*** 参考 ***
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/high-availability
https://www.golinuxcloud.com/kubernetes-tutorial
https://kairen-archived.github.io/2019/09/20/ironman2020/day05
https://github.com/kubernetes/kubeadm/blob/main/docs/ha-considerations.md#options-for-software-load-balancing
https://realsysadmin.com/www/2020/12/10/kicking-the-tires-on-kubernetes-part-4
一、服务器规划
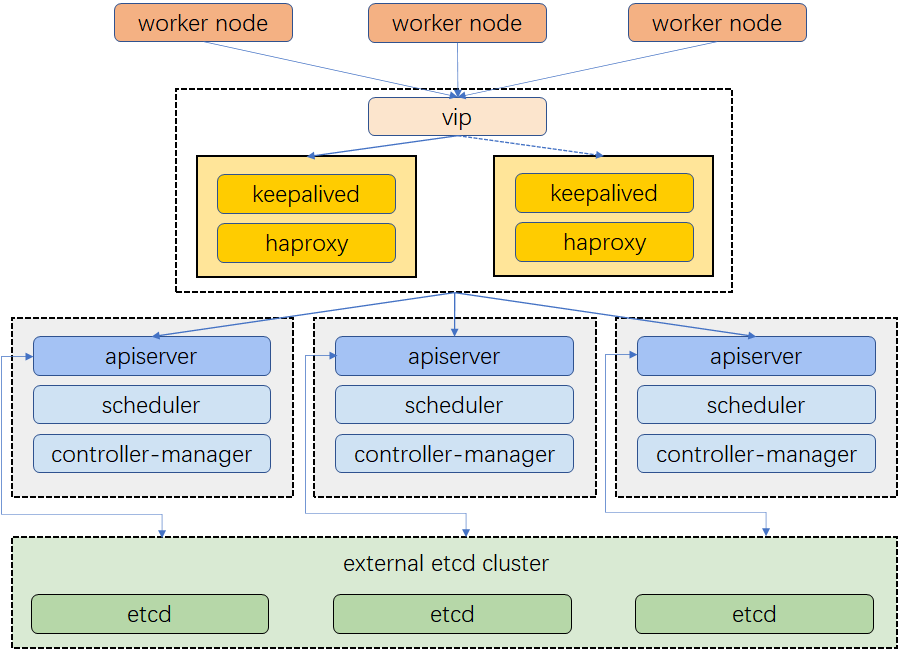
- 使用
堆叠(stacked)控制平面节点,其中etcd节点与控制平面节点共存, 使用外部etcd节点,其中etcd在与控制平面不同节点上运行 - 操作系统
CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)
| hostname | category | hardware | eth0 | eth1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| vip | 192.168.100.190 | |||
| vm-191 | master | core*4 / 4g / 20GB | 192.168.100.191 | 10.0.100.191 |
| vm-192 | master | core*4 / 4g / 20GB | 192.168.100.192 | 10.0.100.192 |
| vm-193 | master | core*4 / 4g / 20GB | 192.168.100.193 | 10.0.100.193 |
| vm-194 | etcd | core*4 / 4g / 20GB | 192.168.100.194 | 10.0.100.194 |
| vm-195 | etcd | core*4 / 4g / 20GB | 192.168.100.195 | 10.0.100.195 |
| vm-196 | etcd | core*4 / 4g / 20GB | 192.168.100.196 | 10.0.100.196 |
| vm-197 | worker | core*4 / 4g / 20GB | 192.168.100.197 | 10.0.100.197 |
| vm-207 | worker | core*4 / 4g / 20GB | 192.168.100.207 | 10.0.100.207 |
| vm-208 | worker | core*4 / 4g / 20GB | 192.168.100.208 | 10.0.100.208 |
| vm-198 | registry | core*4 / 4g / 20GB | 192.168.100.198 | 10.0.100.198 |
二、预安装
1. 静态指向(master & worker & ectd)
cat > /etc/hosts <<EOF
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.100.191 vm-191
192.168.100.192 vm-192
192.168.100.193 vm-193
192.168.100.194 vm-194
192.168.100.195 vm-195
192.168.100.196 vm-196
192.168.100.197 vm-197
192.168.100.207 vm-207
192.168.100.208 vm-208
192.168.100.198 vm-198
EOF
2. ssh信任登录
# vm-191
ssh-keygen -b 1024 -t rsa -P '' -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa
for i in {192..197}; do ssh-copy-id -i .ssh/id_rsa.pub vm-$i; done
for i in {192..197}; do scp /etc/hosts vm-$i:/etc; done
3. 修改内核配置
# master & worker & ectd
cat > /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf <<EOF
br_netfilter
EOF
cat > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf <<EOF
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
sysctl -p
for i in {192..197}; do scp /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf vm-$i:/etc/modules-load.d; done
for i in {192..197}; do scp /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf vm-$i:/etc/sysctl.d; done
for i in {192..197}; do ssh vm-$i 'sysctl -p'; done
4. 加载ipvs模块
cat /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules << EOF
#!/bin/bash
modprobe -- ip_vs
modprobe -- ip_vs_rr
modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr
modprobe -- ip_vs_sh
modprobe -- nf_conntrack_ipv4
EOF
chmod 755 /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules
sh /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules
for i in {192..197}; do scp /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules vm-$i:/etc/sysconfig/modules; done
for i in {192..197}; do ssh vm-$i 'chmod 755 /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules; sh /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules'; done
5. 安装docker
# master & worker & ectd
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo << EOF
[docker-ce-stable]
name=Docker CE Stable - $basearch
baseurl=https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/docker-ce/linux/centos/$releasever/$basearch/stable
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/docker-ce/linux/centos/gpg
EOF
yum install -y docker-ce
cat > /etc/docker/daemon.json << EOF
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://registry.docker-cn.com", "http://hub-mirror.c.163.com", "https://docker.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn"],
"insecure-registries": ["https://192.168.100.198:5000"],
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"]
}
EOF
systemctl restart docker && systemctl enable docker
docker version && docker info
for i in {192..197}; do ssh vm-$i 'yum install -y docker-ce'; done
for i in {192..197}; do scp /etc/docker/daemon.json vm-$i:/etc/docker; done
for i in {192..197}; do ssh vm-$i 'systemctl enable docker && systemctl restart docker'; done
6. 安装kubernetes
# master & worker & ectd
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo << EOF
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
yum install -y kubeadm-1.22.2-0 kubectl-1.22.2-0 kubelet-1.22.2-0
for i in {192..197}; do scp /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo vm-$i:/etc/yum.repos.d; done
for i in {192..197}; do ssh vm-$i 'yum install -y kubeadm-1.22.2-0 kubectl-1.22.2-0 kubelet-1.22.2-0'; done
三、etcd高可用集群
静态pod方式失败,原因未找到,使用docker单独部署
1. 配置kubelet
mkdir -p /var/lib/kubelet
cat > /var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml << EOF
kind: KubeletConfiguration
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
cgroupDriver: "systemd"
address: "127.0.0.1"
staticPodPath: "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
authentication:
x509:
clientCAFile: "/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt"
enabled: true
webhook:
enabled: false
anonymous:
enabled: false
authorization:
mode: "AlwaysAllow"
EOF
systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl restart kubelet
2. 生成kubeadm文件
# etcd-1
cat > /tmp/etcd-1.yaml << EOF
apiVersion: "kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3"
kind: ClusterConfiguration
imageRepository: "192.168.100.198:5000"
etcd:
local:
serverCertSANs:
- "192.168.100.194"
peerCertSANs:
- "192.168.100.194"
extraArgs:
initial-cluster: etcd1=https://192.168.100.194:2380,etcd2=https://192.168.100.195:2380,etcd3=https://192.168.100.196:2380
initial-cluster-state: new
name: etcd1
listen-peer-urls: https://192.168.100.194:2380
listen-client-urls: https://192.168.100.194:2379
advertise-client-urls: https://192.168.100.194:2379
initial-advertise-peer-urls: https://192.168.100.194:2380
EOF
# etcd-2
cat > /tmp/etcd-2.yaml << EOF
apiVersion: "kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3"
kind: ClusterConfiguration
imageRepository: "192.168.100.198:5000"
etcd:
local:
serverCertSANs:
- "192.168.100.195"
peerCertSANs:
- "192.168.100.195"
extraArgs:
initial-cluster: etcd1=https://192.168.100.194:2380,etcd2=https://192.168.100.195:2380,etcd3=https://192.168.100.196:2380
initial-cluster-state: new
name: etcd2
listen-peer-urls: https://192.168.100.195:2380
listen-client-urls: https://192.168.100.195:2379
advertise-client-urls: https://192.168.100.195:2379
initial-advertise-peer-urls: https://192.168.100.195:2380
EOF
# etcd-3
cat > /tmp/etcd-3.yaml << EOF
apiVersion: "kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3"
kind: ClusterConfiguration
imageRepository: "192.168.100.198:5000"
etcd:
local:
serverCertSANs:
- "192.168.100.196"
peerCertSANs:
- "192.168.100.196"
extraArgs:
initial-cluster: etcd1=https://192.168.100.194:2380,etcd2=https://192.168.100.195:2380,etcd3=https://192.168.100.196:2380
initial-cluster-state: new
name: etcd3
listen-peer-urls: https://192.168.100.196:2380
listen-client-urls: https://192.168.100.196:2379
advertise-client-urls: https://192.168.100.196:2379
initial-advertise-peer-urls: https://192.168.100.196:2380
EOF
拷贝
scp /tmp/etcd-2.yaml vm-195:/tmp
scp /tmp/etcd-3.yaml vm-196:/tmp
3. 生成证书
# ca.crt & ca.key
kubeadm init phase certs etcd-ca
# etcd-3
kubeadm init phase certs etcd-server --config=/tmp/etcd-3.yaml
kubeadm init phase certs etcd-peer --config=/tmp/etcd-3.yaml
kubeadm init phase certs etcd-healthcheck-client --config=/tmp/etcd-3.yaml
kubeadm init phase certs apiserver-etcd-client --config=/tmp/etcd-3.yaml
scp -r /etc/kubernetes/pki vm-196:/etc/kubernetes
# etcd-2
find /etc/kubernetes/pki -not -name ca.crt -not -name ca.key -type f -delete
kubeadm init phase certs etcd-server --config=/tmp/etcd-2.yaml
kubeadm init phase certs etcd-peer --config=/tmp/etcd-2.yaml
kubeadm init phase certs etcd-healthcheck-client --config=/tmp/etcd-2.yaml
kubeadm init phase certs apiserver-etcd-client --config=/tmp/etcd-2.yaml
scp -r /etc/kubernetes/pki vm-195:/etc/kubernetes
# etcd-1
find /etc/kubernetes/pki -not -name ca.crt -not -name ca.key -type f -delete
kubeadm init phase certs etcd-server --config=/tmp/etcd-1.yaml
kubeadm init phase certs etcd-peer --config=/tmp/etcd-1.yaml
kubeadm init phase certs etcd-healthcheck-client --config=/tmp/etcd-1.yaml
kubeadm init phase certs apiserver-etcd-client --config=/tmp/etcd-1.yaml
# 查看证书
openssl x509 -in /etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.crt -noout -text
openssl x509 -in /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt -noout -text
openssl x509 -in /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/healthcheck-client.crt -noout -text
openssl x509 -in /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/peer.crt -noout -text
需要有以下信息
Subject: O=system:masters, CN=....
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:localhost, DNS:vm-194, IP Address:192.168.100.1914 IP Address:127.0.0.1, IP Address:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, IP Address:192.168.100.195
4. 生成etcd静态pod配置文件
# 194
kubeadm init phase etcd local --config=/tmp/etcd-1.yaml
# 195
kubeadm init phase etcd local --config=/tmp/etcd-2.yaml
# 196
kubeadm init phase etcd local --config=/tmp/etcd-3.yaml
cat /etc/kubernetes/manifests/etcd.yaml
4. 运行etcd集群
# 194
docker run -d -p 2379:2379 -p 2380:2380 -v /var/lib/etcd:/etcd-data -v /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd:/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd
--name etcd 192.168.100.198:5000/etcd:3.5.0-0
/usr/local/bin/etcd
--advertise-client-urls=https://192.168.100.194:2379
--cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt
--client-cert-auth=true
--data-dir=/var/lib/etcd
--initial-advertise-peer-urls=https://192.168.100.194:2380
--initial-cluster=etcd1=https://192.168.100.194:2380,etcd2=https://192.168.100.195:2380,etcd3=https://192.168.100.196:2380
--initial-cluster-state=new
--key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key
--listen-client-urls=https://0.0.0.0:2379
--listen-metrics-urls=http://127.0.0.1:2381
--listen-peer-urls=https://0.0.0.0:2380
--name=etcd1
--peer-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/peer.crt
--peer-client-cert-auth=true
--peer-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/peer.key
--peer-trusted-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
--snapshot-count=10000
--trusted-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
# 195
docker run -d -p 2379:2379 -p 2380:2380 -v /var/lib/etcd:/etcd-data -v /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd:/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd
--name etcd 192.168.100.198:5000/etcd:3.5.0-0
/usr/local/bin/etcd
--advertise-client-urls=https://192.168.100.195:2379
--cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt
--client-cert-auth=true
--data-dir=/var/lib/etcd
--initial-advertise-peer-urls=https://192.168.100.195:2380
--initial-cluster=etcd1=https://192.168.100.194:2380,etcd2=https://192.168.100.195:2380,etcd3=https://192.168.100.196:2380
--initial-cluster-state=new
--key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key
--listen-client-urls=https://0.0.0.0:2379
--listen-metrics-urls=http://127.0.0.1:2381
--listen-peer-urls=https://0.0.0.0:2380
--name=etcd2
--peer-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/peer.crt
--peer-client-cert-auth=true
--peer-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/peer.key
--peer-trusted-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
--snapshot-count=10000
--trusted-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
# 196
docker run -d -p 2379:2379 -p 2380:2380 -v /var/lib/etcd:/etcd-data -v /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd:/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd
--name etcd 192.168.100.198:5000/etcd:3.5.0-0
/usr/local/bin/etcd
--advertise-client-urls=https://192.168.100.196:2379
--cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt
--client-cert-auth=true
--data-dir=/var/lib/etcd
--initial-advertise-peer-urls=https://192.168.100.196:2380
--initial-cluster=etcd1=https://192.168.100.194:2380,etcd2=https://192.168.100.195:2380,etcd3=https://192.168.100.196:2380
--initial-cluster-state=new
--key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key
--listen-client-urls=https://0.0.0.0:2379
--listen-metrics-urls=http://127.0.0.1:2381
--listen-peer-urls=https://0.0.0.0:2380
--name=etcd3
--peer-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/peer.crt
--peer-client-cert-auth=true
--peer-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/peer.key
--peer-trusted-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
--snapshot-count=10000
--trusted-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
# test
docker run --rm -it
--net host
-v /etc/kubernetes:/etc/kubernetes 192.168.100.198:5000/etcd:3.5.0-0 etcdctl
--cert /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/peer.crt
--key /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/peer.key
--cacert /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
--endpoints https://192.168.100.194:2379 endpoint health --cluster
四、haproxy & keepalive高可用
1. haproxy配置文件
mkdir -p /etc/haproxy
# haproxy 与 kube-api部署同一台物理机,vip端口由6443变为8443
cat > /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg << EOF
global
log 127.0.0.1 local0 info
maxconn 4000
daemon
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
defaults
mode http
log global
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 4000
frontend stats
bind *:9000
mode http
stats enable
stats uri /stats
stats hide-version
stats auth haproxy:@haproxy
frontend apiservers
bind *:8443
mode tcp
option tcplog
default_backend k8s_apiservers
backend k8s_apiservers
mode tcp
option ssl-hello-chk
option log-health-checks
balance roundrobin
default-server inter 10s downinter 5s rise 2 fall 2 slowstart 60s maxconn 250 maxqueue 256 weight 100
server kube-apiserver-1 192.168.100.191:6443 check
server kube-apiserver-2 192.168.100.192:6443 check
server kube-apiserver-3 192.168.100.193:6443 check
EOF
- keepalived配置文
# 191
mkdir -p /etc/keepalived
cat > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf << EOF
global_defs {
router_id vm-191
}
vrrp_script check_haproxy {
script "/usr/sbin/pidof haproxy"
interval 2
weight 2
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
interface eth0
state MASTER
advert_int 1
virtual_router_id 51
priority 300
unicast_src_ip 192.168.100.191
unicast_peer {
192.168.100.192
192.168.100.193
}
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass Password
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.100.190 dev eth0 label eth0:0
}
track_script {
check_haproxy
}
}
EOF
# 192
mkdir -p /etc/keepalived
cat > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf << EOF
global_defs {
router_id vm-192
}
vrrp_script check_haproxy {
script "/usr/sbin/pidof haproxy"
interval 2
weight 2
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
interface eth0
state BACKUP
advert_int 1
virtual_router_id 51
priority 200
unicast_src_ip 192.168.100.192
unicast_peer {
192.168.100.191
192.168.100.193
}
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass Password
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.100.190 dev eth0 label eth0:0
}
track_script {
check_haproxy
}
}
EOF
# 193
mkdir -p /etc/keepalived
cat > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf << EOF
global_defs {
router_id vm-193
}
vrrp_script check_haproxy {
script "/usr/sbin/pidof haproxy"
interval 2
weight 2
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
interface eth0
state BACKUP
advert_int 1
virtual_router_id 51
priority 100
unicast_src_ip 192.168.100.193
unicast_peer {
192.168.100.191
192.168.100.192
}
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass Password
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.100.190 dev eth0 label eth0:0
}
track_script {
check_haproxy
}
}
EOF
4. haproxy静态pod配置文件
cat > /etc/kubernetes/manifests/haproxy.yaml << EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: haproxy
namespace: kube-system
spec:
containers:
- image: 192.168.100.198:5000/haproxy:2.4.7
name: haproxy
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 8
httpGet:
host: localhost
path: /healthz
port: 6443
scheme: HTTPS
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/local/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
name: haproxyconf
readOnly: true
hostNetwork: true
volumes:
- hostPath:
path: /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
type: FileOrCreate
name: haproxyconf
status: {}
EOF
for i in {192..193}; do scp /etc/kubernetes/manifests/haproxy.yaml vm-$i:/etc/kubernetes/manifests; done
5. keepalived静态pod配置文件
cat > /etc/kubernetes/manifests/keepalived.yaml << EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: keepalived
namespace: kube-system
spec:
containers:
- image: 192.168.100.198:5000/keepalived:2.0.20
name: keepalived
resources: {}
securityContext:
capabilities:
add:
- NET_ADMIN
- NET_BROADCAST
- NET_RAW
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/local/etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
name: config
hostNetwork: true
volumes:
- hostPath:
path: /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
name: config
status: {}
EOF
for i in {192..193}; do scp /etc/kubernetes/manifests/keepalived.yaml vm-$i:/etc/kubernetes/manifests; done
6. 测试
docker run --rm -it
-p 6443:6443 -p 9000:9000
-v /etc/haproxy:/usr/local/etc/haproxy:ro
--name haproxy 192.168.100.198:5000/haproxy:2.4.7
haproxy -f /usr/local/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
docker run --rm -it
--privileged --cap-add=NET_ADMIN --net=host
-v /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf:/usr/local/etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
--name keepalived 192.168.100.198:5000/keepalived:2.0.20
/bin/bash
五、kubernetes集群
1. 生成配置文件模板
# kubeadm config print init-defaults > /tmp/kubeadm-config.yaml
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
bootstrapTokens:
- groups:
- system:bootstrappers:kubeadm:default-node-token
token: abcdef.0123456789abcdef
ttl: 24h0m0s
usages:
- signing
- authentication
kind: InitConfiguration
localAPIEndpoint:
advertiseAddress: 1.2.3.4
bindPort: 6443
nodeRegistration:
criSocket: /var/run/dockershim.sock
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: node
taints: null
---
apiServer:
timeoutForControlPlane: 4m0s
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
certificatesDir: /etc/kubernetes/pki
clusterName: kubernetes
controllerManager: {}
dns: {}
etcd:
local:
dataDir: /var/lib/etcd
imageRepository: k8s.gcr.io
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: 1.22.0
networking:
dnsDomain: cluster.local
serviceSubnet: 10.96.0.0/12
scheduler: {}
2. 下载镜像
kubeadm config images pull --image-repository 192.168.100.198:5000
3. 生成配置文件
# haproxy 与 kube-api部署同一台物理机,vip端口由6443变为8443
cat > /tmp/kubeadm-config.yaml << EOF
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: 1.22.2
controlPlaneEndpoint: "192.168.100.190:8443"
networking:
podSubnet: "10.240.0.0/16"
imageRepository: "192.168.100.198:5000"
etcd:
external:
endpoints:
- https://192.168.100.194:2379
- https://192.168.100.195:2379
- https://192.168.100.196:2379
caFile: /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
certFile: /etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.crt
keyFile: /etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.key
EOF
4. 部署
# 191
scp -r vm-194:/etc/kubernetes/pki /etc/kubernetes
kubeadm init --config /tmp/kubeadm-config.yaml --upload-certs --ignore-preflight-errors=all
成功提示
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of the control-plane node running the following command on each as root:
kubeadm join 192.168.100.190:8443 --token aw1vxe.533rm508wmavcj1s
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f50e85f09578b4fffbc8425df50950b21eefe8d2b10bbee234f5947485a588e0
--control-plane --certificate-key 1bd7fb3bab9d601e80c4a13c52f4e1329b10ecfce3a5a3ec4f2dc3afad291bc3
Please note that the certificate-key gives access to cluster sensitive data, keep it secret!
As a safeguard, uploaded-certs will be deleted in two hours; If necessary, you can use
"kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs" to reload certs afterward.
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 192.168.100.190:8443 --token aw1vxe.533rm508wmavcj1s
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f50e85f09578b4fffbc8425df50950b21eefe8d2b10bbee234f5947485a588e0
5. 配置用户环境
# 191
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
# 查看pod
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -o wide
6. 添加控制和工作节点
# 192 & 193
kubeadm join 192.168.100.190:8443 --token aw1vxe.533rm508wmavcj1s
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f50e85f09578b4fffbc8425df50950b21eefe8d2b10bbee234f5947485a588e0
--control-plane --certificate-key 1bd7fb3bab9d601e80c4a13c52f4e1329b10ecfce3a5a3ec4f2dc3afad291bc3
--ignore-preflight-errors=all
# 197
kubeadm join 192.168.100.190:8443 --token aw1vxe.533rm508wmavcj1s
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f50e85f09578b4fffbc8425df50950b21eefe8d2b10bbee234f5947485a588e0
--ignore-preflight-errors=all
# 查看node
kubectl get nodes -o wide
7. 安装flannel网络插件(master)
curl -k https://raw.fastgit.org/flannel-io/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml -o /tmp/kube-flannel.yml
sed -e 's|image: quay.io|image: 192.168.100.198:5000|g'
-e 's|image: rancher|image: 192.168.100.198:5000/rancher|g'
-i /tmp/kube-flannel.yml
kubectl apply -f /tmp/kube-flannel.yml
8. 更换Calico网络插件(master)
kubectl delete -f /tmp/kube-flannel.yml
curl -k https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/calico.yaml -o /tmp/calico.yaml
# pod network cidr = 10.240.0.0/16
sed -e 's|# - name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR|- name: CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR|g'
-e 's|# value: "192.168.0.0/16"| value: "10.240.0.0/16"|g'
-e 's|image: docker.io|image: 192.168.100.198:5000|g'
-e 's|:v3.21.0|:v3.20.2|g'
-i /tmp/calico.yaml
kubectl apply -f /tmp/calico.yaml
curl -k https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/calicoctl.yaml -o /tmp/calicoctl.yaml
sed -e 's|image: calico|image: 192.168.100.198:5000/calico|g' -e 's|:v3.21.0|:v3.20.2|g'
-i /tmp/calicoctl.yaml
kubectl apply -f /tmp/calicoctl.yaml
8. 检查集群状态
# kubectl get pod -A -o wide
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
kube-system calico-kube-controllers-6c6cd485bd-mm77l 1/1 Running 0 29s 10.240.234.1 vm-193 <none> <none>
kube-system calico-node-q76bf 0/1 Running 0 29s 192.168.100.191 vm-191 <none> <none>
kube-system calico-node-qdt62 0/1 Running 0 30s 192.168.100.192 vm-192 <none> <none>
kube-system calico-node-r2cjd 0/1 Running 0 29s 192.168.100.193 vm-193 <none> <none>
kube-system calico-node-ssdxc 0/1 Running 0 30s 192.168.100.197 vm-197 <none> <none>
kube-system calico-node-vw8nv 0/1 Running 0 29s 192.168.100.207 vm-207 <none> <none>
kube-system coredns-c86fdc858-b6gpk 1/1 Running 0 6m8s 10.240.2.129 vm-197 <none> <none>
kube-system coredns-c86fdc858-xxl86 1/1 Running 0 6m8s 10.240.2.130 vm-197 <none> <none>
kube-system haproxy-vm-191 1/1 Running 0 6m10s 192.168.100.191 vm-191 <none> <none>
kube-system haproxy-vm-192 1/1 Running 0 4m33s 192.168.100.192 vm-192 <none> <none>
kube-system haproxy-vm-193 1/1 Running 0 4m26s 192.168.100.193 vm-193 <none> <none>
kube-system keepalived-vm-191 1/1 Running 0 6m10s 192.168.100.191 vm-191 <none> <none>
kube-system keepalived-vm-192 1/1 Running 0 4m33s 192.168.100.192 vm-192 <none> <none>
kube-system keepalived-vm-193 1/1 Running 0 4m25s 192.168.100.193 vm-193 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-apiserver-vm-191 1/1 Running 0 6m10s 192.168.100.191 vm-191 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-apiserver-vm-192 1/1 Running 0 4m34s 192.168.100.192 vm-192 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-apiserver-vm-193 1/1 Running 0 4m25s 192.168.100.193 vm-193 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-controller-manager-vm-191 1/1 Running 0 6m10s 192.168.100.191 vm-191 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-controller-manager-vm-192 1/1 Running 0 4m33s 192.168.100.192 vm-192 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-controller-manager-vm-193 1/1 Running 0 4m25s 192.168.100.193 vm-193 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-proxy-7tlwx 1/1 Running 0 4m4s 192.168.100.197 vm-197 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-proxy-88hf7 1/1 Running 0 4m26s 192.168.100.193 vm-193 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-proxy-gpsb9 1/1 Running 0 6m8s 192.168.100.191 vm-191 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-proxy-w5qdh 1/1 Running 0 4m34s 192.168.100.192 vm-192 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-proxy-zhqn5 1/1 Running 0 3m1s 192.168.100.207 vm-207 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-scheduler-vm-191 1/1 Running 0 6m10s 192.168.100.191 vm-191 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-scheduler-vm-192 1/1 Running 0 4m33s 192.168.100.192 vm-192 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-scheduler-vm-193 1/1 Running 0 4m25s 192.168.100.193 vm-193 <none> <none>
# kubectl get node -A -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
vm-191 Ready control-plane,master 6m24s v1.22.2 192.168.100.191 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
vm-192 Ready control-plane,master 4m42s v1.22.2 192.168.100.192 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
vm-193 Ready control-plane,master 4m34s v1.22.2 192.168.100.193 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
vm-197 Ready <none> 4m11s v1.22.2 192.168.100.197 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
vm-207 Ready <none> 3m9s v1.22.2 192.168.100.207 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64 docker://20.10.9
# kubectl get service -A -o wide
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
default kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 9m38s <none>
kube-system kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 9m27s k8s-app=kube-dns
# kubectl get deployment -A -o wide
NAMESPACE NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
kube-system calico-kube-controllers 1/1 1 1 3m50s calico-kube-controllers 192.168.100.198:5000/calico/kube-controllers:v3.20.2 k8s-app=calico-kube-controllers
kube-system coredns 2/2 2 2 9m34s coredns 192.168.100.198:5000/coredns:v1.8.4 k8s-app=kube-dns
# kubectl cluster-info
Kubernetes control plane is running at https://192.168.100.190:8443
CoreDNS is running at https://192.168.100.190:8443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
9. 测试dns
# kubectl run busybox --image=192.168.100.198:5000/busybox:1.28 --rm=true --restart=Never -it -- nslookup kubernetes
Server: 10.96.0.10
Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local
Name: kubernetes
Address 1: 10.96.0.1 kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local
pod "busybox" deleted
# kubectl run busybox --image=192.168.100.198:5000/busybox:1.28 --rm=true --restart=Never -it -- nslookup kube-dns.kube-system
Server: 10.96.0.10
Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local
Name: kube-dns.kube-system
Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local
pod "busybox" deleted