本文内容
- 并行编程
- 任务并行
- 隐式创建和运行任务
- 显式创建和运行任务
- 任务 ID
- 任务创建选项
- 创建任务延续
- 创建分离的子任务
- 创建子任务
- 等待任务完成
- 组合任务
- 任务中的异常处理
- 取消任务
- TaskFactory 类
- 无委托的任务
- 相关数据结构
- 参考资料
下载 Demo
下载 Samples for Parallel Programming with .net framework
并行编程
多核 CPU 已经相当普遍,使得多个线程能够同时执行。将代码并行化,工作也就分摊到多个 CPU 上。
过去,并行化需要线程和锁的低级操作。而 Visual Studio 2010 和 .NET Framework 4 开始提供了新的运行时、新的类库类型以及新的诊断工具,从而增强了对并行编程的支持。这些功能简化了并行开发,通过固有方法编写高效、细化且可伸缩的并行代码,而不必直接处理线程或线程池。
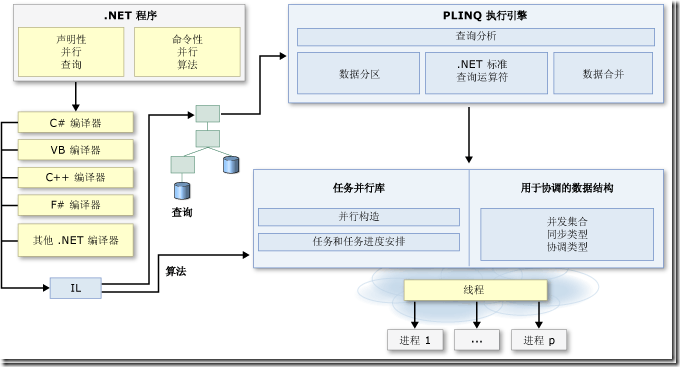
下图从较高层面上概述了 .NET Framework 4 中的并行编程体系结构。
任务并行库(The Task Parallel Library,TPL)是 System.Threading 和 System.Threading.Tasks 空间中的一组公共类型和 API。TPL 的目的是通过简化将并行和并发添加到应用程序的过程来提高开发人员的工作效率。TPL 能动态地最有效地使用所有可用的处理器。此外,TPL 还处理工作分区、ThreadPool 上的线程调度、取消支持、状态管理以及其他低级别的细节操作。通过使用 TPL,你可以将精力集中于程序要完成的工作,同时最大程度地提高代码的性能。
从 .NET Framework 4 开始,TPL 是编写多线程代码和并行代码的首选方法。但并不是所有代码都适合并行化,例如,如果某个循环在每次迭代时只执行少量工作,或它在很多次迭代时都不运行,那么并行化的开销可能导致代码运行更慢。 此外,像任何多线程代码一样,并行化会增加程序执行的复杂性。 尽管 TPL 简化了多线程方案,但建议对线程处理概念(例如,锁、死锁和争用条件)进行基本了解,以便能够有效地使用 TPL。
任务并行
“任务并行”是指一个或多个独立的任务同时运行。好处当然是系统资源的使用效率更高,可伸缩性更好;对于线程或工作项,可以使用更多的编程控件。因此,在 .NET Framework 中,TPL 是用于编写多线程、异步和并行代码的首选 API。
隐式创建和运行任务
Parallel.Invoke 方法提供了一种简便方式,可同时运行任意数量的任意语句。只需为每个工作项传入 Action 委托即可。
下面的示例演示 Invoke 调用,创建并启动同时运行三个任务。将对共享数据达尔文的《物种起源》执行三项操作:最长的词、最频繁出现的词和字数。这些操作都不修改源,因此它们可以直接并行执行。
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ParallelInvokeDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Retrieve Darwin's "Origin of the Species" from Gutenberg.org.
string[] words = CreateWordArray();
// Perform three tasks in parallel on the source array
Parallel.Invoke(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Begin first task...");
GetLongestWord(words);
}, // close first Action
() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Begin second task...");
GetMostCommonWords(words);
}, //close second Action
() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Begin third task...");
GetCountForWord(words, "species");
} //close third Action
); //close parallel.invoke
Console.WriteLine("Returned from Parallel.Invoke");
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static string GetLongestWord(string[] words)
{
var longestWord = (from w in words
orderby w.Length descending
select w).First();
Console.WriteLine("Task 1 -- The longest word is {0}", longestWord);
return longestWord;
}
private static void GetMostCommonWords(string[] words)
{
var frequencyOrder = from word in words
where word.Length > 6
group word by word into g
orderby g.Count() descending
select g.Key;
var commonWords = frequencyOrder.Take(10);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.AppendLine("Task 2 -- The most common words are:");
foreach (var v in commonWords)
{
sb.AppendLine(" " + v);
}
Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString());
}
private static void GetCountForWord(string[] words, string term)
{
var findWord = from word in words
where word.ToUpper().Contains(term.ToUpper())
select word;
Console.WriteLine(@"Task 3 -- The word ""{0}"" occurs {1} times.", term, findWord.Count());
}
static string[] CreateWordArray()
{
string s = System.IO.File.ReadAllText("Origin of the Species.txt");
// Separate string into an array of words, removing some common punctuation.
return s.Split(
new char[] { ' ', 'u000A', ',', '.', ';', ':', '-', '_', '/' },
StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
}
}
}
//RESULT:
//Begin second task...
//Begin first task...
//Begin third task...
//Task 2 -- The most common words are:
// species
// selection
// varieties
// natural
// animals
// between
// different
// distinct
// several
// conditions
//Task 1 -- The longest word is characteristically
//Task 3 -- The word "species" occurs 1927 times.
//Returned from Parallel.Invoke
//Press any key to exit.
为了更好地控制任务执行或从任务返回值,必须更加显式地使用 Task 对象。
显式创建和运行任务
不返回值的任务由 System.Threading.Tasks.Task 类表示。返回值的任务由 System.Threading.Tasks.Task<TResult> 类表示,该类从 Task 继承。
任务对象处理基础结构详细信息,并提供可在任务的整个生存期内从调用线程访问的方法和属性。 例如,可以随时访问任务的 Status 属性,以确定它是已开始运行、已完成运行、已取消还是引发了异常。 状态由 TaskStatus 枚举表示。
在创建任务时,你赋予它一个用户委托,该委托封装该任务将执行的代码。 该委托可以表示为命名的委托、匿名方法或 lambda 表达式。 lambda 表达式可以包含对命名方法的调用,如下面的示例所示。
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExplicitTaskDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main";
// Create a task and supply a user delegate by using a lambda expression.
Task taskA = new Task(() => Console.WriteLine("Hello from taskA."));
// Start the task.
taskA.Start();
// Output a message from the calling thread.
Console.WriteLine("Hello from thread '{0}'.", Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
taskA.Wait();
//Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main";
//// Define and run the task.
//Task taskA = Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine("Hello from taskA."));
//// Output a message from the calling thread.
//Console.WriteLine("Hello from thread '{0}'.", Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
//taskA.Wait();
//Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main";
//// Better: Create and start the task in one operation.
//Task taskA = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => Console.WriteLine("Hello from taskA."));
//// Output a message from the calling thread.
//Console.WriteLine("Hello from thread '{0}'.", Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
//taskA.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("Press any Key to Exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
//TaskParallel1 RESULT:
//Hello from thread 'Main'.
//Hello from taskA.
//Press any Key to Exit.
你可以用 new Task(),也可以用 Task.Run(),还可以用 Task.Factory.StartNew(),创建并启动一个任务。其中,Task.Run() 是首选方法;不必将创建和计划分开并且你需要其他任务创建选项或使用特定计划程序时,或者需要通过 AsyncState 属性将其他状态传递到任务时,使用 Task.Factory.StartNew()。
任务创建选项
创建任务的大多数 API 提供接受 TaskCreationOptions 枚举参数。 通过指定下列选项之一,可指示任务计划程序如何在线程池中安排任务计划。
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TaskCreationOptionsDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var task3 = new Task(() => MyLongRunningMethod(),
TaskCreationOptions.LongRunning | TaskCreationOptions.PreferFairness);
task3.Start();
task3.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to Exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void MyLongRunningMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("A long, long time ago......");
}
}
}
|
TaskCreationOptions 参数值 |
说明 |
|
None |
未指定任何选项时的默认值。 计划程序将使用其默认试探法来计划任务。 |
|
PreferFairness |
指定应当计划任务,以使越早创建的任务将更可能越早执行,而越晚创建的任务将更可能越晚执行。 |
|
LongRunning |
指定该任务表示长时间运行的运算。 |
|
AttachedToParent |
指定应将任务创建为当前任务(如果存在)的附加子级。 有关更多信息,请参见已附加和已分离的子任务。 |
|
DenyChildAttach |
指定如果内部任务指定 AttachedToParent 选项,则该任务不会成为附加的子任务。 |
|
HideScheduler |
指定通过调用特定任务内部的 TaskFactory.StartNew 或 Task<TResult>.ContinueWith 等方法创建的任务的任务计划程序是默认计划程序,而不是正在运行此任务的计划程序。 |
创建任务延续
使用 Task.ContinueWith 和 Task<TResult>.ContinueWith 方法可以指定在先行任务完成时要启动的任务。 延续任务的委托已传递了对先行任务的引用,因此它可以检查先行任务的状态,并通过检索 Task<TResult>.Result 属性的值将先行任务的输出用作延续任务的输入。
var getData = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Random rnd = new Random();
int[] values = new int[100];
for (int ctr = 0; ctr <= values.GetUpperBound(0); ctr++)
values[ctr] = rnd.Next();
return values;
});
var processData = getData.ContinueWith((x) =>
{
int n = x.Result.Length;
long sum = 0;
double mean;
for (int ctr = 0; ctr <= x.Result.GetUpperBound(0); ctr++)
sum += x.Result[ctr];
mean = sum / (double)n;
return Tuple.Create(n, sum, mean);
});
var displayData = processData.ContinueWith((x) =>
{
return String.Format("N={0:N0}, Total = {1:N0}, Mean = {2:N2}",
x.Result.Item1, x.Result.Item2, x.Result.Item3);
});
Console.WriteLine(displayData.Result);
//N=100, Total = 108,192,345,466, Mean = 1,081,923,454.66
//Press any key to Exit.
也可以用链式写法:
var displayData = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Random rnd = new Random();
int[] values = new int[100];
for (int ctr = 0; ctr <= values.GetUpperBound(0); ctr++)
values[ctr] = rnd.Next();
return values;
}).
ContinueWith((x) =>
{
int n = x.Result.Length;
long sum = 0;
double mean;
for (int ctr = 0; ctr <= x.Result.GetUpperBound(0); ctr++)
sum += x.Result[ctr];
mean = sum / (double)n;
return Tuple.Create(n, sum, mean);
}).
ContinueWith((x) =>
{
return String.Format("N={0:N0}, Total = {1:N0}, Mean = {2:N2}",
x.Result.Item1, x.Result.Item2,
x.Result.Item3);
});
Console.WriteLine(displayData.Result);
创建分离的子任务
如果在任务中运行的用户代码创建一个新任务,且未指定 AttachedToParent 选项,则该新任务不采用任何特殊方式与父任务同步。 这种不同步的任务类型称为“分离的嵌套任务”或“分离的子任务”。
var outer = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Outer task beginning.");
var child = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Thread.SpinWait(5000000);
Console.WriteLine("Detached task completed.");
});
});
outer.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("Outer task completed.");
//The example displays the following output:
//Outer task beginning.
//Outer task completed.
//Detached task completed.
从输出信息看,outer 没有等 child。
创建子任务
如果在一个任务中运行的用户代码创建任务时指定了 AttachedToParent 选项,则该新任务称为父任务的“附加子任务”。 因为父任务隐式地等待所有附加子任务完成,所以你可以使用 AttachedToParent 选项表示结构化的任务并行。
var parent = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Parent task beginning.");
for (int ctr = 0; ctr < 10; ctr++)
{
int taskNo = ctr;
Task.Factory.StartNew((x) =>
{
Thread.SpinWait(5000000);
Console.WriteLine("Attached child #{0} completed.",
x);
},
taskNo, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent);
}
});
parent.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("Parent task completed.");
//The example displays the following output:
//Parent task beginning.
//Attached child #9 completed.
//Attached child #0 completed.
//Attached child #8 completed.
//Attached child #1 completed.
//Attached child #3 completed.
//Attached child #7 completed.
//Attached child #4 completed.
//Attached child #5 completed.
//Attached child #2 completed.
//Attached child #6 completed.
//Parent task completed.
等待任务完成
System.Threading.Tasks.Task 类型和 System.Threading.Tasks.Task<TResult> 类型提供了 Task.Wait 和 Task<TResult>.Wait 方法的若干重载,使你能够等待任务完成。
此外,使用静态 Task.WaitAll 和 Task.WaitAny 方法的重载可以等待一批任务中的任一任务或所有任务完成。
通常,会出于以下某个原因等待任务:
- 主线程依赖于任务计算的最终结果。
- 你必须处理可能从任务引发的异常。
- 应用程序可以在所有任务执行完毕之前终止。 例如,执行 Main(应用程序入口点)中的所有同步代码后,控制台应用程序将立即终止。
组合任务
Task 类和 Task<TResult> 类提供多种方法,这些方法能够帮助你组合多个任务以实现常见模式,并更好地使用由 C#、Visual Basic 和 F# 提供的异步语言功能。 本节介绍了 WhenAll、WhenAny、Delay 和 FromResult<TResult> 方法。
Task.WhenAll 和 Task.WhenAny
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TaskWaitAllWaitAnyDemo
{
class Program
{
static Random rand = new Random();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Wait on a single task with no timeout specified.
Task taskA = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => DoSomeWork(10000000));
taskA.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("taskA has completed.");
// Wait on a single task with a timeout specified.
Task taskB = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => DoSomeWork(10000000));
taskB.Wait(100); //Wait for 100 ms.
if (taskB.IsCompleted)
Console.WriteLine("taskB has completed.");
else
Console.WriteLine("Timed out before taskB completed.");
// Wait for all tasks to complete.
Task[] tasks = new Task[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
tasks[i] = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => DoSomeWork(10000000));
}
Task.WaitAll(tasks);
// Wait for first task to complete.
Task<double>[] tasks2 = new Task<double>[3];
// Try three different approaches to the problem. Take the first one.
tasks2[0] = Task<double>.Factory.StartNew(() => TrySolution1());
tasks2[1] = Task<double>.Factory.StartNew(() => TrySolution2());
tasks2[2] = Task<double>.Factory.StartNew(() => TrySolution3());
int index = Task.WaitAny(tasks2);
double d = tasks2[index].Result;
Console.WriteLine("task[{0}] completed first with result of {1}.", index, d);
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void DoSomeWork(int val)
{
// Pretend to do something.
Thread.SpinWait(val);
}
static double TrySolution1()
{
int i = rand.Next(1000000);
// Simulate work by spinning
Thread.SpinWait(i);
return DateTime.Now.Millisecond;
}
static double TrySolution2()
{
int i = rand.Next(1000000);
// Simulate work by spinning
Thread.SpinWait(i);
return DateTime.Now.Millisecond;
}
static double TrySolution3()
{
int i = rand.Next(1000000);
// Simulate work by spinning
Thread.SpinWait(i);
Thread.SpinWait(1000000);
return DateTime.Now.Millisecond;
}
}
}
//The example displays the following output:
//taskA has completed.
//taskB has completed.
//task[0] completed first with result of 353.
最后一个输出结果是不确定的,因为 int index = Task.WaitAny(tasks2); 语句,task2 任务数组中有一个完成,就可以执行该语句下面的语句。
Task.FromResult<TResult>
using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TaskFromResultDemo
{
/// <summary>
/// Demonstrates how to use Task<TResult>.FromResult to create a task that holds a pre-computed result.
/// </summary>
class Program
{
// Holds the results of download operations.
static ConcurrentDictionary<string, string> cachedDownloads = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, string>();
// Asynchronously downloads the requested resource as a string.
public static Task<string> DownloadStringAsync(string address)
{
// First try to retrieve the content from cache.
string content;
if (cachedDownloads.TryGetValue(address, out content))
{
return Task.FromResult<string>(content);
}
// If the result was not in the cache, download the
// string and add it to the cache.
return Task.Run(async () =>
{
content = await new WebClient().DownloadStringTaskAsync(address);
cachedDownloads.TryAdd(address, content);
return content;
});
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// The URLs to download.
string[] urls = new string[]
{
"http://msdn.microsoft.com",
"http://www.contoso.com",
"http://www.microsoft.com"
};
// Used to time download operations.
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
// Compute the time required to download the URLs.
stopwatch.Start();
var downloads = from url in urls
select DownloadStringAsync(url);
Task.WhenAll(downloads).ContinueWith(results =>
{
stopwatch.Stop();
// Print the number of characters download and the elapsed time.
Console.WriteLine("Retrieved {0} characters. Elapsed time was {1} ms.",
results.Result.Sum(result => result.Length),
stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
})
.Wait();
// Perform the same operation a second time. The time required
// should be shorter because the results are held in the cache.
stopwatch.Restart();
downloads = from url in urls
select DownloadStringAsync(url);
Task.WhenAll(downloads).ContinueWith(results =>
{
stopwatch.Stop();
// Print the number of characters download and the elapsed time.
Console.WriteLine("Retrieved {0} characters. Elapsed time was {1} ms.",
results.Result.Sum(result => result.Length),
stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
})
.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to Exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
//The example displays the following output:
//Retrieved 45462 characters. Elapsed time was 23734 ms.
//Retrieved 45462 characters. Elapsed time was 0 ms.
//Press any key to Exit.
任务中的异常处理
当某个任务抛出一个或多个异常时,异常包装在 AggregateException 异常中。 该异常传播回与该任务联接的线程,通常该线程正在等待该任务完成或该线程访问 Result 属性。此行为用于强制实施 .NET Framework 策略 - 默认所有未处理的异常应终止进程。
可以通过将 Wait、WaitAll 或 WaitAny 方法,以及 Result 属性放入 try/catch 块中来处理异常。
捕获 System.AggregateException,然后检查其 InnerExceptions 以查看是否存在任何可由程序代码处理的异常。如下代码所示:
static void HandleExceptions()
{
// Assume this is a user-entered string.
string path = @"C:";
// Use this line to throw UnauthorizedAccessException, which we handle.
Task<string[]> task1 = Task<string[]>.Factory.StartNew(() => GetAllFiles(path));
// Use this line to throw an exception that is not handled.
// Task task1 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); } );
try
{
task1.Wait();
}
catch (AggregateException ae)
{
ae.Handle((x) =>
{
if (x is UnauthorizedAccessException) // This we know how to handle.
{
Console.WriteLine("You do not have permission to access all folders in this path.");
Console.WriteLine("See your network administrator or try another path.");
return true;
}
return false; // Let anything else stop the application.
});
}
Console.WriteLine("task1 has completed.");
}
static string[] GetAllFiles(string str)
{
// Should throw an AccessDenied exception on Vista.
return System.IO.Directory.GetFiles(str, "*.txt", System.IO.SearchOption.AllDirectories);
}
在此示例中,捕获 System.AggregateException,但不尝试处理任何其内部异常。 而是使用 Flatten 方法从任何嵌套的 AggregateException 实例中提取内部异常,并再次引发直接包含所有内部未处理异常的单个 AggregateException。 展平异常将使其更便于供客户端代码处理。
static void RethrowAllExceptions()
{
// Assume this is a user-entered string.
string path = @"C:";
Task<string[]>[] tasks = new Task<string[]>[3];
tasks[0] = Task<string[]>.Factory.StartNew(() => GetAllFiles(path));
tasks[1] = Task<string[]>.Factory.StartNew(() => GetValidExtensions(path));
tasks[2] = Task<string[]>.Factory.StartNew(() => new string[10]);
//int index = Task.WaitAny(tasks2);
//double d = tasks2[index].Result;
try
{
Task.WaitAll(tasks);
}
catch (AggregateException ae)
{
throw ae.Flatten();
}
Console.WriteLine("task1 has completed.");
}
static string[] GetValidExtensions(string path)
{
if (path == @"C:")
throw new ArgumentException("The system root is not a valid path.");
return new string[10];
}
取消任务
Task 类支持协作取消,并与 .NET Framework 4 中新增的 System.Threading.CancellationTokenSource 类和 System.Threading.CancellationToken 类完全集成。
创建任务的大多数 API 提供接受 CancellationToken 参数。
var tokenSource2 = new CancellationTokenSource();
CancellationToken ct = tokenSource2.Token;
var task = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
// Were we already canceled?
ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
bool moreToDo = true;
while (moreToDo)
{
// Poll on this property if you have to do
// other cleanup before throwing.
if (ct.IsCancellationRequested)
{
// Clean up here, then...
ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
}
}
}, tokenSource2.Token); // Pass same token to StartNew.
tokenSource2.Cancel();
// Just continue on this thread, or Wait/WaitAll with try-catch:
try
{
task.Wait();
}
catch (AggregateException e)
{
foreach (var v in e.InnerExceptions)
Console.WriteLine(e.Message + " " + v.Message);
}
TaskFactory 类
TaskFactory 类提供静态方法,这些方法封装了用于创建和启动任务和延续任务的一些常用模式。
- 最常用模式为 StartNew,它在一个语句中创建并启动任务。
- 从多个先行任务创建延续任务时,请使用 ContinueWhenAll 方法或 ContinueWhenAny 方法,或者它们在 Task<TResult> 类中的等效方法。 有关更多信息,请参见延续任务。
- 若要在 Task 或 Task<TResult> 实例中封装异步编程模型 BeginX 和 EndX 方法,请使用 FromAsync 方法。
默认的 TaskFactory 可作为 Task 类或 Task<TResult> 类上的静态属性访问。 你还可以直接实例化 TaskFactory 并指定各种选项,包括 CancellationToken、TaskCreationOptions 选项、TaskContinuationOptions 选项或 TaskScheduler。 创建任务工厂时所指定的任何选项将应用于它创建的所有任务,除非 Task 是通过使用 TaskCreationOptions 枚举创建的(在这种情况下,任务的选项重写任务工厂的选项)。
无委托的任务
在某些情况下,可能需要使用 Task 封装由外部组件(而不是你自己的用户委托)执行的某个异步操作。 如果该操作基于异步编程模型 Begin/End 模式,你可以使用 FromAsync 方法。 如果不是这种情况,你可以使用 TaskCompletionSource<TResult> 对象将该操作包装在任务中,并因而获得 Task 可编程性的一些好处,例如对异常传播和延续的支持。
在许多方案中,启用一个 Task<TResult> 来表示外部异步操作非常有用。 出于此目的,提供了 TaskCompletionSource<TResult>。 它允许创建可以分发到使用者的任务,这些使用者可以同其他情况下一样使用该任务的成员。 但是,与大多数任务不同,TaskCompletionSource 创建的任务的状态由 TaskCompletionSource 上的方法显式控制。 这使得要传播到基础任务的外部异步操作能够完成。 分离还确保使用者没有访问对应的 TaskCompletionSource 时不能转换状态。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TaskCompletionSourceDemo
{
class Program
{
// Demonstrated features:
// TaskCompletionSource ctor()
// TaskCompletionSource.SetResult()
// TaskCompletionSource.SetException()
// Task.Result
// Expected results:
// The attempt to get t1.Result blocks for ~1000ms until tcs1 gets signaled. 15 is printed out.
// The attempt to get t2.Result blocks for ~1000ms until tcs2 gets signaled. An exception is printed out.
// Documentation:
// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd449199(VS.100).aspx
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TaskCompletionSource<int> tcs1 = new TaskCompletionSource<int>();
Task<int> t1 = tcs1.Task;
// Start a background task that will complete tcs1.Task
Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
tcs1.SetResult(15);
});
// The attempt to get the result of t1 blocks the current thread until the completion source gets signaled.
// It should be a wait of ~1000 ms.
Stopwatch sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
int result = t1.Result;
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("(ElapsedTime={0}): t1.Result={1} (expected 15) ", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds, result);
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// Alternatively, an exception can be manually set on a TaskCompletionSource.Task
TaskCompletionSource<int> tcs2 = new TaskCompletionSource<int>();
Task<int> t2 = tcs2.Task;
// Start a background Task that will complete tcs2.Task with an exception
Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
tcs2.SetException(new InvalidOperationException("SIMULATED EXCEPTION"));
});
// The attempt to get the result of t2 blocks the current thread until the completion source gets signaled with either a result or an exception.
// In either case it should be a wait of ~1000 ms.
sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
try
{
result = t2.Result;
Console.WriteLine("t2.Result succeeded. THIS WAS NOT EXPECTED.");
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to Exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
catch (AggregateException e)
{
Console.Write("(ElapsedTime={0}): ", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
Console.WriteLine("The following exceptions have been thrown by t2.Result: (THIS WAS EXPECTED)");
for (int j = 0; j < e.InnerExceptions.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("
-------------------------------------------------
{0}", e.InnerExceptions[j].ToString());
}
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to Exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
}
相关数据结构
TPL 有几种在并行和顺序方案中都有用的新公共类型。 它们包括 System.Collections.Concurrent 命名空间中的一些线程安全的、快速且可缩放的集合类,还包括一些新的同步类型(例如 System.Threading.Semaphore 和 System.Threading.ManualResetEventSlim),对特定类型的工作负荷而言,这些新同步类型比旧的同步类型效率更高。 .NET Framework 4 中的其他新类型(例如 System.Threading.Barrier 和 System.Threading.SpinLock)提供了早期版本中未提供的功能。
参考资料