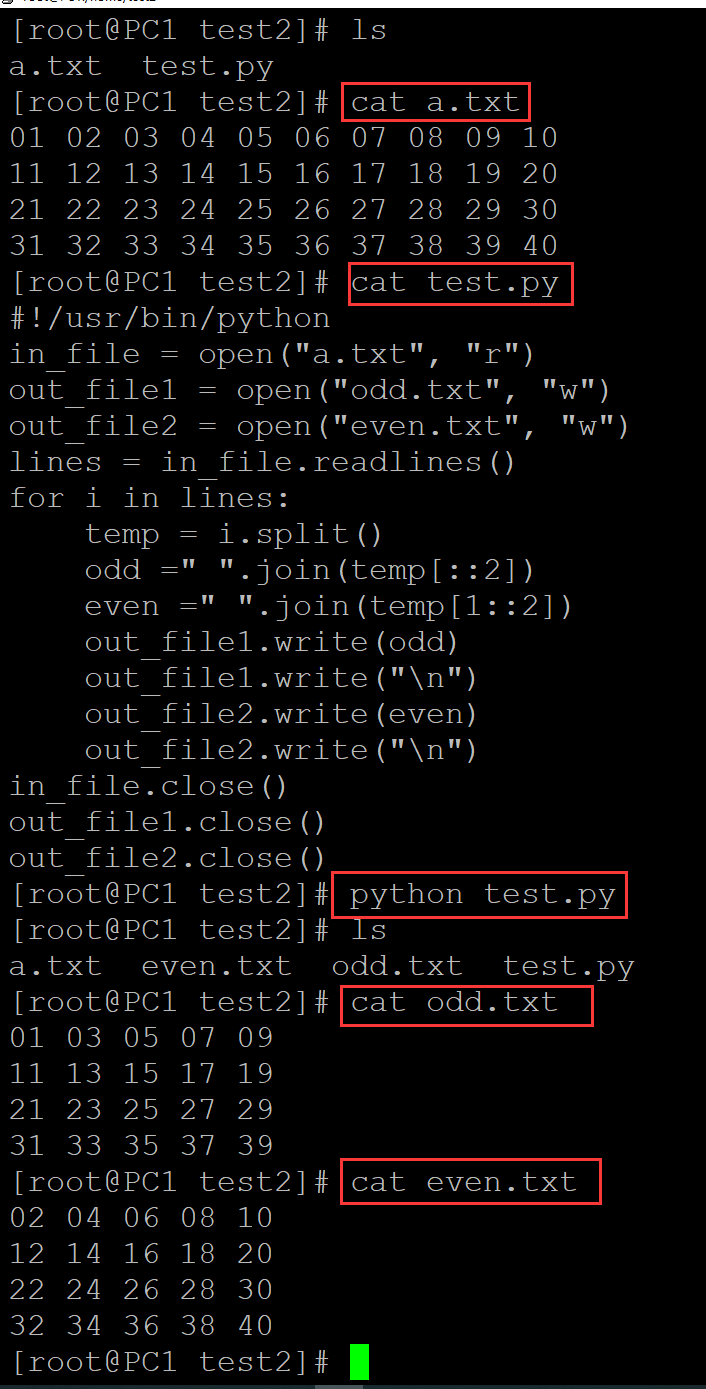
1、提取第一列
[root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat a.txt ## 测试数据 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [root@PC1 test2]# cat test.py ## 提取程序 #!/usr/bin/python in_file = open("a.txt", "r") out_file = open("result.txt", "w") lines = in_file.readlines() for i in lines: temp = i.split() out_file.write(temp[1 - 1]) out_file.write("\n") in_file.close() out_file.close() [root@PC1 test2]# python test.py ## 执行程序 [root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt result.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat result.txt ## 提取结果 01 11 21 31
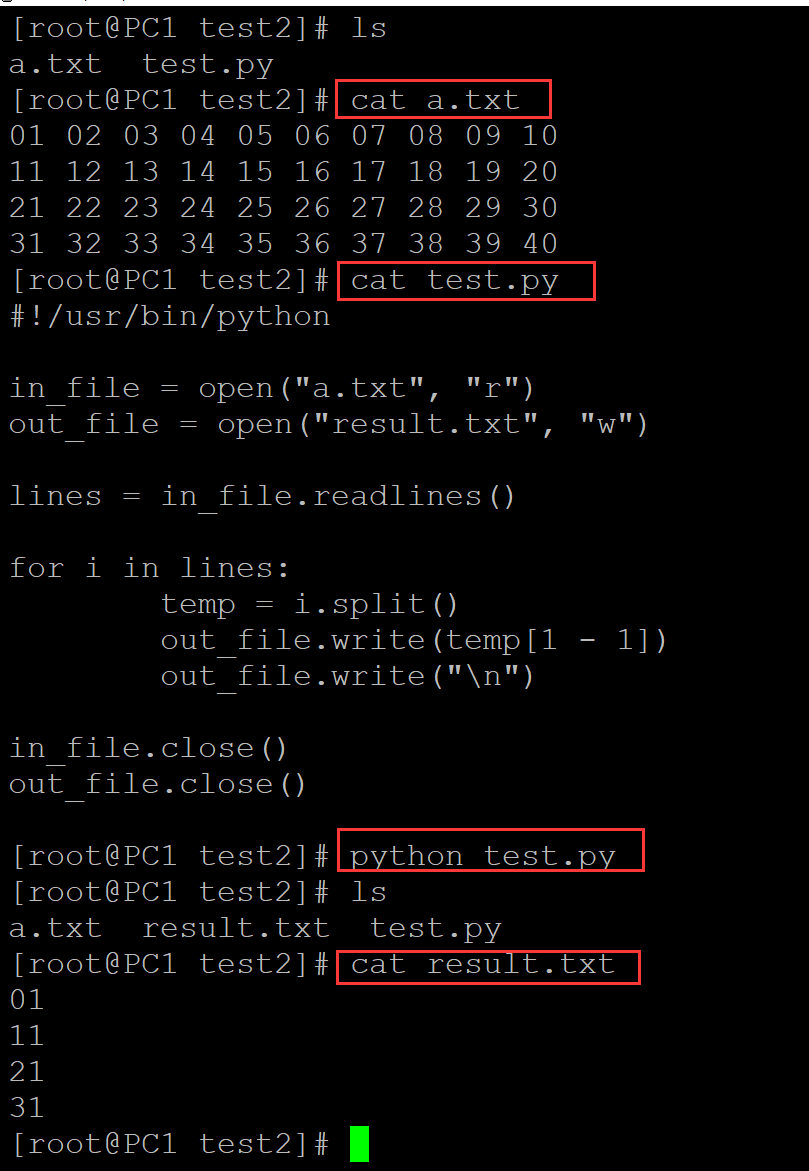
2、提取第三列
[root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat a.txt 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [root@PC1 test2]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/python in_file = open("a.txt", "r") out_file = open("result.txt", "w") lines = in_file.readlines() for i in lines: temp = i.split() out_file.write(temp[3 - 1]) out_file.write("\n") in_file.close() out_file.close() [root@PC1 test2]# python test.py [root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt result.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat result.txt 03 13 23 33
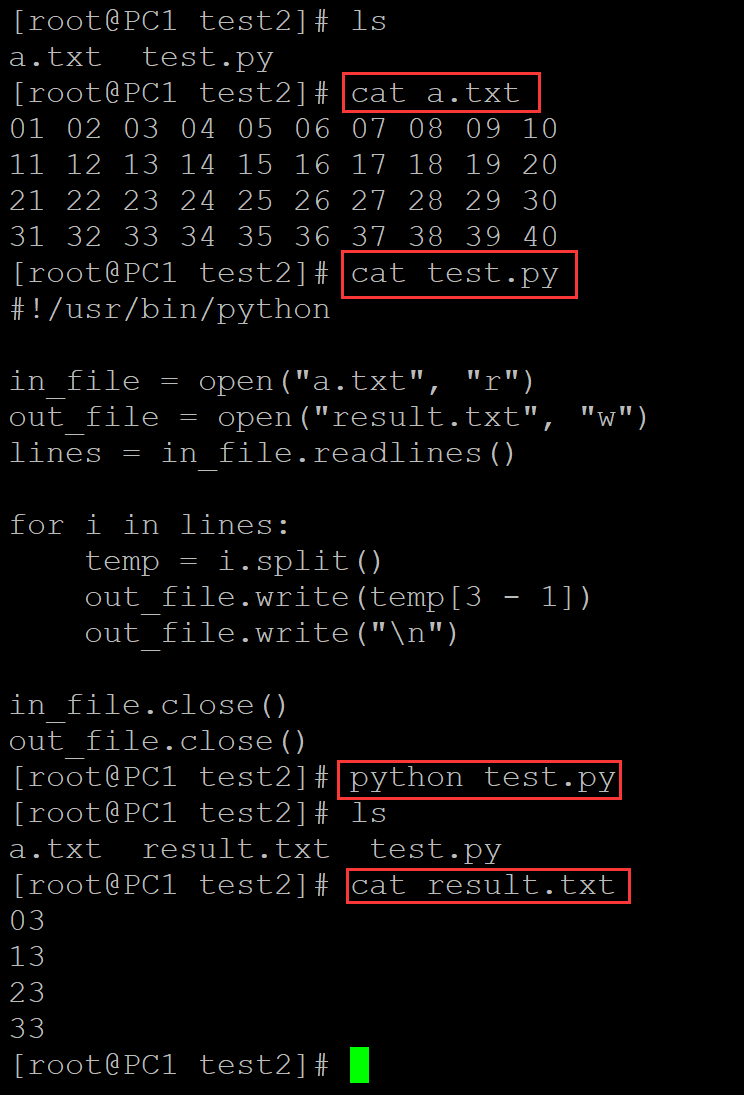
3、提取1-3列
[root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat a.txt 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [root@PC1 test2]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/python in_file = open("a.txt", "r") out_file = open("result.txt", "w") lines = in_file.readlines() for i in lines: temp = i.split() #temp = " ".join(temp[:3]) out_file.write(" ".join(temp[:3])) out_file.write("\n") in_file.close() out_file.close() [root@PC1 test2]# python test.py [root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt result.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat result.txt 01 02 03 11 12 13 21 22 23 31 32 33
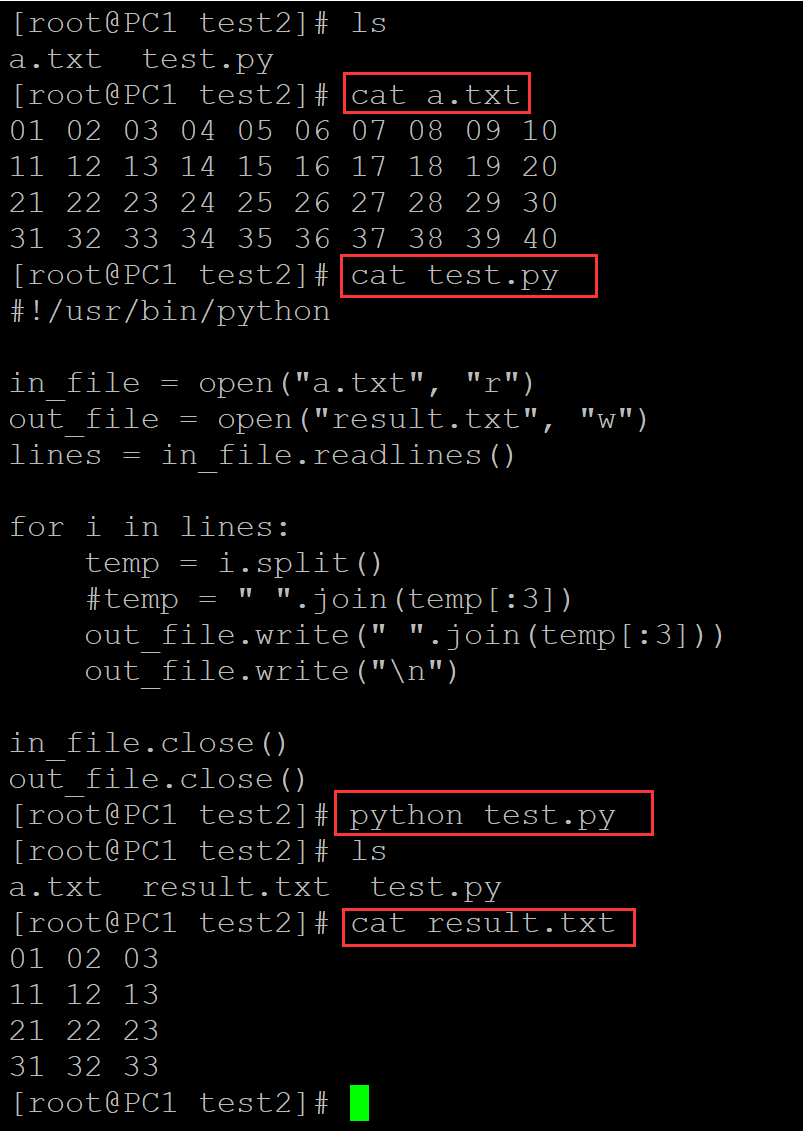
4、提取1、3、7列
[root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat a.txt 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [root@PC1 test2]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/python import numpy as np in_file = open("a.txt", "r") out_file = open("result.txt", "w") lines = in_file.readlines() for i in lines: temp = i.split() np_temp = np.array(temp) temp2 = list(np_temp[[1 - 1, 3 - 1, 7 - 1]]) temp3 = " ".join(temp2) out_file.write(temp3) out_file.write("\n") in_file.close() out_file.close() [root@PC1 test2]# python test.py [root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt result.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat result.txt 01 03 07 11 13 17 21 23 27 31 33 37
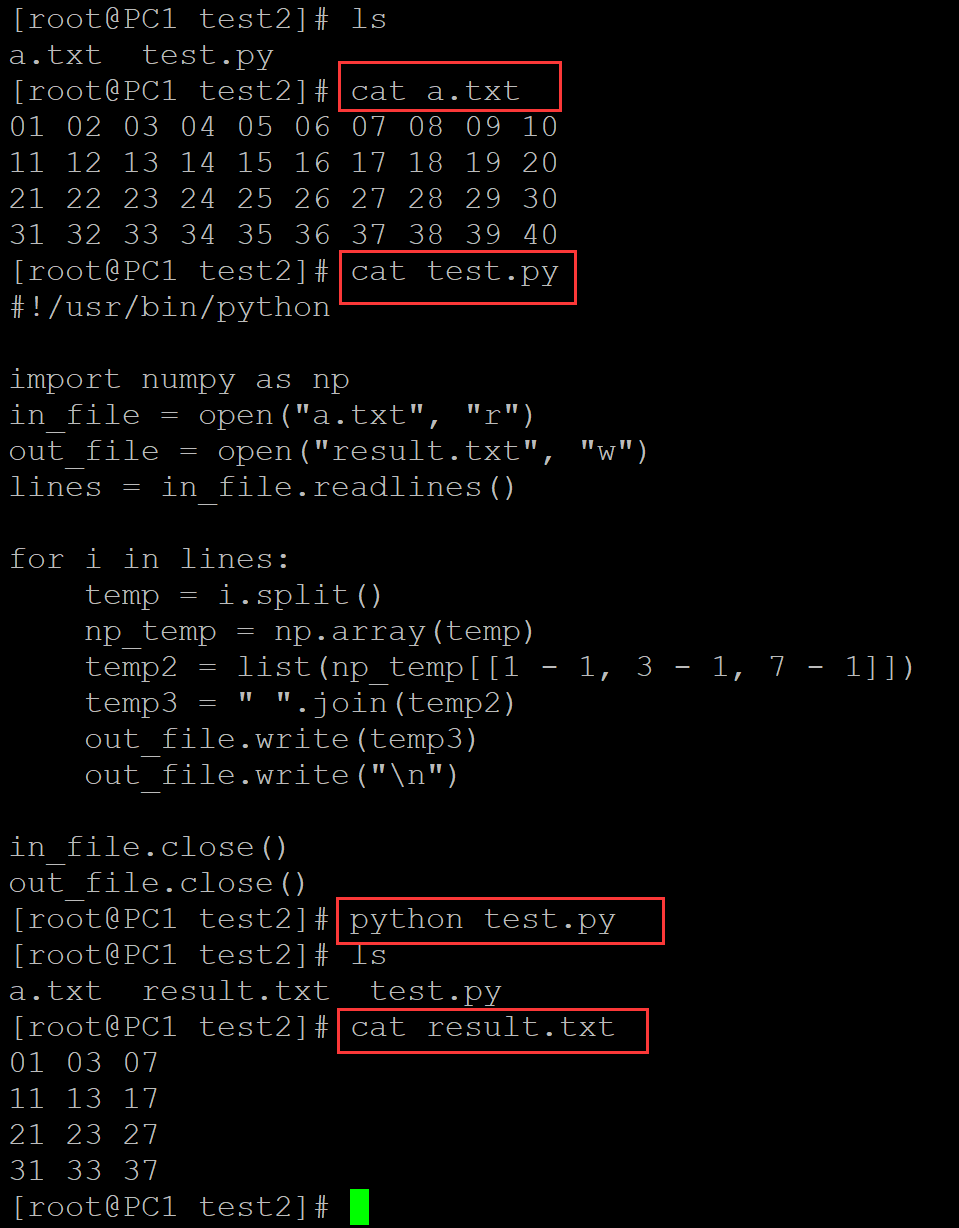
5、提取最后一列
[root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat a.txt 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [root@PC1 test2]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/python in_file = open("a.txt", "r") out_file = open("result.txt", "w") lines = in_file.readlines() for i in lines: i = i.split() out_file.write(i[-1]) out_file.write("\n") in_file.close() out_file.close() [root@PC1 test2]# python test.py [root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt result.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat result.txt 10 20 30 40
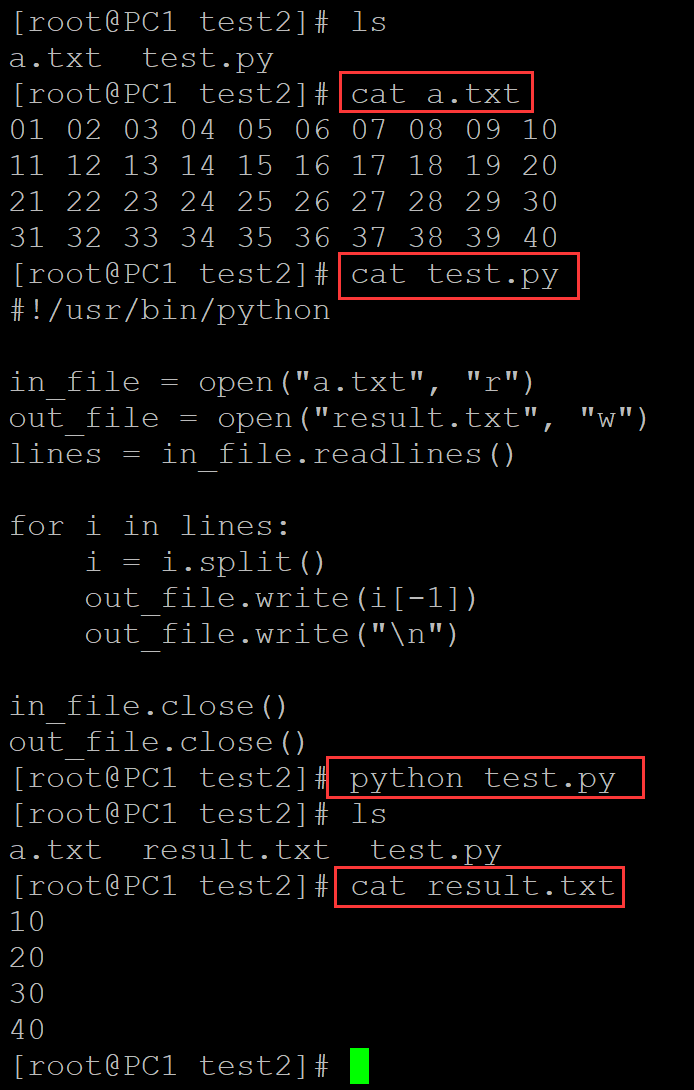
6、提取倒数第3列
[root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat a.txt 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [root@PC1 test2]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/python in_file = open("a.txt", "r") out_file = open("result.txt", "w") lines = in_file.readlines() for i in lines: temp = i.split() out_file.write(temp[-3]) out_file.write("\n") in_file.close() out_file.close() [root@PC1 test2]# python test.py [root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt result.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat result.txt 08 18 28 38
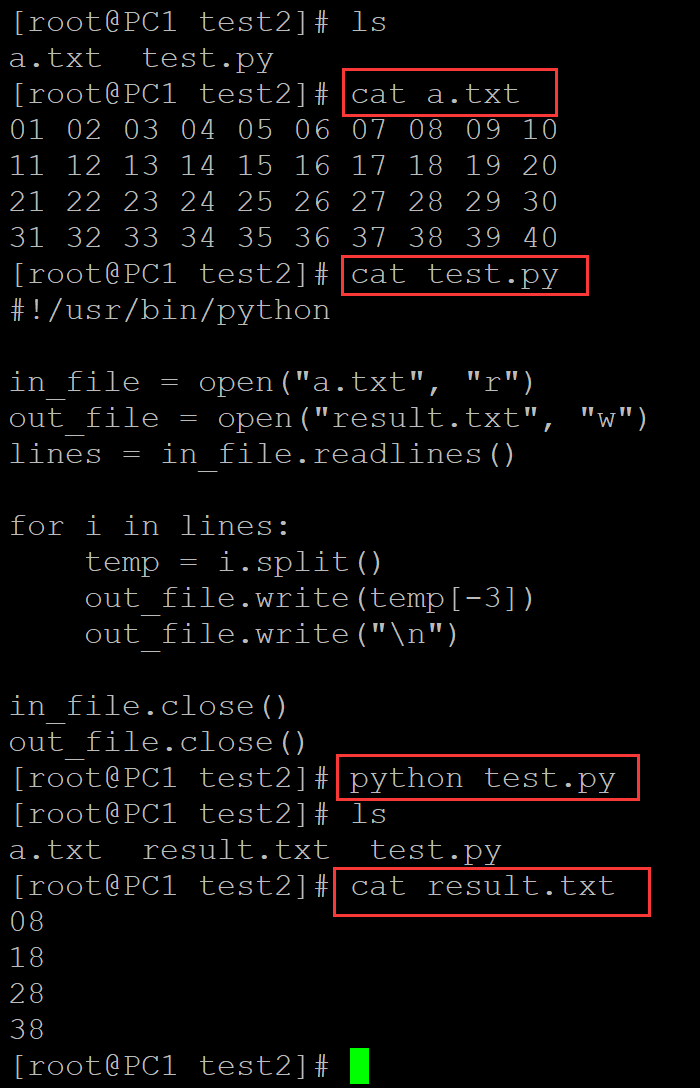
7、输出最后5列
[root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat a.txt 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [root@PC1 test2]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/python in_file = open("a.txt", "r") out_file = open("result.txt", "w") lines = in_file.readlines() for i in lines: temp = i.split() temp2 = " ".join(temp[-5:]) out_file.write(temp2) out_file.write("\n") in_file.close() out_file.close() [root@PC1 test2]# python test.py [root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt result.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat result.txt 06 07 08 09 10 16 17 18 19 20 26 27 28 29 30 36 37 38 39 40
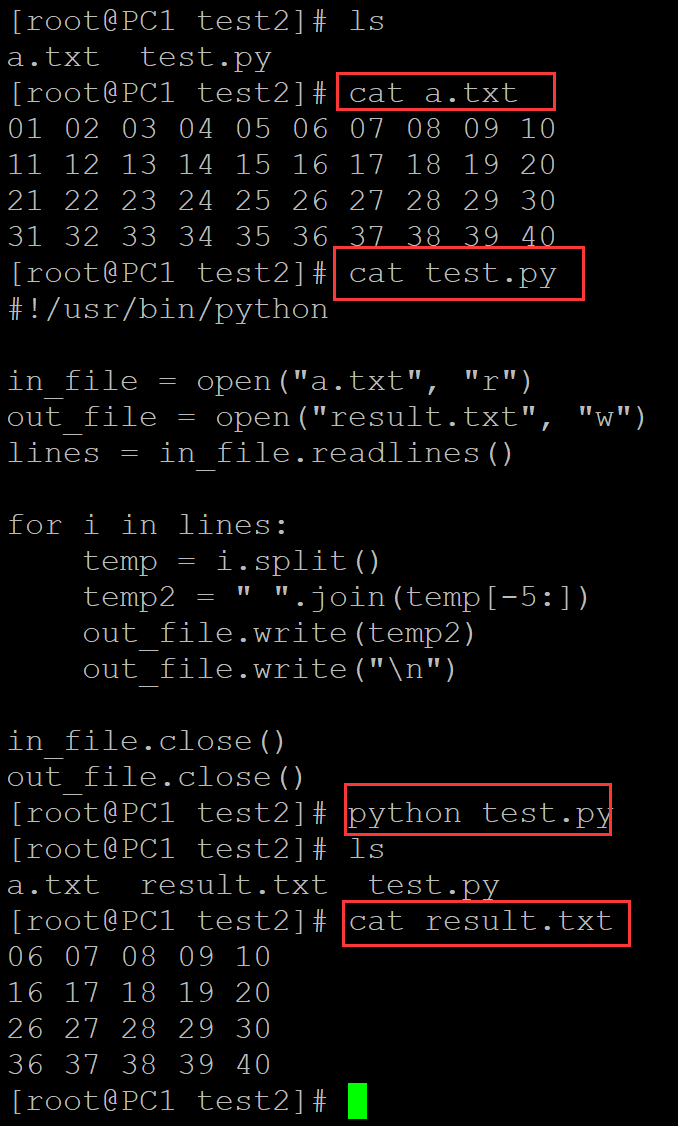
8、所有列逆向输出
[root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat a.txt 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [root@PC1 test2]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/python in_file = open("a.txt", "r") out_file = open("result.txt", "w") lines = in_file.readlines() for i in lines: temp = i.split() temp2 = " ".join(temp[::-1]) out_file.write(temp2) out_file.write("\n") in_file.close() out_file.close() [root@PC1 test2]# python test.py [root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt result.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat result.txt 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31
9、输出奇数列、偶数列
[root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat a.txt 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [root@PC1 test2]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/python in_file = open("a.txt", "r") out_file1 = open("odd.txt", "w") out_file2 = open("even.txt", "w") lines = in_file.readlines() for i in lines: temp = i.split() odd =" ".join(temp[::2]) even =" ".join(temp[1::2]) out_file1.write(odd) out_file1.write("\n") out_file2.write(even) out_file2.write("\n") in_file.close() out_file1.close() out_file2.close() [root@PC1 test2]# python test.py [root@PC1 test2]# ls a.txt even.txt odd.txt test.py [root@PC1 test2]# cat odd.txt 01 03 05 07 09 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 [root@PC1 test2]# cat even.txt 02 04 06 08 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40