LSTM的推导与实现
前言
最近在看CS224d,这里主要介绍LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory)的推导过程以及用Python进行简单的实现。LSTM是一种时间递归神经网络,是RNN的一个变种,非常适合处理和预测时间序列中间隔和延迟非常长的事件。假设我们去试着预测‘I grew up in France...(很长间隔)...I speak fluent French’最后的单词,当前的信息建议下一个此可能是一种语言的名字(因为speak嘛),但是要准确预测出‘French’我们就需要前面的离当前位置较远的‘France’作为上下文,当这个间隔比较大的时候RNN就会难以处理,而LSTM则没有这个问题。
LSTM的原理
为了弄明白LSTM的实现,我下载了alex的原文,但是被论文上图片和公式弄的晕头转向,无奈最后在网上收集了一些资料才总算弄明白。我这里不介绍就LSTM的前置RNN了,不懂的童鞋自己了解一下吧。
LSTM的前向过程
首先看一张LSTM节点的内部示意图:
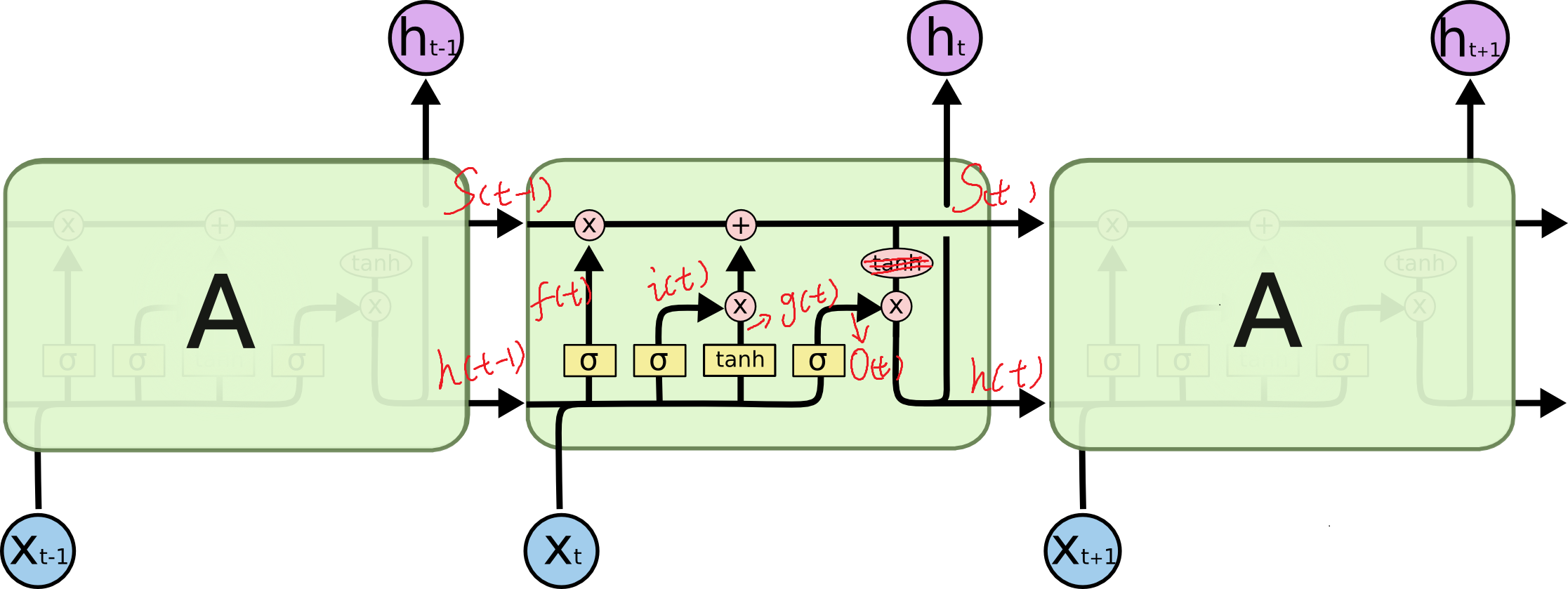
图片来自一篇讲解LSTM的blog(http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/)
这是我认为网上画的最好的LSTM网络节点图(比论文里面画的容易理解多了),LSTM前向过程就是看图说话,关键的函数节点已经在图中标出,这里我们忽略了其中一个tanh计算过程。
这里(phi(x)=tanh(x),sigma(x)=frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}),(x(t),h(t))分别是我们的输入序列和输出序列。如果我们把(x(t))与(h(t-1))这两个向量进行合并:
那么可以上面的方程组可以重写为:
其中(f(t))被称为忘记门,所表达的含义是决定我们会从以前状态中丢弃什么信息。(i(t),g(t))构成了输入门,决定什么样的新信息被存放在细胞状态中。(o(t))所在位置被称作输出门,决定我们要输出什么值。这里表述的不是很准确,感兴趣的读者可以去http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/ NLP这块我也不太懂。
前向过程的代码如下:
def bottom_data_is(self, x, s_prev = None, h_prev = None):
# if this is the first lstm node in the network
if s_prev == None: s_prev = np.zeros_like(self.state.s)
if h_prev == None: h_prev = np.zeros_like(self.state.h)
# save data for use in backprop
self.s_prev = s_prev
self.h_prev = h_prev
# concatenate x(t) and h(t-1)
xc = np.hstack((x, h_prev))
self.state.g = np.tanh(np.dot(self.param.wg, xc) + self.param.bg)
self.state.i = sigmoid(np.dot(self.param.wi, xc) + self.param.bi)
self.state.f = sigmoid(np.dot(self.param.wf, xc) + self.param.bf)
self.state.o = sigmoid(np.dot(self.param.wo, xc) + self.param.bo)
self.state.s = self.state.g * self.state.i + s_prev * self.state.f
self.state.h = self.state.s * self.state.o
self.x = x
self.xc = xc
LSTM的反向过程
LSTM的正向过程比较容易,反向过程则比较复杂,我们先定义一个loss function (l(t)=f(h(t),y(t)))=||h(t)-y(t)||^2),(h(t),y(t))分别为输出序列与样本标签,我们要做的就是最小化整个时间序列上的(l(t)),即最小化
其中(T)代表整个时间序列,下面我们通过(L)来计算梯度,假设我们要计算(frac{dL}{dw}),其中(w)是一个标量(例如是矩阵(W_{gx})的一个元素),由链式法则可以导出
其中(h_i(t))是第i个单元的输出,(M)是LSTM单元的个数,网络随着时间t前向传播,(h_i(t))的改变不影响t时刻之前的loss,我们可以写出:
为了书写方便我们令(L(t)=sum_{s=t}^{T}l(s))来简化我们的书写,这样(L(1))就是整个序列的loss,重写上式有:
这样我们就可以将梯度重写为:
我们知道(L(t)=l(t)+L(t+1)),那么(frac{dL(t)}{dh_i(t)}=frac{dl(t)}{dh_i(t)} + frac{dL(t+1)}{dh_i(t)}),这说明得到下一时序的导数后可以直接得出当前时序的导数,所以我们可以计算(T)时刻的导数然后往前推,在(T)时刻有(frac{dL(T)}{dh_i(T)}=frac{dl(T)}{dh_i(T)})。
def y_list_is(self, y_list, loss_layer):
"""
Updates diffs by setting target sequence
with corresponding loss layer.
Will *NOT* update parameters. To update parameters,
call self.lstm_param.apply_diff()
"""
assert len(y_list) == len(self.x_list)
idx = len(self.x_list) - 1
# first node only gets diffs from label ...
loss = loss_layer.loss(self.lstm_node_list[idx].state.h, y_list[idx])
diff_h = loss_layer.bottom_diff(self.lstm_node_list[idx].state.h, y_list[idx])
# here s is not affecting loss due to h(t+1), hence we set equal to zero
diff_s = np.zeros(self.lstm_param.mem_cell_ct)
self.lstm_node_list[idx].top_diff_is(diff_h, diff_s)
idx -= 1
### ... following nodes also get diffs from next nodes, hence we add diffs to diff_h
### we also propagate error along constant error carousel using diff_s
while idx >= 0:
loss += loss_layer.loss(self.lstm_node_list[idx].state.h, y_list[idx])
diff_h = loss_layer.bottom_diff(self.lstm_node_list[idx].state.h, y_list[idx])
diff_h += self.lstm_node_list[idx + 1].state.bottom_diff_h
diff_s = self.lstm_node_list[idx + 1].state.bottom_diff_s
self.lstm_node_list[idx].top_diff_is(diff_h, diff_s)
idx -= 1
return loss
从上面公式可以很容易理解diff_h的计算过程。这里的loss_layer.bottom_diff定义如下:
def bottom_diff(self, pred, label):
diff = np.zeros_like(pred)
diff[0] = 2 * (pred[0] - label)
return diff
该函数结合上文的loss function很明显。下面来推导(frac{dL(t)}{ds(t)}),结合前面的前向公式我们可以很容易得出(s(t))的变化会直接影响(h(t))和(h(t+1)),进而影响(L(t)),即有:
因为(h(t+1))不影响(l(t))所以有(frac{dL(t)}{dh_i(t+1)}=frac{dL(t+1)}{dh_i(t+1)}),因此有:
同样的我们可以通过后面的导数逐级反推得到前面的导数,代码即diff_s的计算过程。
下面我们计算(frac{dL(t)}{dh_i(t)}*frac{dh_i(t)}{ds_i(t)}),因为(h(t)=s(t)*o(t)),那么(frac{dL(t)}{dh_i(t)}*frac{dh_i(t)}{ds_i(t)}=frac{dL(t)}{dh_i(t)}*o_i(t)=o_i(t)[diff\_h]),即(frac{dL(t)}{ds_i(t)}=o(t)[diff\_h]_i+[diff\_s]_i),其中([diff\_h]_i,[diff\_s]_i)分别表述当前t时序的(frac{dL(t)}{dh_i(t)})和t+1时序的(frac{dL(t)}{ds_i(t)})。同样的,结合上面的代码应该比较容易理解。
下面我们根据前向过程挨个计算导数:
因此有以下代码:
def top_diff_is(self, top_diff_h, top_diff_s):
# notice that top_diff_s is carried along the constant error carousel
ds = self.state.o * top_diff_h + top_diff_s
do = self.state.s * top_diff_h
di = self.state.g * ds
dg = self.state.i * ds
df = self.s_prev * ds
# diffs w.r.t. vector inside sigma / tanh function
di_input = (1. - self.state.i) * self.state.i * di #sigmoid diff
df_input = (1. - self.state.f) * self.state.f * df
do_input = (1. - self.state.o) * self.state.o * do
dg_input = (1. - self.state.g ** 2) * dg #tanh diff
# diffs w.r.t. inputs
self.param.wi_diff += np.outer(di_input, self.xc)
self.param.wf_diff += np.outer(df_input, self.xc)
self.param.wo_diff += np.outer(do_input, self.xc)
self.param.wg_diff += np.outer(dg_input, self.xc)
self.param.bi_diff += di_input
self.param.bf_diff += df_input
self.param.bo_diff += do_input
self.param.bg_diff += dg_input
# compute bottom diff
dxc = np.zeros_like(self.xc)
dxc += np.dot(self.param.wi.T, di_input)
dxc += np.dot(self.param.wf.T, df_input)
dxc += np.dot(self.param.wo.T, do_input)
dxc += np.dot(self.param.wg.T, dg_input)
# save bottom diffs
self.state.bottom_diff_s = ds * self.state.f
self.state.bottom_diff_x = dxc[:self.param.x_dim]
self.state.bottom_diff_h = dxc[self.param.x_dim:]
这里top_diff_h,top_diff_s分别是上文的diff_h,diff_s。这里我们讲解下wi_diff的求解过程,其他变量类似。
上式化简之后即得到以下代码
wi_diff += np.outer((1.-i)*i*di, xc)
其它的导数可以同样得到,这里就不赘述了。
LSTM完整例子
#lstm在输入一串连续质数时预估下一个质数
import random
import numpy as np
import math
def sigmoid(x):
return 1. / (1 + np.exp(-x))
# createst uniform random array w/ values in [a,b) and shape args
def rand_arr(a, b, *args):
np.random.seed(0)
return np.random.rand(*args) * (b - a) + a
class LstmParam:
def __init__(self, mem_cell_ct, x_dim):
self.mem_cell_ct = mem_cell_ct
self.x_dim = x_dim
concat_len = x_dim + mem_cell_ct
# weight matrices
self.wg = rand_arr(-0.1, 0.1, mem_cell_ct, concat_len)
self.wi = rand_arr(-0.1, 0.1, mem_cell_ct, concat_len)
self.wf = rand_arr(-0.1, 0.1, mem_cell_ct, concat_len)
self.wo = rand_arr(-0.1, 0.1, mem_cell_ct, concat_len)
# bias terms
self.bg = rand_arr(-0.1, 0.1, mem_cell_ct)
self.bi = rand_arr(-0.1, 0.1, mem_cell_ct)
self.bf = rand_arr(-0.1, 0.1, mem_cell_ct)
self.bo = rand_arr(-0.1, 0.1, mem_cell_ct)
# diffs (derivative of loss function w.r.t. all parameters)
self.wg_diff = np.zeros((mem_cell_ct, concat_len))
self.wi_diff = np.zeros((mem_cell_ct, concat_len))
self.wf_diff = np.zeros((mem_cell_ct, concat_len))
self.wo_diff = np.zeros((mem_cell_ct, concat_len))
self.bg_diff = np.zeros(mem_cell_ct)
self.bi_diff = np.zeros(mem_cell_ct)
self.bf_diff = np.zeros(mem_cell_ct)
self.bo_diff = np.zeros(mem_cell_ct)
def apply_diff(self, lr = 1):
self.wg -= lr * self.wg_diff
self.wi -= lr * self.wi_diff
self.wf -= lr * self.wf_diff
self.wo -= lr * self.wo_diff
self.bg -= lr * self.bg_diff
self.bi -= lr * self.bi_diff
self.bf -= lr * self.bf_diff
self.bo -= lr * self.bo_diff
# reset diffs to zero
self.wg_diff = np.zeros_like(self.wg)
self.wi_diff = np.zeros_like(self.wi)
self.wf_diff = np.zeros_like(self.wf)
self.wo_diff = np.zeros_like(self.wo)
self.bg_diff = np.zeros_like(self.bg)
self.bi_diff = np.zeros_like(self.bi)
self.bf_diff = np.zeros_like(self.bf)
self.bo_diff = np.zeros_like(self.bo)
class LstmState:
def __init__(self, mem_cell_ct, x_dim):
self.g = np.zeros(mem_cell_ct)
self.i = np.zeros(mem_cell_ct)
self.f = np.zeros(mem_cell_ct)
self.o = np.zeros(mem_cell_ct)
self.s = np.zeros(mem_cell_ct)
self.h = np.zeros(mem_cell_ct)
self.bottom_diff_h = np.zeros_like(self.h)
self.bottom_diff_s = np.zeros_like(self.s)
self.bottom_diff_x = np.zeros(x_dim)
class LstmNode:
def __init__(self, lstm_param, lstm_state):
# store reference to parameters and to activations
self.state = lstm_state
self.param = lstm_param
# non-recurrent input to node
self.x = None
# non-recurrent input concatenated with recurrent input
self.xc = None
def bottom_data_is(self, x, s_prev = None, h_prev = None):
# if this is the first lstm node in the network
if s_prev == None: s_prev = np.zeros_like(self.state.s)
if h_prev == None: h_prev = np.zeros_like(self.state.h)
# save data for use in backprop
self.s_prev = s_prev
self.h_prev = h_prev
# concatenate x(t) and h(t-1)
xc = np.hstack((x, h_prev))
self.state.g = np.tanh(np.dot(self.param.wg, xc) + self.param.bg)
self.state.i = sigmoid(np.dot(self.param.wi, xc) + self.param.bi)
self.state.f = sigmoid(np.dot(self.param.wf, xc) + self.param.bf)
self.state.o = sigmoid(np.dot(self.param.wo, xc) + self.param.bo)
self.state.s = self.state.g * self.state.i + s_prev * self.state.f
self.state.h = self.state.s * self.state.o
self.x = x
self.xc = xc
def top_diff_is(self, top_diff_h, top_diff_s):
# notice that top_diff_s is carried along the constant error carousel
ds = self.state.o * top_diff_h + top_diff_s
do = self.state.s * top_diff_h
di = self.state.g * ds
dg = self.state.i * ds
df = self.s_prev * ds
# diffs w.r.t. vector inside sigma / tanh function
di_input = (1. - self.state.i) * self.state.i * di
df_input = (1. - self.state.f) * self.state.f * df
do_input = (1. - self.state.o) * self.state.o * do
dg_input = (1. - self.state.g ** 2) * dg
# diffs w.r.t. inputs
self.param.wi_diff += np.outer(di_input, self.xc)
self.param.wf_diff += np.outer(df_input, self.xc)
self.param.wo_diff += np.outer(do_input, self.xc)
self.param.wg_diff += np.outer(dg_input, self.xc)
self.param.bi_diff += di_input
self.param.bf_diff += df_input
self.param.bo_diff += do_input
self.param.bg_diff += dg_input
# compute bottom diff
dxc = np.zeros_like(self.xc)
dxc += np.dot(self.param.wi.T, di_input)
dxc += np.dot(self.param.wf.T, df_input)
dxc += np.dot(self.param.wo.T, do_input)
dxc += np.dot(self.param.wg.T, dg_input)
# save bottom diffs
self.state.bottom_diff_s = ds * self.state.f
self.state.bottom_diff_x = dxc[:self.param.x_dim]
self.state.bottom_diff_h = dxc[self.param.x_dim:]
class LstmNetwork():
def __init__(self, lstm_param):
self.lstm_param = lstm_param
self.lstm_node_list = []
# input sequence
self.x_list = []
def y_list_is(self, y_list, loss_layer):
"""
Updates diffs by setting target sequence
with corresponding loss layer.
Will *NOT* update parameters. To update parameters,
call self.lstm_param.apply_diff()
"""
assert len(y_list) == len(self.x_list)
idx = len(self.x_list) - 1
# first node only gets diffs from label ...
loss = loss_layer.loss(self.lstm_node_list[idx].state.h, y_list[idx])
diff_h = loss_layer.bottom_diff(self.lstm_node_list[idx].state.h, y_list[idx])
# here s is not affecting loss due to h(t+1), hence we set equal to zero
diff_s = np.zeros(self.lstm_param.mem_cell_ct)
self.lstm_node_list[idx].top_diff_is(diff_h, diff_s)
idx -= 1
### ... following nodes also get diffs from next nodes, hence we add diffs to diff_h
### we also propagate error along constant error carousel using diff_s
while idx >= 0:
loss += loss_layer.loss(self.lstm_node_list[idx].state.h, y_list[idx])
diff_h = loss_layer.bottom_diff(self.lstm_node_list[idx].state.h, y_list[idx])
diff_h += self.lstm_node_list[idx + 1].state.bottom_diff_h
diff_s = self.lstm_node_list[idx + 1].state.bottom_diff_s
self.lstm_node_list[idx].top_diff_is(diff_h, diff_s)
idx -= 1
return loss
def x_list_clear(self):
self.x_list = []
def x_list_add(self, x):
self.x_list.append(x)
if len(self.x_list) > len(self.lstm_node_list):
# need to add new lstm node, create new state mem
lstm_state = LstmState(self.lstm_param.mem_cell_ct, self.lstm_param.x_dim)
self.lstm_node_list.append(LstmNode(self.lstm_param, lstm_state))
# get index of most recent x input
idx = len(self.x_list) - 1
if idx == 0:
# no recurrent inputs yet
self.lstm_node_list[idx].bottom_data_is(x)
else:
s_prev = self.lstm_node_list[idx - 1].state.s
h_prev = self.lstm_node_list[idx - 1].state.h
self.lstm_node_list[idx].bottom_data_is(x, s_prev, h_prev)
测试代码
import numpy as np
from lstm import LstmParam, LstmNetwork
class ToyLossLayer:
"""
Computes square loss with first element of hidden layer array.
"""
@classmethod
def loss(self, pred, label):
return (pred[0] - label) ** 2
@classmethod
def bottom_diff(self, pred, label):
diff = np.zeros_like(pred)
diff[0] = 2 * (pred[0] - label)
return diff
def example_0():
# learns to repeat simple sequence from random inputs
np.random.seed(0)
# parameters for input data dimension and lstm cell count
mem_cell_ct = 100
x_dim = 50
concat_len = x_dim + mem_cell_ct
lstm_param = LstmParam(mem_cell_ct, x_dim)
lstm_net = LstmNetwork(lstm_param)
y_list = [-0.5,0.2,0.1, -0.5]
input_val_arr = [np.random.random(x_dim) for _ in y_list]
for cur_iter in range(100):
print "cur iter: ", cur_iter
for ind in range(len(y_list)):
lstm_net.x_list_add(input_val_arr[ind])
print "y_pred[%d] : %f" % (ind, lstm_net.lstm_node_list[ind].state.h[0])
loss = lstm_net.y_list_is(y_list, ToyLossLayer)
print "loss: ", loss
lstm_param.apply_diff(lr=0.1)
lstm_net.x_list_clear()
if __name__ == "__main__":
example_0()
参考
略