Bean配置
简单记录-Java EE企业级应用开发教程(Spring+Spring MVC+MyBatis)-Spring中的Bean
什么是Spring中的Bean?
Spring可以被看作是一个大型工厂,这个工厂的作用就是生产和管理Spring容器中的Bean。如果想要在项目中使用这个工厂,就需要开发者对Spring的配置文件进行配置,配置的时候要在配置文件中告诉它需要哪些Bean,以及需要使用何种方式将这些Bean装配到一起。
提示: Bean的本质就是Java中的类,而Spring中的Bean其实就是对实体类的引用,来生产Java类对象,从而实现生产和管理Bean 。
Spring容器支持XML和Properties两种格式的配置文件,在实际开发中,最常使用的就是XML格式的配置方式。这种配置方式通过XML文件来注册并管理Bean之间的依赖关系。
使用XML文件的形式对Bean的属性和定义进行详细的讲解。
在Spring中,XML配置文件的根元素是, 中包含了多个子元素,每一个子元素定义了一个Bean,并描述了该Bean如何被装配到Spring容器中。元素中同样包含了多个属性以及子元素,其常用属性及子元素如表所示。
表元素的常用属性及其子元素
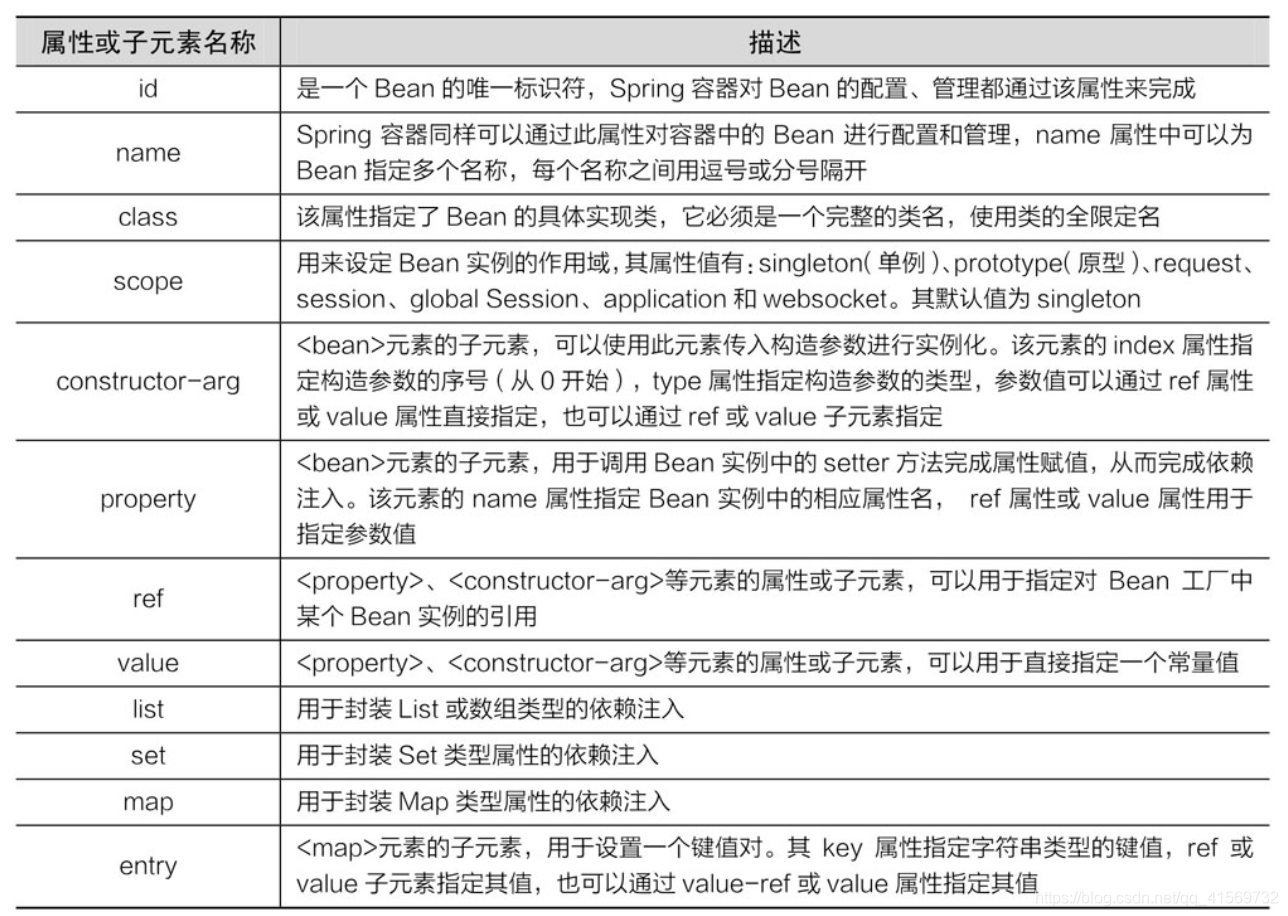
表中只介绍了元素的一些常用属性和子元素,实际上元素还有很多属性和子元素,我们可以到网上查阅相关资料进行获取。
在Spring的配置文件中,通常一个普通的Bean只需要定义id(或name)和class两个属性即可,定义Bean的方式如下所示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--将指定类配置给Spring,让Spring创建其对象的实例 -->
<!-- 使用id 属性定义bean1,其对应的实现类为com.awen.instance.constructor.Bean1-->
<bean id="bean1" class="com.awen.instance.constructor.Bean1"/>
<!-- 使用name 属性定义bean1,其对应的实现类为com.awen.instance.static_factory.Bean2-->
<bean name="bean2" class="com.awen.instance.static_factory.Bean2"
</beans>
在上述代码中,分别使用id属性和name属性定义了两个Bean,并使用class元素指定其对应的实现类
注意:如果在Bean中未指定id和name,则Spring会将class值当作id使用。
- 一般情况下,装配一个Bean时,通过指定一个id属性作为Bean的名称
- id属性在IOC容器中必须是唯一的
- 如果Bean的名称中含有特殊字符,就需要使用name属性
实例
1、复杂类型
public class Address {
private String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
2、真实测试对象
public class Student {
private String name;
private Address address;
private String[] books;
private List<String> hobbies;
private Map<String,String> card;
private Set<String> games;
private String wife;
private Properties info;
}
Address的对象address在Student类作为属性
3、beans.xml
完整注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address" class="com.kuang.pojo.Address"/>
<bean id="student" class="com.kuang.pojo.Student">
<!--第一种,普通值注入,value-->
<property name="name" value="憨批"/>
<!--第二种,Bean注入,ref-->
<property name="address" ref="address"/>
<!--数组注入-->
<property name="books">
<array>
<value>红楼梦</value>
<value>西游记</value>
<value>水浒传</value>
<value>三国演义</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--List注入-->
<property name="hobbies">
<list>
<value>听歌</value>
<value>敲代码</value>
<value>看电影</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--Map-->
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="身份证" value="1555555555"/>
<entry key="银行卡" value="5555555555"/>
</map>
</property>
<!--Set-->
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>lol</value>
<value>wow</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--null-->
<property name="wife">
<null/>
</property>
<!--Properties-->
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="driver">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/news</prop>
<prop key="root">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
4、测试类
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
}