复习题 9
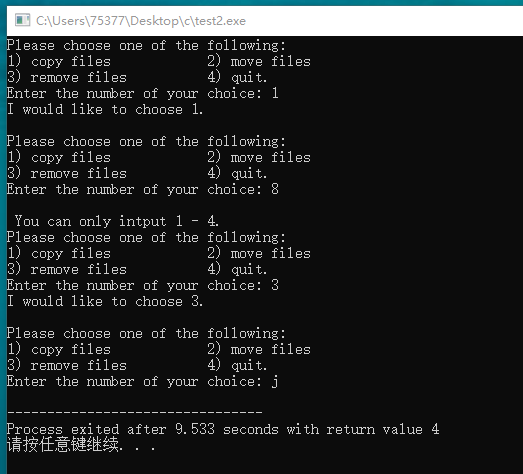
#include <stdio.h> void show_menu(void); int getchoice(int low, int high); int main(void) { int res; show_menu(); while((res = getchoice(1,4)) != 4) { printf("I would like to choose %d. ", res); show_menu(); } } void show_menu(void) { printf("Please choose one of the following: "); printf("1) copy files 2) move files "); printf("3) remove files 4) quit. "); printf("Enter the number of your choice: "); } int getchoice(int low, int high) { int choice; int status; while((status = scanf("%d", &choice)) == 1 && ( choice < low || choice > high )) { printf(" You can only intput %d - %d. ", low, high); show_menu(); } if(status != 1) choice = 4; return choice; }
1、
#include <stdio.h> double smaller(double x, double y); int main(void) { double a = 3.0, b = 1.0; printf("the smaller is: %.2f. ", smaller(a, b)); return 0; } double smaller(double x, double y) { double smaller; if (x < y) smaller = x; else smaller = y; return smaller; }

#include <stdio.h> double smaller(double x, double y); int main(void) { double a = 3.0, b = 1.0; printf("the smaller is: %.2f. ", smaller(a, b)); return 0; } double smaller(double x, double y) { return x < y ? x : y; }

2、
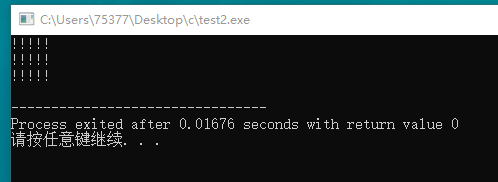
#include <stdio.h> void chline(char ch, int i, int j); int main(void) { char ch = '!'; int a = 5, b = 3; chline(ch, a, b); return 0; } void chline(char ch, int i, int j) { int x, y; for(x = 1; x <= j; x++) { for(y = 1; y <= i; y++) putchar(ch); putchar(' '); } }
3、
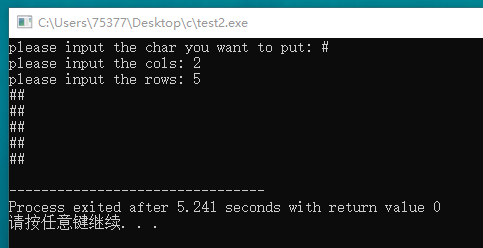
#include <stdio.h> void putstr(char ch, int x, int y); int main(void) { char ch; int rows, cols; printf("please input the char you want to put: "); scanf("%c", &ch); printf("please input the cols: "); scanf("%d", &cols); printf("please input the rows: "); scanf("%d", &rows); putstr(ch, cols, rows); return 0; } void putstr(char ch, int x, int y) { int i, j; for(i = 1; i <= y; i++) { for(j = 1; j <= x; j++) { putchar(ch); } putchar(' '); } }
4、
#include <stdio.h> double harmean(double x, double y); int main(void) { double a, b; printf("please input two double num. "); printf("a = "); scanf("%lf", &a); printf("b = "); scanf("%lf", &b); printf("the harmean is : %.2f. ", harmean(a, b)); return 0; } double harmean(double x, double y) { double temp1; temp1 = 1/((1/x + 1/y)/2); return temp1; }
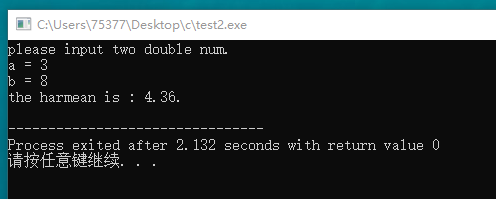
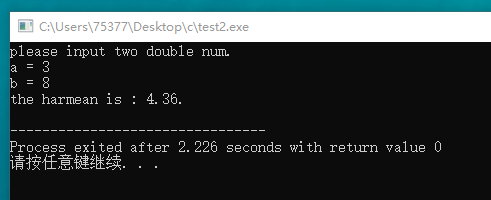
#include <stdio.h> double harmean(double x, double y); int main(void) { double a, b; printf("please input two double num. "); printf("a = "); scanf("%lf", &a); printf("b = "); scanf("%lf", &b); printf("the harmean is : %.2f. ", harmean(a, b)); return 0; } double harmean(double x, double y) { double temp1; temp1 = 2/(1/x + 1/y); return temp1; }
5、
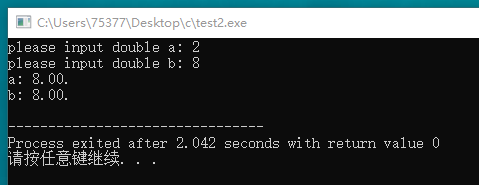
#include <stdio.h> void larger(double * x, double * y); int main(void) { double a, b; printf("please input double a: "); scanf("%lf", &a); printf("please input double b: "); scanf("%lf", &b); larger(&a, &b); printf("a: %.2f. ", a); printf("b: %.2f. ", b); return 0; } void larger(double * x, double * y) { if(*x > *y) *y = *x; else *x = *y; }
6、
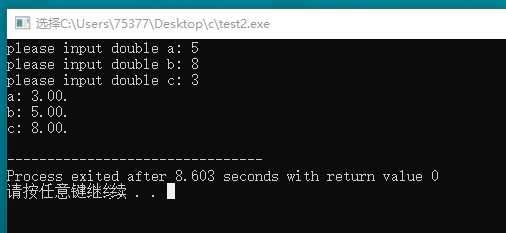
#include <stdio.h> void sort(double * x, double * y, double * z); int main(void) { double a, b, c; printf("please input double a: "); scanf("%lf", &a); printf("please input double b: "); scanf("%lf", &b); printf("please input double c: "); scanf("%lf", &c); sort(&a, &b, &c); printf("a: %.2f. ", a); printf("b: %.2f. ", b); printf("c: %.2f. ", c); return 0; } void sort(double * x, double * y, double * z) { double min, med, max; min = *x; min = min < *y ? min : *y; min = min < *z ? min : *z; max = *x; max = max > *y ? max : *y; max = max > *z ? max : *z; if(*x > min && *x < max) med = *x; if(*y > min && *y < max) med = *y; if(*z > min && *z < max) med = *z; *x = min; *y = med; *z = max; }

#include <stdio.h> void sort(double * x, double * y, double * z); int main(void) { double a, b, c; printf("please input double a: "); scanf("%lf", &a); printf("please input double b: "); scanf("%lf", &b); printf("please input double c: "); scanf("%lf", &c); sort(&a, &b, &c); printf("a: %.2f. ", a); printf("b: %.2f. ", b); printf("c: %.2f. ", c); return 0; } void sort(double * x, double * y, double * z) { double temp; if(*x > *y) { temp = *x; *x = *y; *y = temp; } if(*x > *z) { temp = *x; *x = *z; *z = temp; } if(*y > *z) { temp = *y; *y = *z; *z = temp; } }
7、
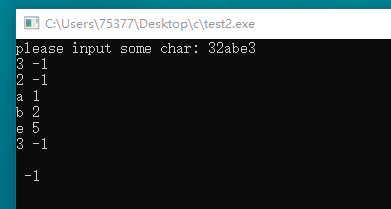
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> void report(void); int main(void) { printf("please input some char: "); report(); return 0; } void report(void) { char ch; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(isalpha(ch)) { if(isupper(ch)) { putchar(ch); putchar(' '); printf("%d ", 26 - ('Z' - ch)); } else { putchar(ch); putchar(' '); printf("%d ", 26 - ('z' - ch)); } } else { putchar(ch); putchar(' '); printf("%d ", -1); } } }
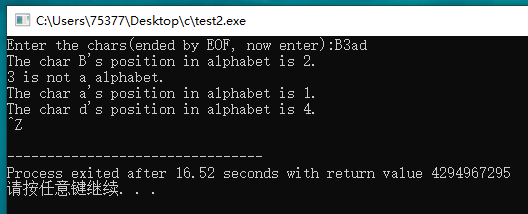
#include <stdio.h> void get_char_pos(void); int position(char ch); int main(void) { get_char_pos(); } void get_char_pos(void) { char ch; printf("Enter the chars(ended by EOF, now enter):" ); while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(ch == ' ') continue; if(position(ch) != -1) { printf("The char %c's position in alphabet is %d. ", ch, position(ch)); } else printf("%c is not a alphabet. ", ch); } } int position(char ch) { if(ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') return ch - 'A' + 1; if(ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') return ch - 'a' + 1; return -1; }
#include <stdio.h> void getch(void); int show(char ch); int main(void) { getch(); return 0; } void getch(void) { char ch; printf("please input str: "); while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(ch == ' ') continue; if(show(ch) != -1) { printf("%c is %d. ", ch, show(ch)); } else { printf("%c is not alpha. "); } } } int show(char ch) { if(ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') return ch - 'A' + 1; if(ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') return ch - 'a' + 1; return -1; }

8、
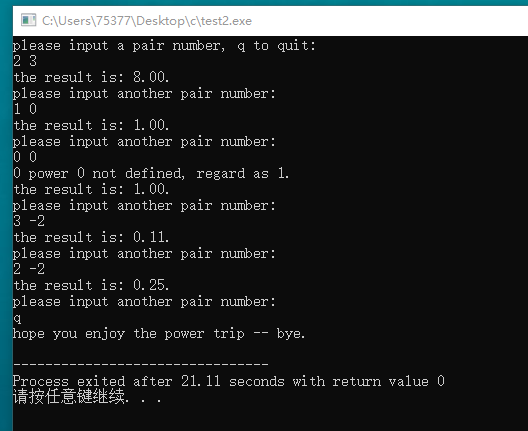
#include <stdio.h> double power(double x, int y); int main(void) { double a; int b; double result; printf("please input a pair number, q to quit: "); while((scanf("%lf %d", &a, &b)) == 2) { result = power(a, b); printf("the result is: %.2f. ", result); printf("please input another pair number: "); } printf("hope you enjoy the power trip -- bye. "); return 0; } double power(double x, int y) { int i; double power = 1.0; if(x == 0) { if(y != 0) power = 0; else { printf("0 power 0 not defined, regard as 1. "); power = 1; } } else { if(y > 0) { for(i = 1; i <= y; i++) { power *= x; } } else if(y < 0) { for(i = 1; i <= -y; i++) { power *= x; } power = 1/power; } else { power = 1; } } return power; }
9、
#include <stdio.h> double power(double n, int p); int main(void) { double x, xpow; int exp; printf("Enter a number and the integer power:(q to quit). "); while(scanf("%lf %d", &x, &exp) == 2) { xpow = power(x, exp); printf("%.3g to the power %d is %.5g ", x, exp, xpow); printf("Enter the next pair of number or q to quit. "); } printf("Hope you enjoy this power trip -- bye! "); return 0; } double power(double n, int p) { double pow = 1; int i; if(n == 0 && p == 0) { printf("The %g to the power %c is not define, return 1! ", n, p); return 1; } if(n == 0) return 0; if(p == 0) return 1; if(p > 0) { return n * power(n, p-1); } else { return power(n, p+1)/n; } }

10、
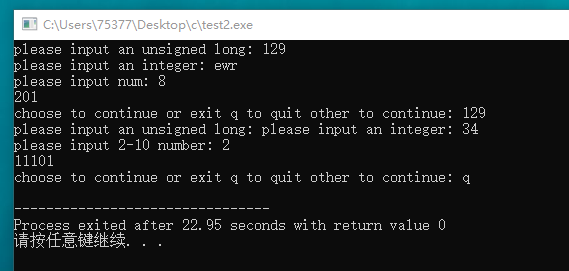
#include <stdio.h> unsigned long get_long(void); int get_unit(void); void to_binary(unsigned long x, int y); int main(void) { unsigned long a; int b; char ch; do { a = get_long(); b = get_unit(); to_binary(a, b); putchar(' '); while(getchar() != ' ') continue; printf("choose to continue or exit q to quit other to continue: "); while((ch = getchar()) == 'q') break; } while(ch != 'q'); return 0; } void to_binary(unsigned long x, int y) { int temp; temp = x % y; if(x >= y) to_binary(x/y, y); printf("%d",temp); } unsigned long get_long(void) { unsigned temp; printf("please input an unsigned long: "); while(scanf("%lu", &temp) != 1) { scanf("%*s"); printf("please input an unsigned long num: "); } return temp; } int get_unit(void) { int temp; int status; printf("please input an integer: "); while((status = scanf("%d", &temp)) != 1 || (temp < 2 || temp > 10)) { if(status != 1) { scanf("%*s"); printf("please input num: "); } else { printf("please input 2-10 number: "); } } return temp; }
#include <stdio.h> void to_base_n(unsigned long n, unsigned short int t); int main(void) { unsigned long number; unsigned short int target; printf("please enter the integer and N for natation(q to quit): "); while(scanf("%lu %hu", &number, &target) == 2) { if(target < 2 || target > 10) { printf("please input N between 2 and 10! "); printf("Enter the integer and N for notation(q to quit): "); continue; } printf("conber %lu to %hu notation is: ", number, target); to_base_n(number, target); putchar(' '); printf("Enter the integer and N for notation(q to quit): "); } return 0; } void to_base_n(unsigned long n, unsigned short t) { int r; r = n % t; if(n >= t) to_base_n(n/t, t); printf("%d", r); }
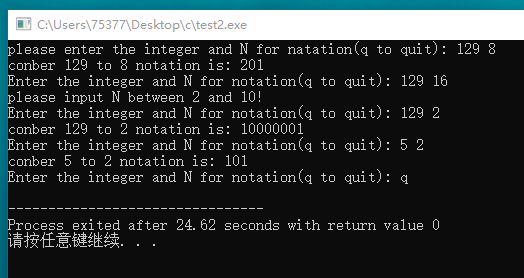
11、
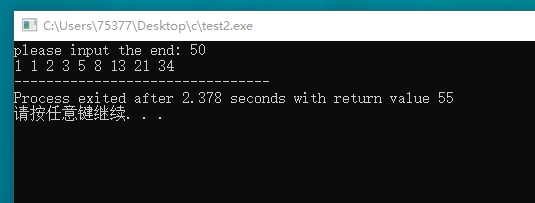
#include <stdio.h> void fibonacci(int x); int main(void) { int end; printf("please input the end: "); scanf("%d", &end); fibonacci(end); } void fibonacci(int x) { int i; int temp1 = 1; int temp2 = 1; int temp3 = 0; printf("%d ", 1); printf("%d ", 1); for(i = 1; 1 ;i++) { temp3 = temp1 + temp2; if(temp3 > x) break; printf("%d ", temp3); temp1 = temp2; temp2 = temp3; } }
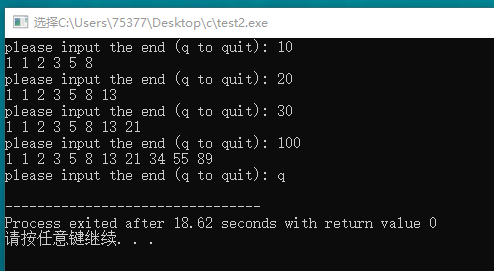
#include <stdio.h> void fibonacci(int x); int main(void) { int end; int status; printf("please input the end (q to quit): "); while(scanf("%d", &end) == 1) { fibonacci(end); printf("please input the end (q to quit): "); } return 0; } void fibonacci(int x) { int i; int temp1 = 1; int temp2 = 1; int temp3 = 0; printf("%d ", 1); printf("%d ", 1); for(i = 1; 1 ;i++) { temp3 = temp1 + temp2; if(temp3 > x) break; printf("%d ", temp3); temp1 = temp2; temp2 = temp3; } putchar(' '); }
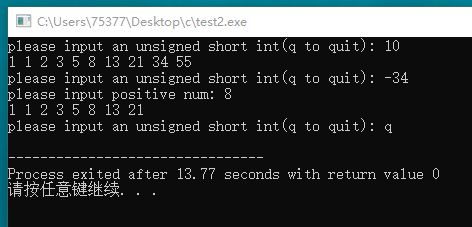
#include <stdio.h> void fibonacci(int x); int main(void) { int n; printf("please input an unsigned short int(q to quit): "); while(scanf("%uh",&n) == 1) { if(n < 1) { printf("please input positive num: "); continue; } fibonacci(n); printf("please input an unsigned short int(q to quit): "); }
return 0; } void fibonacci(int x) { int f1 = 1, f2 = 1; int i, temp; for(i = 1; i <= x; i++) { printf("%d ", f1); temp = f1 + f2; f1 = f2; f2 = temp; } putchar(' '); }