目录:
1、Core 处理HTTP请求流程
2、中间件(Middleware)&&处理流程
3、创建自定义中间件&&模拟Core的请求管道
Core 处理HTTP请求流程
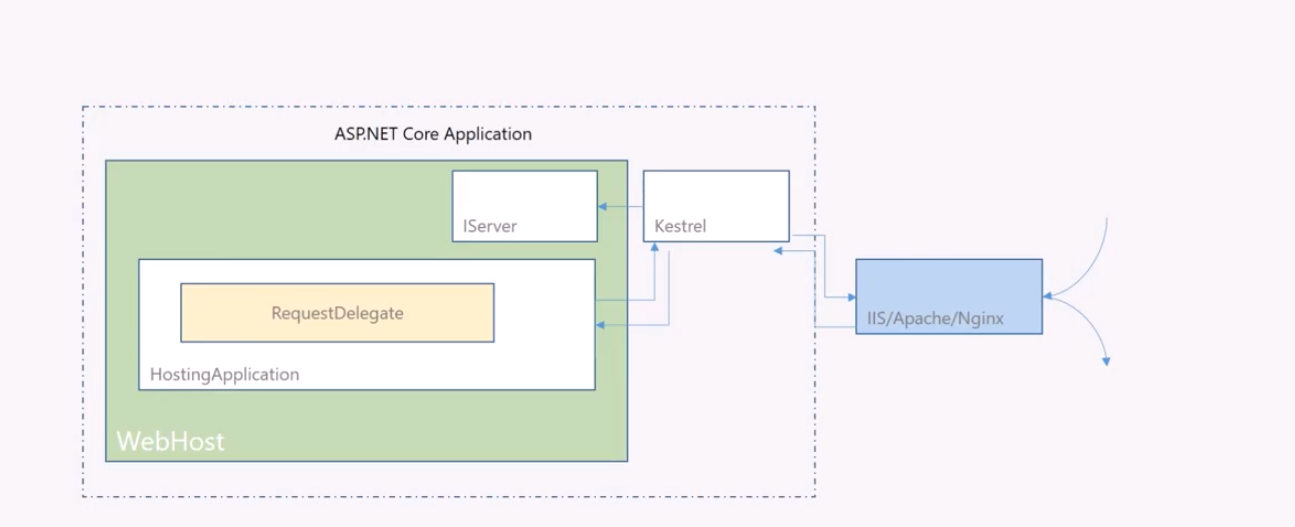
Http请求来到之后,会先由WebServer( 例如IIS,Nginx) 拿到然后丢给Kestrel WebServer,再有Kestrel 将Http请求封装为HttpContext后传入给.net core 请求管道(RequestDelegate)。HttpContext经过一系列middleware后返回response给WebServer。
中间件(Middleware)&&处理流程
微软官方文档给出的解释是这样的:中间件是加载在应用程序管道中以处理和相应请求的组件。其中每个组件都可以 选择是否可以将请求传递给管道中下一个组件;可以在调用管道的下一个组件之前或之后执行。下面是官方文档给出的一张图。
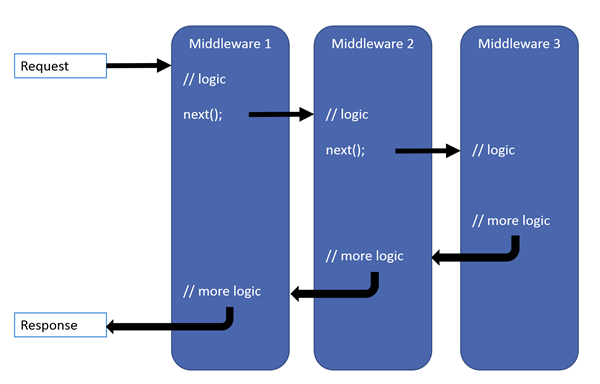
也就是说一个http请求的处理过程为,经过中间件1的处理逻辑(这个时候可以在中间件1中对httpcontext做一些处理,例如写入一段内容),调用next()方法,进入到中间件2中,重复以上步骤。最终,所有中间件的处理逻辑的输出结果都会叠加到HttpResponse中去。
.net core 中有三种方式调用中间件。在StartUp的Configure方法中,分别可以调用app.Use(),app.Run(),app.Map() 来调用中间件。接下来让我们来看下:
app.Use方法有两个重载形式:


第一个方法接收一个中间件,第二个方法接收一个上下文和一个中间件。让我们来分别调用下:
1 app.Use(next => 2 { 3 return context => 4 { 5 context.Response.WriteAsync("this is middleware1 start... "); 6 return next(context); 7 }; 8 }); 9 app.Use(async (context, next) => 10 { 11 await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is middleware2 start... "); 12 await next(); 13 });
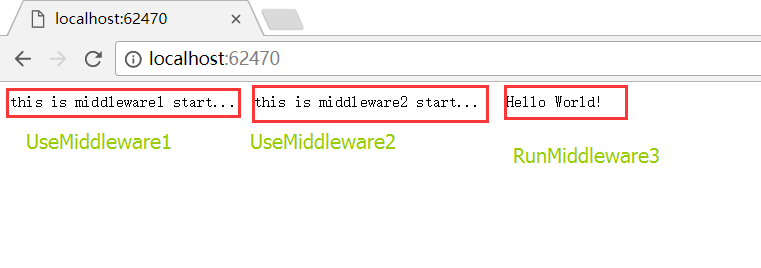
app.Run方法会终止管道,返回HttpResponse。在我们Configure方法中,默认最后一个方法就是app.Run 输出一句HelloWorld ,如下图

Use和Run都比较简单,不再详细介绍了。来看一眼程序运行结果:
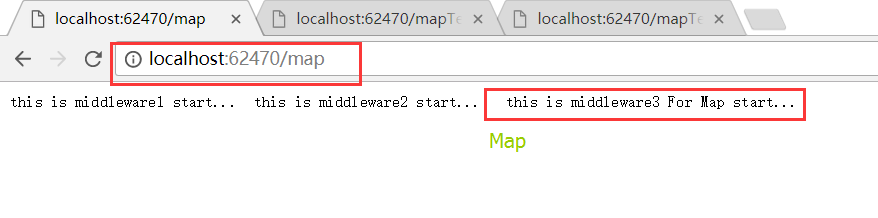
app.Map 方法用来构建分支管线,它会启用一个新的ApplicationBuilder。Map根据请求的路径来匹配分支管线。Map方法也可以根据不同的PathString来匹配多个分支管线或嵌套匹配。
app.Map("/task", build => { build.Run(async (context) => { await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is middleware3 For Map start... "); }); });
1 app.Map("/map", build => 2 { 3 build.Map("/mapTest2", MapHandleTest2); 4 build.Run(async (context) => 5 { 6 await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is middleware3 For Map start... "); 7 }); 8 }); 9 app.Map("/mapTest1", MapHandleTest1);
1 private void MapHandleTest1(IApplicationBuilder applicationBuilder) 2 { 3 applicationBuilder.Run(async context => 4 { 5 await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is middleware3HandleTest1 For Map start... "); 6 }); 7 } 8 private void MapHandleTest2(IApplicationBuilder applicationBuilder) 9 { 10 applicationBuilder.Run(async context => 11 { 12 await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is middleware3HandleTest2 For Map start... "); 13 }); 14 }
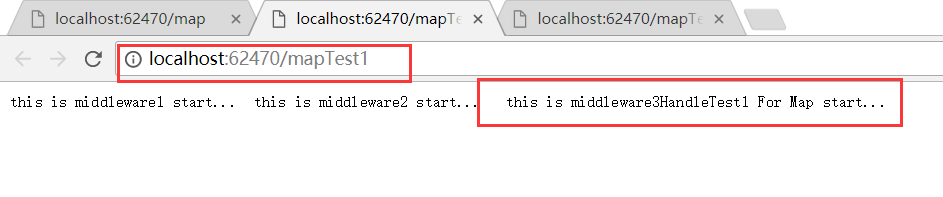

Map还有个特殊的方法,MapWhen, 它接收一个Func<HttpContext, bool>的参数,可以根据Http请求上下文做一些逻辑判断。然后继续执行管道
1 app.MapWhen(context => context.Request.Query.ContainsKey("branch"), 2 build => 3 build.Run(async context => 4 { 5 var branchVer = context.Request.Query["branch"]; 6 await context.Response.WriteAsync($"Branch used = {branchVer}"); 7 }) 8 );
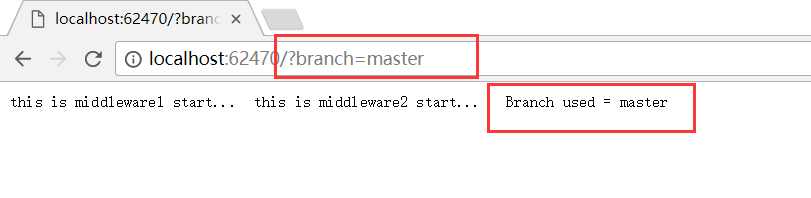 ,这里再贴张.net core 自带的中间件
,这里再贴张.net core 自带的中间件

创建自定义中间件&&模拟Core的请求管道
管道的实现机制由ApplicationBuilder 和 RequestDelegate 组成。RequestDelegate是Middleware的核心,Use方法会将RequestDelegate加入到ApplicationBuilder 中去,最后执行Build方法,把所有RequestDelegate reverse之后挨个执行一遍。

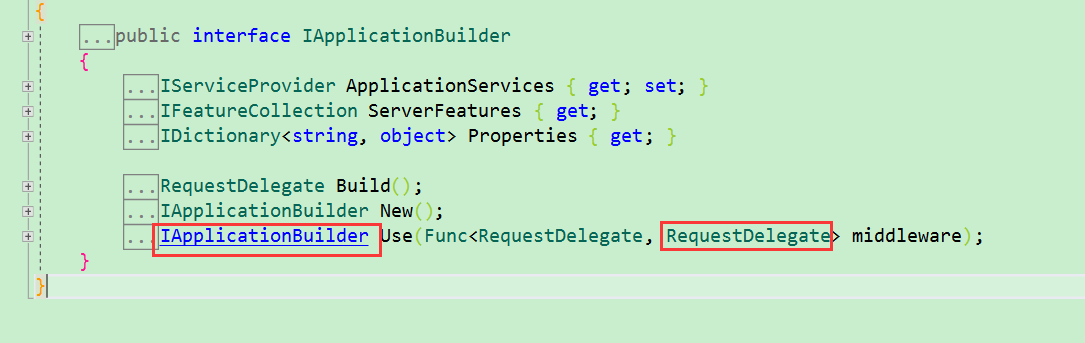
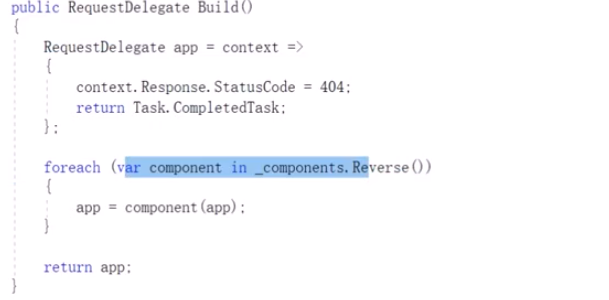
接下来编写一个自定义的Middleware。
public class RequestTestMiddleware { private readonly RequestDelegate _next; //中间件核心RequestDelegate,_next 表示执行下一个中间件。 public RequestTestMiddleware(RequestDelegate next) { _next = next; } public Task Invoke(HttpContext context) { context.Response.WriteAsync("hello this is my RequestTestMiddleware"); return _next(context); //覆盖delegate 的Inboke方法,将http上下文传入下一个中间件 } } public static class RequestTestMiddlewareExtensions { public static IApplicationBuilder UseRequestTest(this IApplicationBuilder builder) //使用扩展方法使我们的中间件对外开放。 { return builder.UseMiddleware<RequestTestMiddleware>(); //将我们中间件加入到IApplicationBuilder中去。 } } //在StartUp 中使用我们的自定义中间件。 app.UseRequestTest();
Http请求管道的模拟构建

1 /// <summary> 2 /// 拿到请求上下文,返回一个委托 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <param name="contex"></param> 5 /// <returns></returns> 6 public delegate Task RequestDelegate(Context contex); 7 /// <summary> 8 /// 模拟http请求上下文 9 /// </summary> 10 public class Context 11 { 12 13 }

1 public static IList<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>> _list = new 2 List<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>(); 3 static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 Use(next => //加入中间件1 6 { 7 return context => 8 { 9 Console.WriteLine("this is use middleware1"); 10 return next.Invoke(context); 11 }; 12 }); 13 Use(next => //加入中间件2 14 { 15 return context => 16 { 17 Console.WriteLine("this is use middleware2"); 18 return next.Invoke(context); 19 }; 20 }); 21 RequestDelegate end = context => 22 { 23 Console.WriteLine("this is end..."); //管道 24 return Task.CompletedTask; 25 }; 26 _list.Reverse(); 27 foreach (var middleware in _list) 28 { 29 end = middleware.Invoke(end); 30 } 31 end.Invoke(new Context()); //实例化一个上下文实例 32 Console.ReadLine(); 33 } 34 /// <summary> 35 /// 将middleware 加入到list(applicationbuilder)中 36 /// </summary> 37 public static void Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> iMiddleware) 38 { 39 _list.Add(iMiddleware); 40 }

Jesse博客学习笔记。传送门=》 http://video.jessetalk.cn/
