1. 输入系统框架
android输入系统官方文档 // 需FQ
http://source.android.com/devices/input/index.html
《深入理解Android 卷III》第五章 深入理解Android输入系统 // 主要讲EventHub
http://blog.csdn.net/innost/article/details/47660387
图解Android - Android GUI 系统 (5) - Android的Event Input System - 漫天尘沙 - 博客园.htm // 关注里面的Dispatcher处理流程
http://www.cnblogs.com/samchen2009/p/3368158.html
输入系统可分为三部分:
(1)读取(linux驱动(生成设备节点)、APP处理(open/read设备节点、监测有无数据及热拔插、处理(比如映射)))
a、支持多设备:GPIO键盘(/dev/input/event0)、红外遥控器(/dev/input/event1)、USB键盘鼠标、触摸屏
b、即插即用
c、多语言:同一键盘同一按键在不同语言下得到不同字符,因此存在映射
(2)分发
a、分辨:对于按键分为systemkey(音量、电源)、Globalkey(特殊键:启动一个应用程序)、UserKey(发给应用程序);对于触摸屏分为VirtualKey、手势(两个手指放大缩小)
b、发送:找到当前APP,发给他
(3)处理
APP收到后,处理
点击动作:执行某系函数
输入框:启动输入法或者直接生成文字
android系统代码框架:
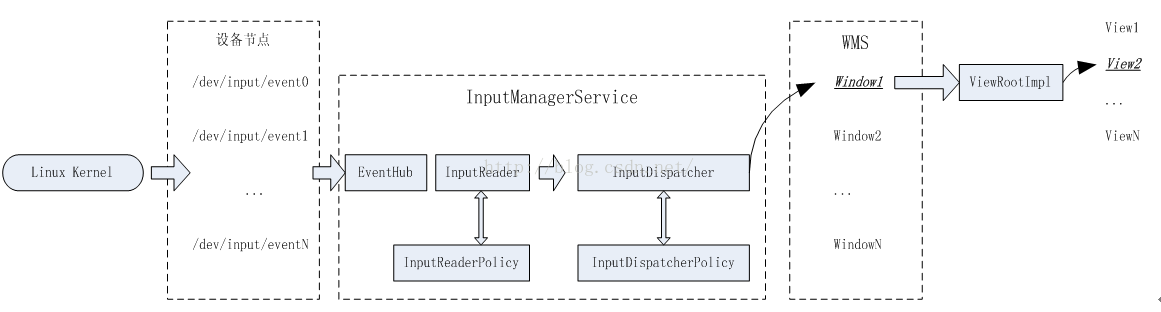
2. 编写一个万能模拟输入驱动程序
测试方法:
android系统中范问evdev驱动获得输入系统的原始数据
/dev/input/event1,2这个设备节点是通过evdev驱动创建的
对于鼠标设备,可以通过访问/dev/input/event获得鼠标的原始数据,也可以通过访问/dev/mouse1,2....得到加工后的鼠标数据
怎么写输入驱动:
(1)分配/构造input_device结构体
(2)注册input_register_device后和evdev、keyboard、mouse上层框架建立联系
(3)有输入事件产生时,中断程序通过input_event上报数据
总结输入流程
APP:
d、open("/dev/input/event5")
f、read
驱动
(1)evdev.c
c、注册input的时候如果支持调用evdev的connect函数来创建设备节点
e、evdev_open被调用,并与input_dev建立联系
g、evdev_read被调用,无数据会休眠
j、input_event会调用evdev中的某个函数把数据放入buf,并唤醒休眠的进程
(2)硬件相关
a、构造input_dev
b、注册input_register_device
i、中断服务创新被调用,input_event被调用
(3)硬件
h、用户按下按键,产生中断
inputemulator.c
static struct input_dev *input_emulator_dev;
static int input_emulator_init(void)
{
int i;
input_emulator_dev = input_allocate_device();
//设置能产生哪类事情
set_bit(EV_KEY,input_emulator_dev->evbit);
set_bit(EV_REP,input_emulator_dev->evbit);
//设置能产生所有的按键事件
for(i=0;i<BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT);i++)
input_emulator_dev->keybit[i] = ~0UL;
//为android构造一些设备信息
input_emulator_dev ->name = "InputEmulatorFrom100ask.net";
input_emulator_dev ->id.bustype =1;
input_emulator_dev ->id.vendor = 0x1234;
input_emulator_dev ->id.product = 0x5678;
input_emulator_dev ->id.version = 1;
//注册
input_register_device(input_emulator_dev);
return 0;
}
static void input_emulator_exit(void)
{
input_unregister_device(input_emulator_dev);
input_free_device(input_emulator_dev);
}
module_init(input_emulator_init);
module_exit(input_emulator_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile:
LERN_DIR = /work/linux-3.0.86
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=‘pwd’ modules
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=‘pwd’ modules clean
rm -rf modules.order
obj-m += InputEmulator .o
安装驱动后:使用sendevent指令开上报数据给指定的input设备
sendevent /dev/input/event5 1 2 1 // 1 2 1 : EV_KEY, KEY_1, down
sendevent /dev/input/event5 1 2 0 // 1 2 0 : EV_KEY, KEY_1, up
sendevent /dev/input/event5 0 0 0 // sync
sendevent /dev/input/event5 1 3 1
sendevent /dev/input/event5 1 3 0
sendevent /dev/input/event5 0 0 0
3. reader/dispatcher线程启动过程源码分析
涉及使用bouml制作时序图,先看 第0课第3节:使用bouml制作时序图
uml_tmp_file.rar
reader线程监控输入系统的设备节点,dispatcher线程负责分发,这两个线程由InputManagerService创建
InputReaderThread实例化对象mReaderTHread,其里面调用threadLoop循环;mReaderTHread只是创建线程,实现循环,在循环操作中用到mReader对象的函数
InputDispatcherThread实例化对象mDispatcherTHread,其里面调用threadLoop循环;mDispatcherTHread只是创建线程,实现循环,在循环操作中用到mDispatcher对象的函数
因此主进程还要创建两个实例化对象InputReader类对象mReader、InputDispatcher对象mDispatcher
还有个重要的EventHub类,其实例化对象时mEventHub,用这个对象监控输入设备
上述所有类使用InputManager类的mInputManager对象来管理,并且都是用C++实现的
Java层次通过JNI NativeInputManager来访问C++ InputManager
InputManager = new InputManagerService(context)//SystemServer.java
nativeInit();//在构造函数中通过JNI调用C++中的方法
nativeInit(JNIEnv*env,jclass clazz)//com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
NativeInputManager* im = new NativeInputManager(contextObj)
eventHub = new EventHub()//在NativeInputManager的构造函数中
eEpollFd = epoll_create(EPOLL_SIZE_HINT);
mInotify = inotify_init();
mInputManager = new InputManager(eventHub,this,this)
mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy)//dispatcherPolicy=im
mReader = new InputReader(eventHub,readerPolicy,mDispatcher)readerPolicy=im
mEventHub = .....
mPolicy = im
mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener)
initialize()
mReaderThread = new InputReaderThread(mReader)
mDispatcherThread = new InputDispatcherTHread(mDispatcher)
inputManager.start()
nativeStart()
im->getInputManager()->start()
mDispatcherThread->run()
mReaderThread->run()
