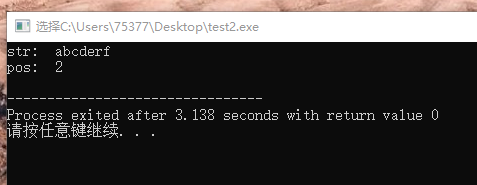
1、线性查找法
#include <stdio.h> #define FAILED -1 int len(char x[]) { int len = 0; while(x[len]) len++; return len; } int search(char x[], char key) { int i = 0; while(1) { if(i == len(x)) return FAILED; if(x[i] == key) return i; i++; } } int main(void) { char str[128]; printf("str: "); scanf("%s", str); printf("position: %d ", search(str, 'c')); return 0; }
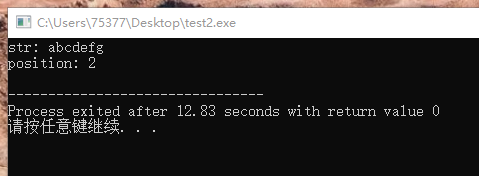
2、线性查找法
#include <stdio.h> #define FAILED -1 int len(char x[]) { int i = 0; while(1) { if(x[i] == '�') return i; i++; } } int search(char x[], char key) { int i = 0; while(1) { if(i == len(x)) return FAILED; if(x[i] == key) return i; i++; } } int main(void) { char str[128]; printf("str: "); scanf("%s", str); printf("position: %d ", search(str, 'c')); return 0; }

3、线性查找法
#include <stdio.h> #define FAILED -1 int length(char x[]) { int i = 0; while(1) { if(x[i] == '�') return i; i++; } } int search(char x[], char key) { int len, i; len = length(x); for(i = 0; i < len; i++) { if(x[i] == key) return i; } if(i == len) return FAILED; } int main(void) { char str[128]; printf("str: "); scanf("%s", str); printf("position: %d ", search(str, 'c')); return 0; }
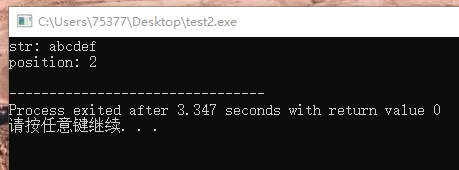
4、哨兵查找法
#include <stdio.h> #define FAILED -1 int length(char x[]) { int i = 0; while(1) { if(x[i] == '�') return i; i++; } } int search(char x[], char key) { int len = length(x); x[len] = key; int i = 0; while(1) { if(x[i] == key) break; i++; } return i < len ? i : FAILED; } int main(void) { char str[128]; printf("str: "); scanf("%s", str); printf("pos: %d ", search(str, 'c')); return 0; }

5、简化
#include <stdio.h> #define FAILED -1 int search(char x[], char key) { int i = 0; while(1) { if(x[i] == key) return i; if(x[i] == '�') return FAILED; i++; } } int main(void) { char str[128]; printf("str: "); scanf("%s", str); printf("pos: %d ", search(str, 'c')); return 0; }