/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>>res;
vector<int>buffer;
static bool cmp( const vector<int> &a, const vector<int> &b)
{
return a.size() > b.size();
}
vector<vector<int> > FindPath1(TreeNode* root,int expectNumber)
{
if(root == NULL)return res;
buffer.push_back(root->val);
if(expectNumber-root->val == 0 && root->left ==NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
res.push_back(buffer);
}
if(root->left != NULL)FindPath(root->left,expectNumber-root->val);
if(root->right !=NULL)FindPath(root->right,expectNumber-root->val);
if(buffer.size()!=0)
buffer.pop_back();//每次压进来多少,就弹出去多少。
//if(res.size() != 0)
return res;
}
vector<vector<int> > FindPath(TreeNode* root,int expectNumber)
{
FindPath1(root,expectNumber);//这个子函数是为了进行筛选出来这些路径
sort(res.begin(), res.end(), cmp);//这个函数是为了对给出的路径进行排序
return res;
}
};
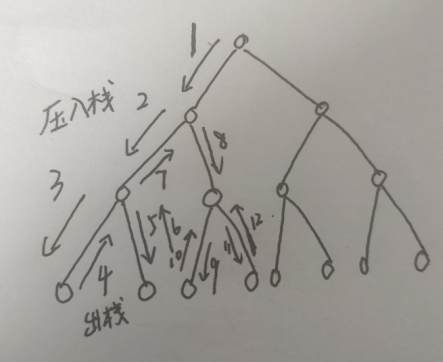
每一个递归函数的结束,就会把这个节点弹出去,然后将这个节点的父节点的右孩子节点进行压入。
直到再一次到达端点,然后再进行重新的一次弹出。大家直接看图把,上面都标着序号呢。