一、Java IO的定义
I/O:输入输出系统,由输入输出控制系统和外围设备两部分组成。
Java中I/O操作主要是指使用Java进行输入,输出操作. Java所有的I/O机制都是基于数据流进行输入输出,这些数据流表示了字符或者字节数据的流动序列。java类库中的I/O类分为输入和输出两部分。
Java IO模型 :Java的IO模型设计是非常典型的装饰器模式---Decorator模式,按功能划分Stream,可以动态装配这些Stream,以便获得您需要的功能。例如,需要一个具有缓冲的文件输入流,则应当组合使用FileInputStream和BufferedInputStream。
二、流的分类
1.按流的方向分类
按流的方向分为:输入和输出流,注意输入流和输出流是相对于程序而言的。输入流即从不同数据源输入进程序或者说内存。输出流则相反。
输入流的数据源包括:字节数组、String对象、文件、管道、一个由其他种类的流组成的序列、其他数据源,如intenet连接等。
2.按传输单位分类
按传输单位分为:字节流和字符流,例如:InputStream和OutStream、Reader和Writer。
|
输入/输出 |
字节流 |
字符流 |
|
输入流 |
Inputstream |
Reader |
|
输出流 |
OutputStream |
Writer |
3.按功能分类
按功能分为:节点流和处理流,节点流:可以从或向一个特定的地方(节点)读写数据。如FileReader。处理流:是对一个已存在的流的连接和封装,通过所封装的流的功能调用实现数据读写。如BufferedReader。
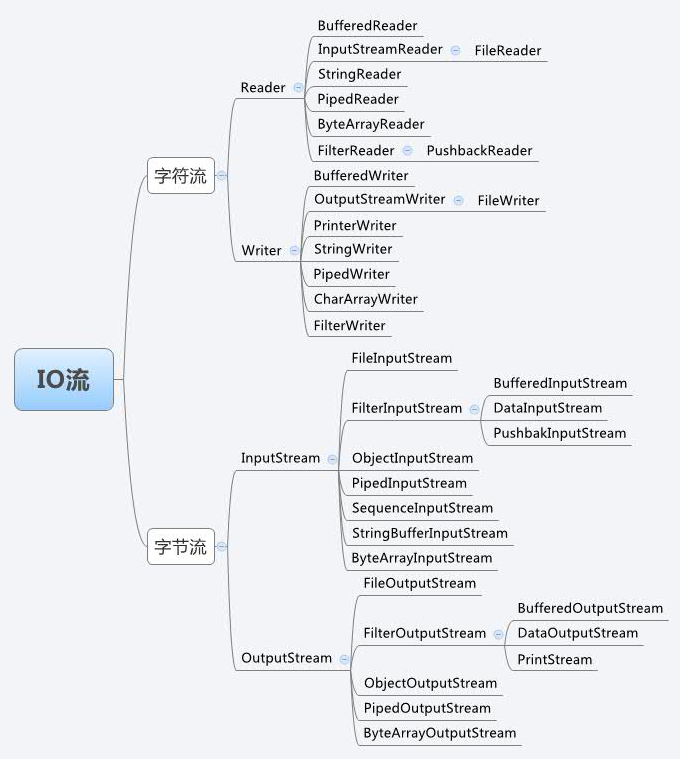
三、Java IO 流的整体架构图
从网上找到一张关于java IO流的整体架构图,一目了然。
四、输入输出字节流
1 public class FileStreamDemo { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 //字节输入/输出流,并且以文件为数据源,即文件字节输入输出流 6 try { 7 //1.确定数据源与流类型 8 File targetFile = new File("E:\a.txt"); 9 OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(targetFile, true);//第二参数,表示写入的数据是否追加到文件后面 10 //2.借助流进行具体的IO操作 11 /** 12 * void write(int b):把一个字节写入到文件中 13 * void write(byte[] b):把数组b 中的所有字节写入到文件中 14 * void write(byte[] b,int off,int len):把数组b 中的从 off 索引开始的 len 个字节写入到文件中 15 */ 16 os.write(45); 17 os.write("aaa".getBytes()); 18 os.write("bbbbb".getBytes(), 1, 3); 19 //操作完毕,关闭流 20 os.close(); 21 22 //通过字节输入流将目标文件的数据读取进内存中 23 InputStream is = new FileInputStream(targetFile); 24 25 //读取一个字节 26 int data1 = is.read(); 27 System.out.println((char)data1); 28 29 byte [] bytes = new byte[10]; 30 is.read(bytes); 31 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes)); 32 33 is.close(); 34 35 36 37 } catch (Exception e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 41 42 43 } 44 45 }
结果输出:
-
[97, 97, 97, 98, 98, 98, 0, 0, 0, 0]
五、输入输出字符流
Java中字符是采用Unicode标准,一个字符是16位,即一个字符使用两个字节来表示。为此,JAVA中引入了处理字符的流。一般可以用记事本打开的文件,我们可以看到内容不乱码的。就是文本文件,可以使用字符流。而操作二进制文件(比如图片、音频、视频)必须使用字节流。
1 public class FileStreamDemo2 { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 //1.定义数据源对象 5 File targetFile = new File("E:\test.txt"); 6 try { 7 //2.定义输出字符流 8 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(targetFile,true); 9 //3.借助字符流进行IO操作 10 fw.write(65); 11 fw.write("lplp"); 12 fw.write(new char[]{'a','b','c'}, 1, 2); 13 fw.close(); 14 15 FileReader fr = new FileReader(targetFile); 16 char [] ch= new char[5]; 17 System.out.println(fr.read()); 18 int count = fr.read(ch);//读取流中字符填充到字符数组ch中 19 System.out.println(count+":"+Arrays.toString(ch)); 20 fr.close(); 21 } catch (Exception e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } 24 } 25 26 }
结果输出:
65 5:[l, p, l, p, b]
六、包装流的使用
包装流,又称处理流,主要用来对已存在的流进行修饰和封装,进一步丰富或拓展流的功能。常用的处理流主要有下面几种
1.缓冲流
缓冲流:是一个包装流,目的是缓存作用,加快读取和写入数据的速度。
字节缓冲流:BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream
字符缓冲流:BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
1 public class BufferStreamDemo { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 //1.定义数据源对象 6 File targetFile = new File("E:\test2.txt"); 7 8 try { 9 //2.定义字节缓冲输出流 10 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(targetFile)); 11 /* 12 *通过缓冲流将字节数组写入到文件输出流,最终是写入到文件,与通过文件字节输出流的区别在于,具备一个缓冲的作用,并不会立即将字节数组或者字节 13 * 写入到文件中,而先将字节写入到缓冲字节数组中,最后一次性写入到输出流中,避免多次操流,减少IO操作,提高效率,写到内存中比写到硬盘上快的多 14 */ 15 bos.write("aaa".getBytes()); 16 bos.write(100); 17 bos.write("sdjlksdjkl".getBytes(), 1, 5); 18 19 bos.flush();//将缓冲字节数组的字节写入文件 20 bos.close(); 21 //3.定义字节缓冲输入流,本质上也是较少IO操作 22 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(targetFile)); 23 24 System.out.println((char)bis.read()); 25 byte [] bs = new byte[8]; 26 bis.read(bs); 27 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bs)); 28 System.out.println(new String(bs)); 29 30 bis.close(); 31 } catch (Exception e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 35 } 36 37 }
结果输出:
a
[97, 97, 100, 100, 106, 108, 107, 115]
aaddjlks
字符缓冲流,BufferedReader和BufferedWriter的使用和上面异曲同工。
2.转换流
InputStreamReader:把字节输入流转换为字符输入流
OutputStreamWriter:把字节输出流转换为字符输出流
1 public class BufferStreamDemo2 { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 //1.定义数据源对象 6 File targetFile = new File("E:\test2.txt"); 7 8 try { 9 //定义缓冲字符流,将字节输出流转换为字符流,再包装为字符输出缓冲流,并且字符在转字节的时候,采用的编码为UTF-8 10 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(targetFile),"UTF-8")); 11 bw.write("aaabababcc"); 12 bw.flush(); 13 bw.close(); 14 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(targetFile))); 15 String line = br.readLine();//读取文件中的一行 16 System.out.println(line); 17 br.close(); 18 19 } catch (Exception e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 }
结果输出:
aaabababcc
3.内存流
字节内存流:ByteArrayOutputStream 、ByteArrayInputStream
字符内存流:CharArrayReader、CharArrayWriter
字符串流:StringReader,StringWriter(把数据临时存储到字符串中)
1 public class ArrayStreamDemo { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 //1.字节内存流,数据源为字节数组 5 ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream("aaa".getBytes()); 6 //2通过字节流从字节数组从读取字节 7 int len =-1; 8 while((len=bais.read())!=-1){ 9 System.out.println((char)len); 10 } 11 //3.定义字节数组输出流 12 ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(5);//10表示指定字节数组的大小 13 try { 14 baos.write("abcdef".getBytes()); 15 16 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(baos.toByteArray())); 17 System.out.println("--------------"); 18 //4.定义字符数组输出流 19 CharArrayWriter caw = new CharArrayWriter(); 20 caw.write("ppll"); 21 System.out.println(new String(caw.toCharArray())); 22 //5.定义字符数组输入流 23 CharArrayReader car = new CharArrayReader(caw.toCharArray());//从字符数组中读取字符 24 int len2 =-1; 25 while((len2=car.read())!=-1){ 26 System.out.print((char)len2); 27 } 28 System.out.println(); 29 System.out.println("--------------"); 30 //7.字符串输入流 31 StringReader sr = new StringReader("aaaa"); 32 //8.字符串输出流 33 StringWriter sw = new StringWriter(); 34 int len3=-1; 35 while((len3=sr.read())!=-1){ 36 sw.write(len3); 37 } 38 System.out.println(sw.getBuffer().toString()); 39 40 } catch (Exception e) { 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } 43 44 45 } 46 47 }
输出结果:
a a a [97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102] -------------- ppll ppll -------------- aaaa