There is a kind of balanced binary search tree named red-black tree in the data structure. It has the following 5 properties:
- (1) Every node is either red or black.
- (2) The root is black.
- (3) Every leaf (NULL) is black.
- (4) If a node is red, then both its children are black.
- (5) For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes.
For example, the tree in Figure 1 is a red-black tree, while the ones in Figure 2 and 3 are not.
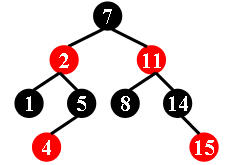 | 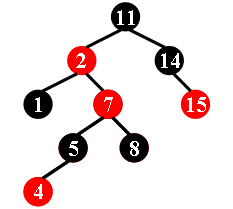 | 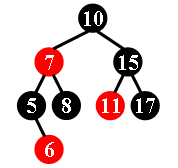 |
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
For each given binary search tree, you are supposed to tell if it is a legal red-black tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives a positive integer K (≤30) which is the total number of cases. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the preorder traversal sequence of the tree. While all the keys in a tree are positive integers, we use negative signs to represent red nodes. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space. The sample input cases correspond to the trees shown in Figure 1, 2 and 3.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line "Yes" if the given tree is a red-black tree, or "No" if not.
Sample Input:
3
9
7 -2 1 5 -4 -11 8 14 -15
9
11 -2 1 -7 5 -4 8 14 -15
8
10 -7 5 -6 8 15 -11 17
Sample Output:
Yes
No
No
代码:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 struct node 4 { 5 int val; 6 node* l, *r; 7 }; 8 int v[40]; 9 node* root; 10 11 void build(node *now, int val) 12 { 13 int v = now->val; 14 if (abs(val) < abs(v)) 15 { 16 if (now->l == NULL) 17 now->l = new node(), now->l->val = val; 18 else build(now->l, val); 19 } 20 else 21 { 22 if (now->r == NULL) 23 now->r = new node(), now->r->val = val; 24 else build(now->r, val); 25 } 26 } 27 28 bool judge(node* x) 29 { 30 if (!x) return true; 31 if (x->val < 0) 32 if (x->l && x->l->val < 0 || x->r && x->r->val < 0) return false; 33 return judge(x->l) && judge(x->r); 34 } 35 36 int cal(node* x) 37 { 38 if (!x) return 0; 39 int numl = cal(x->l), numr = cal(x->r); 40 if (numl == numr && numl != -1) 41 return x->val > 0 ? numl + 1 : numl; 42 return -1; 43 } 44 int main() 45 { 46 int t; cin >> t; 47 while (t--) 48 { 49 int n; cin >> n; 50 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 51 cin >> v[i]; 52 root = new node(); 53 root->val = v[1], root->l = root->r = NULL; 54 for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) 55 build(root, v[i]); 56 if (v[1] > 0 && judge(root) && cal(root) != -1) cout << "Yes" << endl; 57 else cout << "No" << endl; 58 } 59 }