There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively.
Find the median of the two sorted arrays. The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
You may assume nums1 and nums2 cannot be both empty.
Example 1:
nums1 = [1, 3] nums2 = [2] The median is 2.0
Example 2:
nums1 = [1, 2] nums2 = [3, 4] The median is (2 + 3)/2 = 2.5
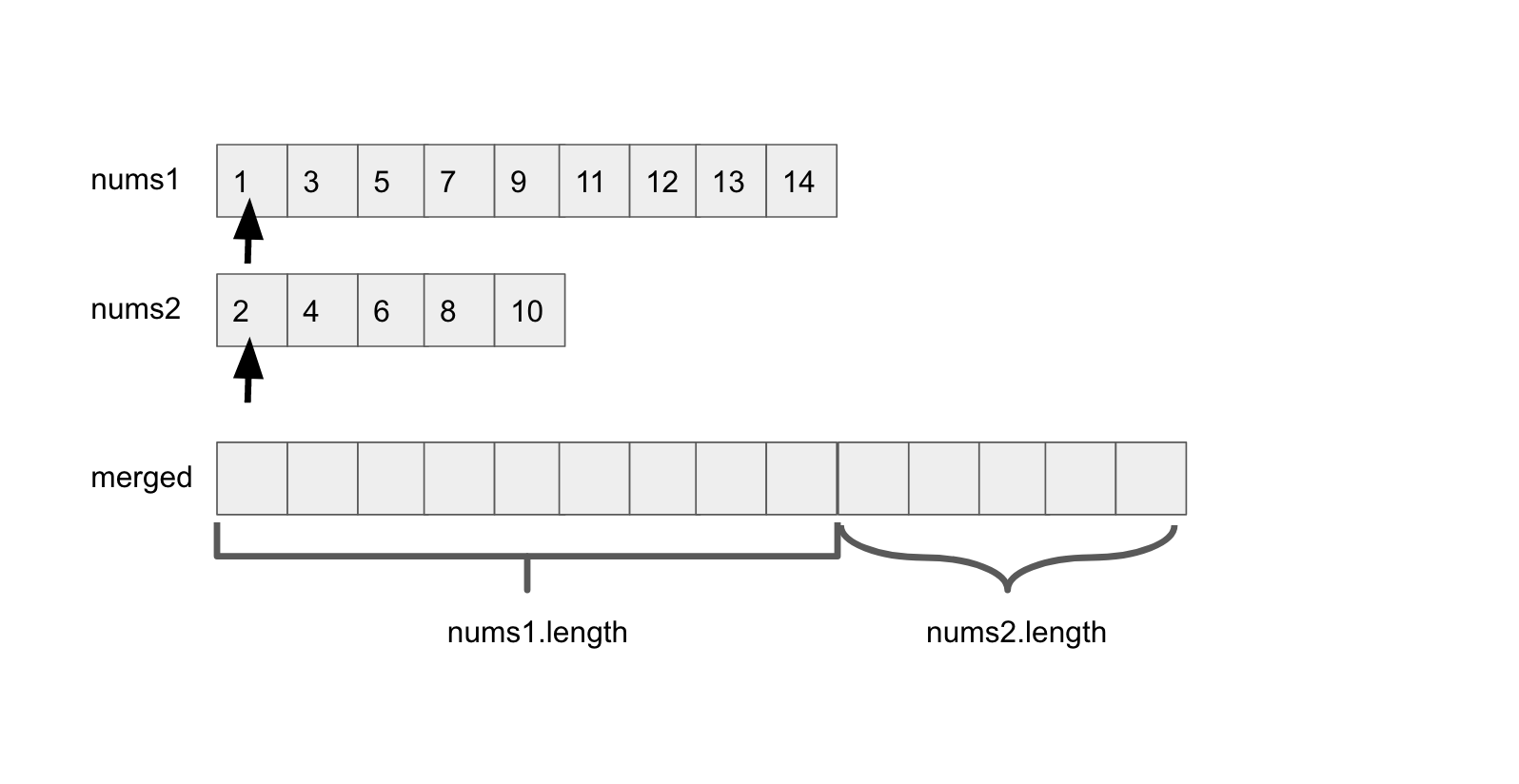
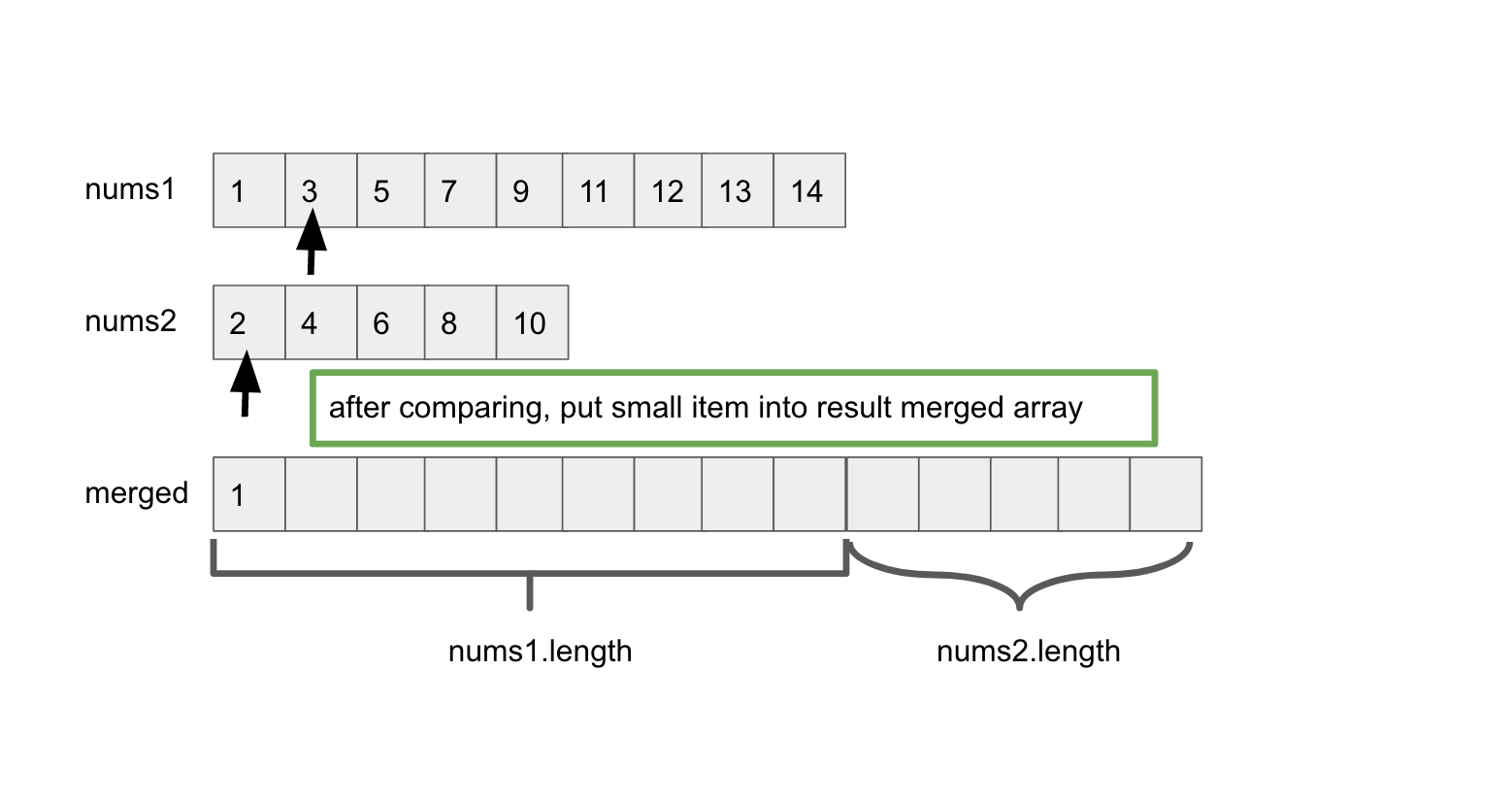
Solution1: time complexity is O(m+n). merge two sorted array, then find the median
code:
1 /* 2 Time Complexity: O(m+n) 3 Space Complexity: O(m+n) 4 */ 5 6 class Solution { 7 public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) { // find median 8 int[] mergedArray = mergeTwoSortedArray(nums1, nums2); 9 int n = mergedArray.length; 10 if( n % 2 == 0){ 11 return (mergedArray[(n-1)/2] + mergedArray[n/2])/2.0; 12 }else{ 13 return mergedArray[n/2]; 14 } 15 } 16 17 public int[] mergeTwoSortedArray(int[] nums1, int[] nums2){ // merge sort 18 int[] merged = new int[nums1.length + nums2.length]; 19 int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; 20 // 两个array同时扫 21 while( i < nums1.length && j < nums2.length){ 22 merged[k++] = (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) ? nums1[i++] : nums2[j++]; 23 } 24 //扫到只剩下较长的那个array, either nums1 or nums2 25 while ( i < nums1.length ){ 26 merged[k++] = nums1[i++]; 27 } 28 while(j < nums2.length){ 29 merged[k++] = nums2[j++]; 30 } 31 return merged; 32 } 33 }
Solution2: time complexity is O(log (m+n)).
这个题的思路可以是找出2个sorted array 所有元素中,Kth 元素
因此我们可以把问题转化成,
“Given 2 sorted arrays, A, B of sizes m, n respectively, find the numbers which are NOT medians of the two sorted arrays”
如果我们能找到那些NOT medians的数字,删掉,并不断缩小范围,那最终剩下的一定就是actual median
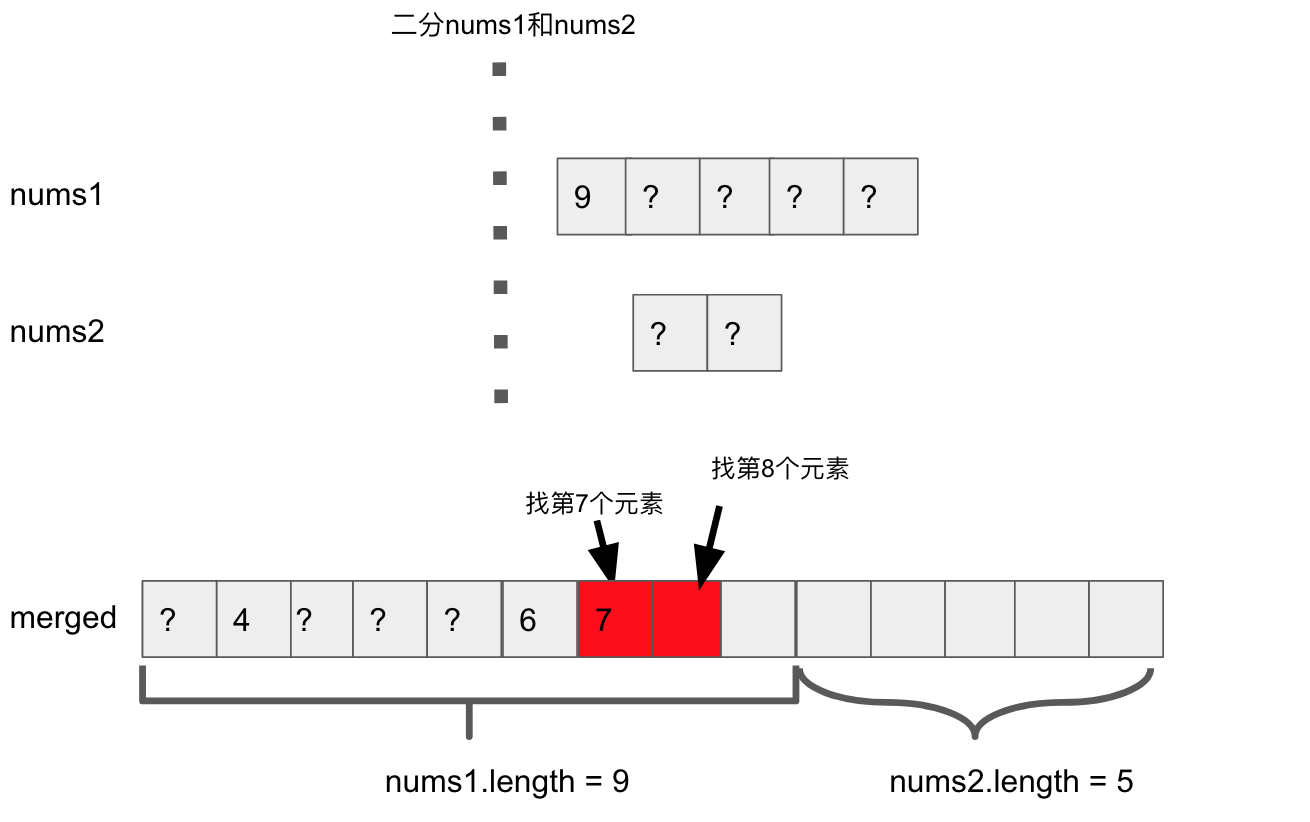
Step1, 确定要找的median是merged之后array中的第几个元素

Step2, 用binary search切开nums1, nums2。发现nums1左半边的长度为4, nums2左半边的长度为2。

Step3, nums1左半边长度+ nums2左半边长度为6
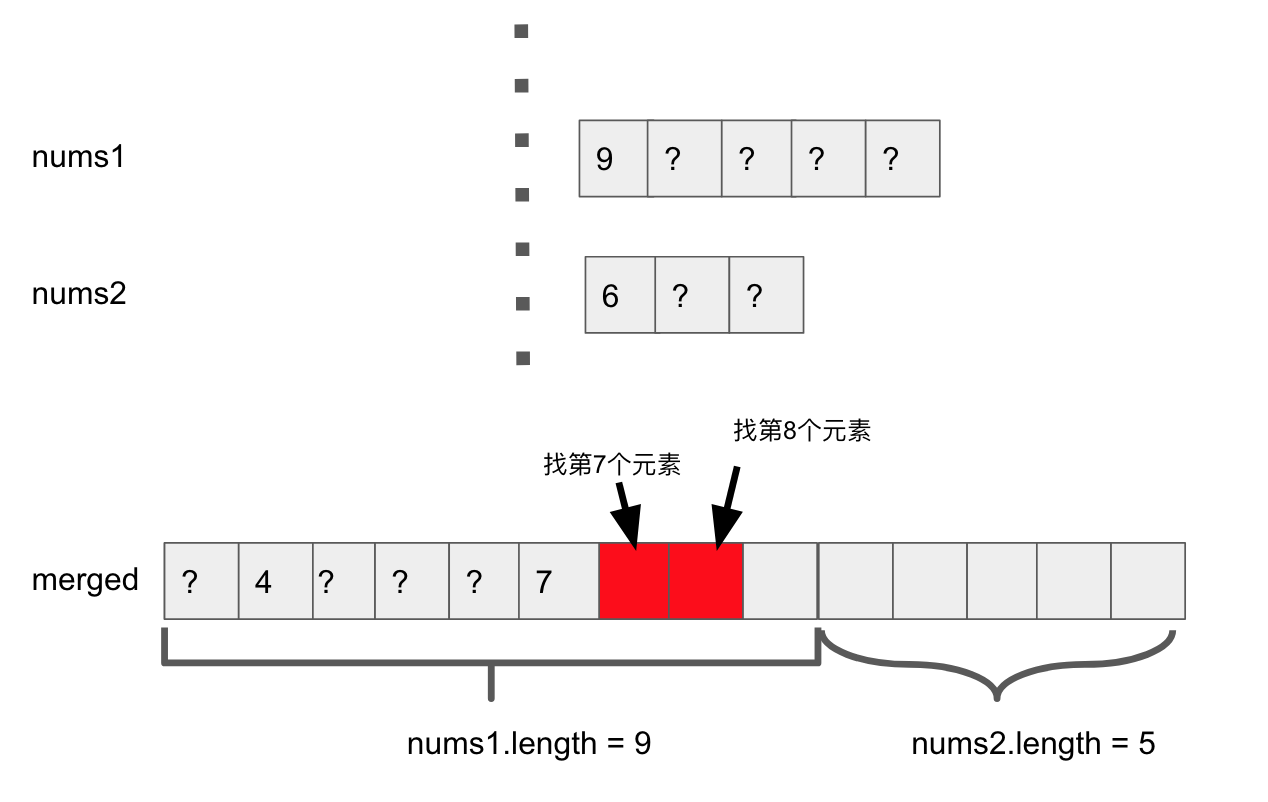
Step4, 所以第7个元素可能在nums1的右半边pivot上,或者在nums2的右半边pivot上
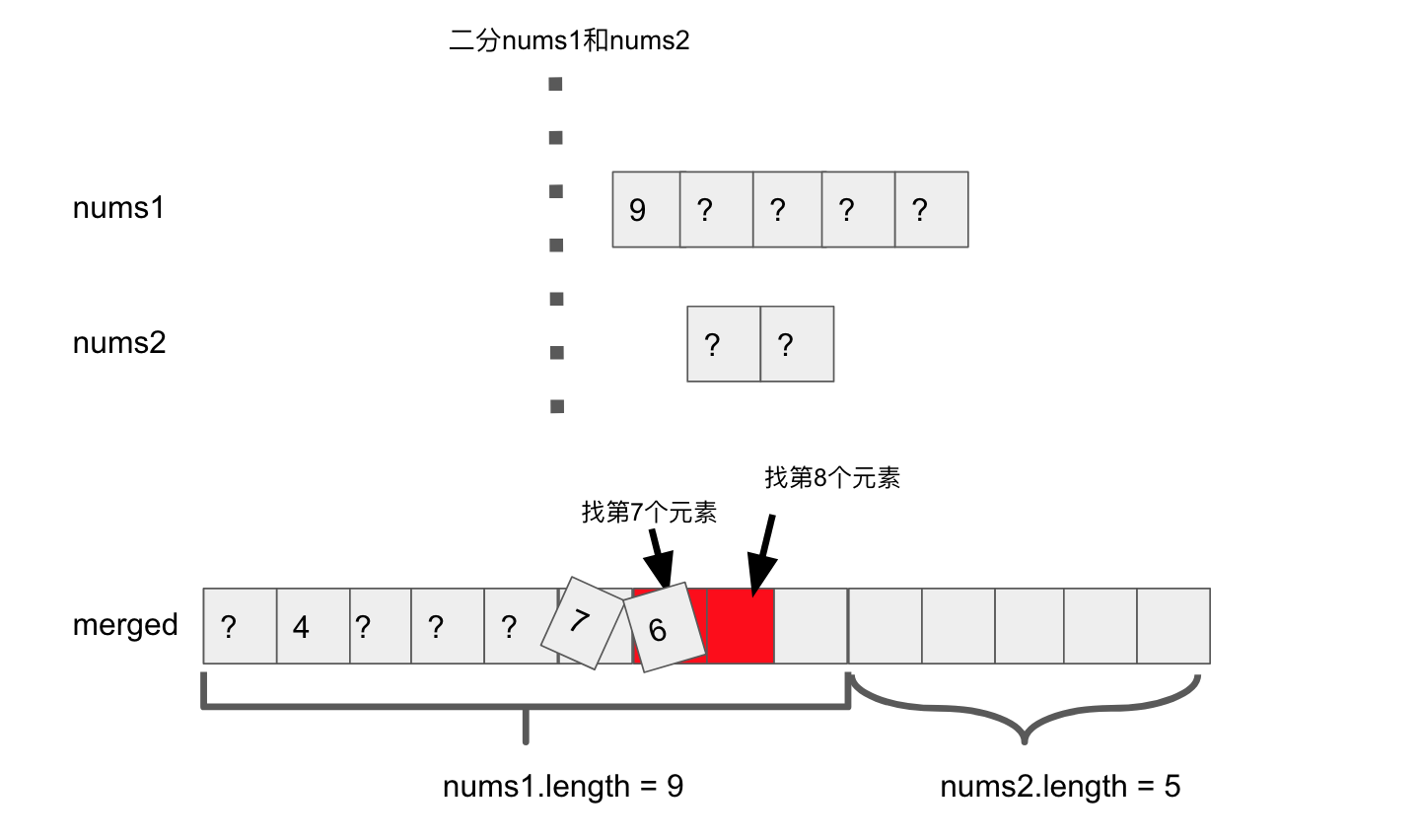
比较发现,第7个元素应该是7
code:
1 /* 2 Time Complexity: O(log(m+n)) 3 Space Complexity: O(log(m+n)) 4 */ 5 6 class Solution { 7 public double findMedianSortedArrays(final int[] A, final int[] B) { 8 int total = A.length + B.length; 9 if (total %2 == 0){ 10 return (findKth(A, 0, B, 0, total / 2) + findKth(A, 0, B, 0, total / 2 + 1)) / 2.0; 11 }else{ 12 return findKth(A, 0, B, 0, total / 2 + 1); 13 } 14 } 15 16 private static int findKth(final int[] A, int ai, final int[] B, int bi, int k) { 17 //always assume that A is shorter than B 18 if (A.length - ai > B.length - bi) { 19 return findKth(B, bi, A, ai, k); 20 } 21 if (A.length - ai == 0) return B[bi + k - 1]; 22 if (k == 1) return Math.min(A[ai], B[bi]); 23 24 //divide k into two parts 25 int k1 = Math.min(k / 2, A.length - ai), k2 = k - k1; 26 if (A[ai + k1 - 1] < B[bi + k2 - 1]) 27 return findKth(A, ai + k1, B, bi, k - k1); 28 else if (A[ai + k1 - 1] > B[bi + k2 - 1]) 29 return findKth(A, ai, B, bi + k2, k - k2); 30 else 31 return A[ai + k1 - 1]; 32 } 33 }