocationDegrees latitude = firstPlacemark.location.coordinate.latitude; CLLocationDegrees longitude = firstPlacemark.location.coordinate.longitude; self.latitudeLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%.2f", latitude]; self.longitudeLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%.2f", longitude]; } }]; } /** * 反地理编码:经纬度 -> 地名 */ - (void)reverseGeocode { NSString *longtitudeText = self.longtitudeField.text; NSString *latitudeText = self.latitudeField.text; if (longtitudeText.length == 0 || latitudeText.length == 0) return; CLLocationDegrees latitude = [latitudeText doubleValue]; CLLocationDegrees longtitude = [longtitudeText doubleValue]; // 开始反向编码 CLLocation *location = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:latitude longitude:longtitude]; [self.geocoder reverseGeocodeLocation:location completionHandler:^(NSArray *placemarks, NSError *error) { if (error || placemarks.count == 0) { self.reverseDetailAddressLabel.text = @"你输入的经纬度找不到,可能在火星上"; } else { // 编码成功(找到了具体的位置信息) // 输出查询到的所有地标信息 for (CLPlacemark *placemark in placemarks) { NSLog(@"name=%@ locality=%@ country=%@ postalCode=%@", placemark.name, placemark.locality, placemark.country, placemark.postalCode); } // 显示最前面的地标信息 CLPlacemark *firstPlacemark = [placemarks firstObject]; self.reverseDetailAddressLabel.text = firstPlacemark.name; CLLocationDegrees latitude = firstPlacemark.location.coordinate.latitude; CLLocationDegrees longitude = firstPlacemark.location.coordinate.longitude; self.latitudeField.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%.2f", latitude]; self.longtitudeField.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%.2f", longitude]; } }]; } - (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { [self.view endEditing:YES]; } @end
