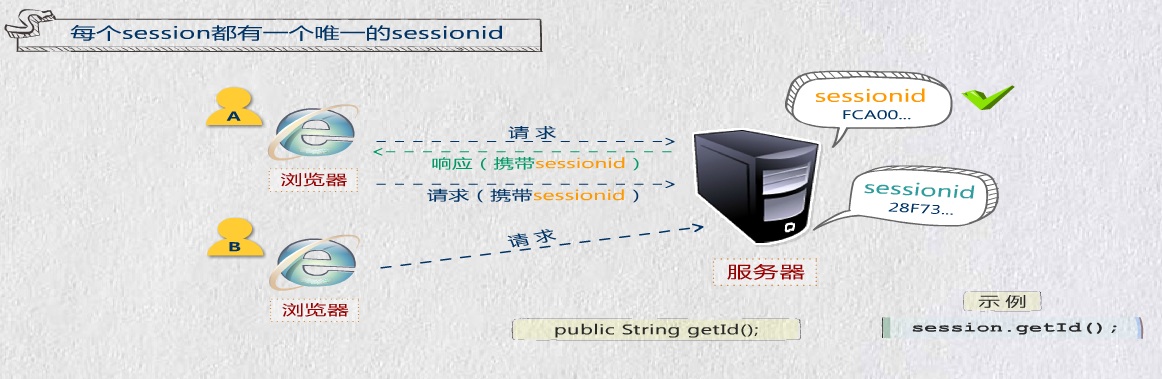
session对象:

//服务端设置Session属性 session.setAttribute("user", username); //客户端接收Session Object obj = session.getAttribute("user"); //判断是否为空,不是空就输出 if(obj==null){ //如果为空就提示用户登录 %> <%}else{ //不为空就输出用户名,和欢迎信息 out.println("欢迎您"+obj.toString()); } %>
Session清理机制
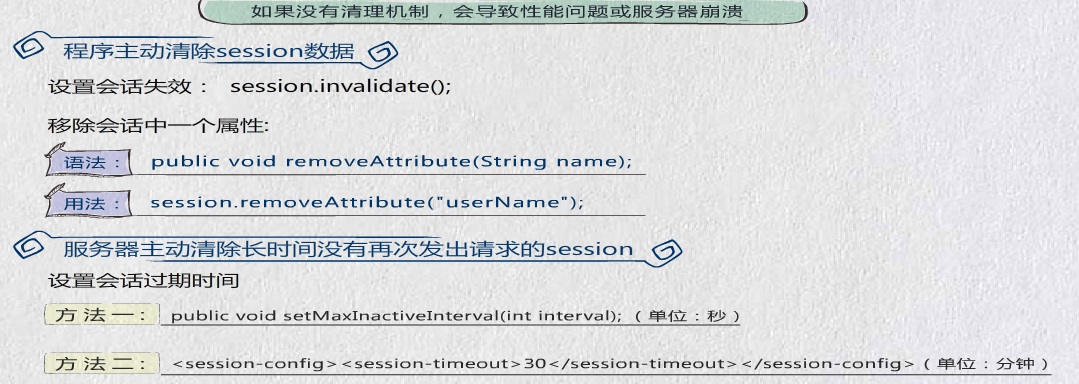
在服务端设置过期时间
//设置服务器端session过期日期(单位为:秒),如设置为10秒 session.setMaxInactiveInterval(10);
在客户端中设置
<% //在客户端设置session,如点击注销之后,直接设置session过期 //第一种删除session中的数据 session.removeAttribute("user"); //第二种 或者直接使用session过期 session.invalidate(); //以2选一 //重定向主页 response.sendRedirect("index.jsp"); %>
在tomcat中直接设置,在tomact中设置时间为分钟conf/web.xml中
<!--在最下方的</webapp>之前添加,并设置为10分种--> <session-config> <session-timeout>10</session-timeout> </session-config> </web-app>
Session过程
cookie

在服务端设置Cookie
//声明cookie变量,并添加要保存的参数和值如:用户名
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("user",username);
//设置cookie的有效时间以秒为单位60秒*60秒int类型的值
cookie.setMaxAge(60*60);
//将cookies对象发回客户端
response.addCookie(cookie);
在客户端接收cookie,
//接收cookies返回值为cookies的数组 Cookie [] cookies = request.getCookies(); //声明字符串变量用来接收cookies的值 String user=""; for(int i=0;i<cookies.length;i++){ //获取cookies的名字,并判断如果是服务端的名称 if(cookies[i].getName().equals("user")){ //将cookes的值赋为字符串变量 user=cookies[i].getValue(); } }
Application对象

计数器的实现原理
<% //计数器 //取出application属性中的count值为object值 Object count = application.getAttribute("count"); //判断是否为空 if(count==null){ //如果是空,表示第一次访问将值设置为1 application.setAttribute("count", new Integer(1)); }else{ //不是空,则将结果+1 Integer i=(Integer)count; application.setAttribute("count", i.intValue()+1); } Integer iCount=(Integer)application.getAttribute("count"); out.println("访问: "+iCount+"次"); %>
<% //获取application对象的count属性值 Object count = application.getAttribute("count"); //判断是否为空 if(count==null){ //为空就设置为1 application.setAttribute("count", new Integer(1)); }else{ //不空就取值+1 application.setAttribute("count", (Integer)count+1); } Integer icount = (Integer)application.getAttribute("count"); out.println("访问了: "+icount+"次"); %>
Request、Session和Application的区别
Request:中存储的数据仅在一个请求中可用
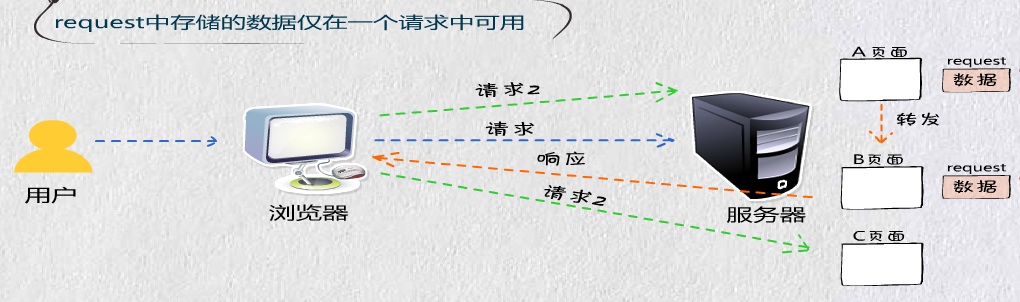
Session:中存储的数据在一个会话有效期内可用

Application:中存储的数据在整个WEB项目中可用,直到WEB服务器停止运行
