题目传送门
一、题意分析
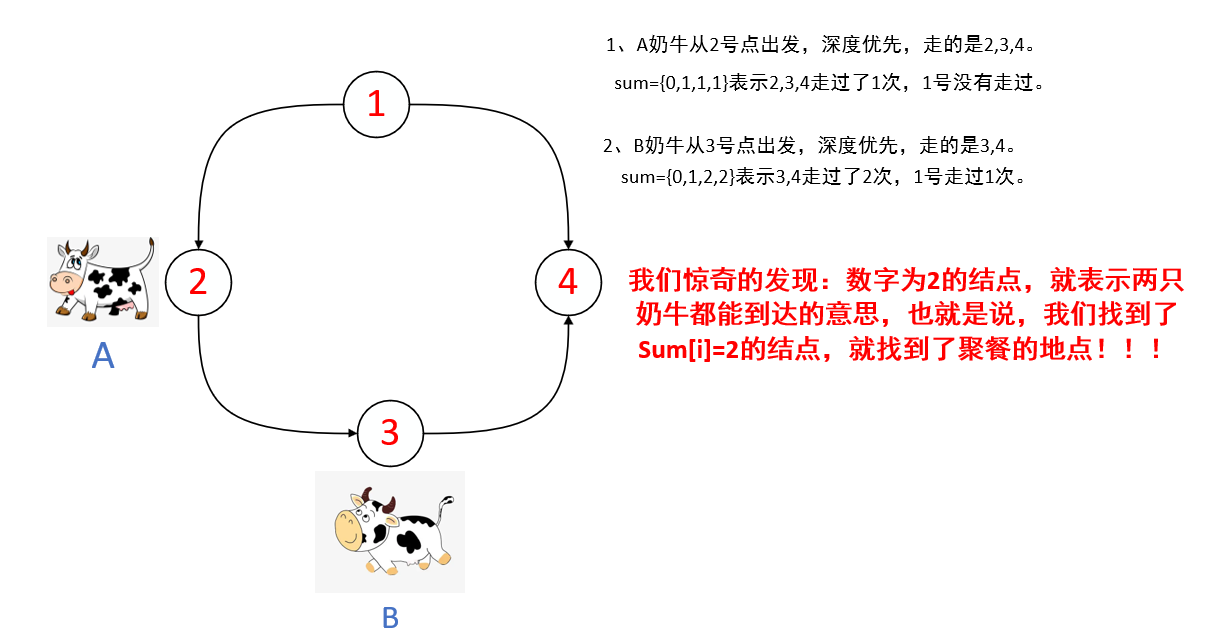
二、bfs解法
1、链式前向星
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010; //10000条边
queue<int> q;
bool st[N]; //走过了没
int n; //n个牧场
int m; //m条有向路连接
int k; //k只奶牛
int a[N]; //记录第i个奶牛在a[i]这个牧场里
int sum[N]; //记录每个结点被bfs遍历到的次数
int ans;
//链式前向星建图
int idx, head[N];
struct Edge {
int to, next;
} edge[N];
int add(int from, int to) {
edge[++idx].to = to;
edge[idx].next = head[from];
head[from] = idx;
}
int main() {
//k:奶牛数,n:牧场数,m:路线数
cin >> k >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) cin >> a[i];//读入奶牛在哪个牧场里
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
add(x, y);//读入m条路径,建图,x->y有一条边
}
//从每个奶牛所在的牧场出发
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
//清空状态标识
memset(st, 0, sizeof(st));
//将第i个奶牛所在的第a[i]个牧场放入队列
q.push(a[i]);
//标识这个牧场已使用过,防止走回头路
st[a[i]] = true;
//广度优先搜索
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
//链式前向星找每一条邻接边
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].next) {
//目标结点
int to = edge[i].to;
if (!st[to]) {//如果目标结点未使用过
st[to] = true;//标识为已使用
q.push(to); //入队列
}
}
}
//记录每个结点被遍历到的次数
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) sum[j] += st[j];
}
//如果n个结点中,存在遍历次数等于k的结点,就是表示k个奶牛都可以到达这个位置
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (sum[i] == k) ans++;
//输出结果
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
2、邻接表
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010; //10000条边
queue<int> q;
bool st[N]; //走过了没
int n; //n个牧场
int m; //m条有向路连接
int k; //k只奶牛
int a[N]; //记录第i个奶牛在a[i]这个牧场里
int sum[N]; //记录每个结点被BFS遍历到的次数
vector<int> p[N]; //邻接表
int ans;
int main() {
//k:奶牛数,n:牧场数,m:路线数
cin >> k >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) cin >> a[i];//读入奶牛在哪个牧场里
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
p[x].push_back(y);//读入m条路径,建图,x->y有一条边
}
//从每个奶牛所在的牧场出发
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
//清空状态标识
memset(st, 0, sizeof(st));
//将第i个奶牛所在的第a[i]个牧场放入队列
q.push(a[i]);
//标识这个牧场已使用过,防止走回头路
st[a[i]] = true;
//广度优先搜索
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
//邻接表的遍历
for (int to:p[x]) {
if (!st[to]) {//如果目标结点未使用过
st[to] = true;//标识为已使用
q.push(to); //入队列
}
}
}
//记录每个结点被遍历到的次数
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) sum[j] += st[j];
}
//如果n个结点中,存在遍历次数等于k的结点,就是表示k个奶牛都可以到达这个位置
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (sum[i] == k) ans++;
//输出结果
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
3、邻接矩阵
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010; //10000条边
queue<int> q;
bool st[N]; //走过了没
int n; //n个牧场
int m; //m条有向路连接
int k; //k只奶牛
int a[N]; //记录第i个奶牛在a[i]这个牧场里
int sum[N]; //记录每个结点被bfs遍历到的次数
int g[N][N]; //邻接矩阵
int ans;
int main() {
//k:奶牛数,n:牧场数,m:路线数
cin >> k >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) cin >> a[i];//读入奶牛在哪个牧场里
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
g[x][y] = 1;//读入m条路径,建图,x->y有一条边
}
//从每个奶牛所在的牧场出发
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
//清空状态标识
memset(st, 0, sizeof(st));
//将第i个奶牛所在的第a[i]个牧场放入队列
q.push(a[i]);
//标识这个牧场已使用过,防止走回头路
st[a[i]] = true;
//广度优先搜索
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
//邻接矩阵的遍历
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (g[x][i] && !st[i]) {
st[i] = true;//标识为已使用
q.push(i); //入队列
}
}
//记录每个结点被遍历到的次数
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) sum[j] += st[j];
}
//如果n个结点中,存在遍历次数等于k的结点,就是表示k个奶牛都可以到达这个位置
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (sum[i] == k) ans++;
//输出结果
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
三、dfs解法
1、链式前向星
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010 * 1010; //牧场数上限,这里不算上乘积,就会有3个WA点,
// 原因很简单,装不下!!这是边的数量上限,要注意,邻接表没有这个问题,一定要区别好!
int n; //n个牧场
int m; //m条有向路连接
int k; //k只奶牛
int ans; //ans为最终答案
int a[N]; //a数组存储牛的位置
int sum[N]; //sum数组为每个点被遍历的次数
bool st[N]; //st数组用来判断点是否已经被访问过
//链式前向星建图
int idx, head[N];
struct Edge {
int to, next;
} edge[N];
int add_edge(int from, int to) {
edge[++idx].to = to;
edge[idx].next = head[from];
head[from] = idx;
}
//进行图的深度优先遍历
void dfs(int x) {
st[x] = true;
sum[x]++; //将这个点遍历的次数+1
//枚举节点编号
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].next) {
int v = edge[i].to;
if (!st[v]) dfs(v);//就遍历i号节点
}
}
int main() {
cin >> k >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) cin >> a[i];//输入每只奶牛的顺序
//使用链式前向星保存数据边
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
add_edge(x, y);
}
//对奶牛的位置进行枚举
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
dfs(a[i]); //从每一只奶牛的位置开始遍历
}
//统计答案,如果当前节点被访问的次数恰好为奶牛的只数
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (sum[i] == k) ans++;
//输出最后答案
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
2、邻接表
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010; //牧场数上限
int n; //n个牧场
int m; //m条有向路连接
int k; //k只奶牛
int ans; //ans为最终答案
vector<int> p[N]; //p数组为邻接表
int a[N]; //a数组存储牛的位置
int sum[N]; //sum数组为每个点被遍历的次数
bool st[N]; //st数组用来判断点是否已经被访问过
//进行图的深度优先遍历
void dfs(int x) {
st[x] = true; //将现在访问的点标记为已遍历,防止走回头路
sum[x]++; //将这个点遍历的次数+1
//枚举节点编号
for (int v:p[x])
if (!st[v]) dfs(v);//就遍历i号节点
}
int main() {
cin >> k >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) cin >> a[i];//输入每只奶牛的顺序
//使用邻接表保存数据边
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
//连接两边(注意不是双向边,是单向边)
p[u].push_back(v);
}
//对奶牛的位置进行枚举
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
dfs(a[i]); //从每一只奶牛的位置开始遍历
memset(st, false, sizeof(st)); //记得每次遍历完都需要清空标记数组
}
//统计答案,如果当前节点被访问的次数恰好为奶牛的只数
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (sum[i] == k) ++ans;
//输出最后答案
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
3、邻接矩阵
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010; //牧场数上限
int n; //n个牧场
int m; //m条有向路连接
int k; //k只奶牛
int ans; //ans为最终答案
int g[N][N]; //g数组为邻接矩阵
int a[N]; //a数组存储牛的位置
int sum[N]; //sum数组为每个点被遍历的次数
bool st[N]; //st数组用来判断点是否已经被访问过
//进行图的深度优先遍历
void dfs(int x) {
st[x] = true; //将现在访问的点标记为已遍历,防止走回头路
sum[x]++; //将这个点遍历的次数+1
//枚举节点编号
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
//如果当前节点没有被访问过并且与当前节点有边连接
if (!st[i] && g[x][i]) dfs(i);//就遍历i号节点
}
int main() {
cin >> k >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) cin >> a[i];//输入每只奶牛的顺序
//使用邻接矩阵保存数据边
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
//连接两边(注意不是双向边,是单向边)
g[u][v] = 1;
}
//对奶牛的位置进行枚举
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
dfs(a[i]); //从每一只奶牛的位置开始遍历
memset(st, false, sizeof(st)); //记得每次遍历完都需要清空标记数组
}
//统计答案,如果当前节点被访问的次数恰好为奶牛的只数
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (sum[i] == k) ++ans;
//输出最后答案
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;//完美结束
}
