python:yaml模块
一、yaml文件介绍
YAML是一种简洁的非标记语言。其以数据为中心,使用空白,缩进,分行组织数据,从而使得表示更加简洁。
1. yaml文件规则
基本规则:
大小写敏感
使用缩进表示层级关系
缩进时不允许使用Tab键,只允许使用空格。
缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
使用#表示注释
字符串可以不用引号标注
2. yaml文件数据结构
对象:键值对的集合(简称 "映射或字典")
键值对用冒号 “:” 结构表示,冒号与值之间需用空格分隔
数组:一组按序排列的值(简称 "序列或列表")
数组前加有 “-” 符号,符号与值之间需用空格分隔
纯量(scalars):单个的、不可再分的值(如:字符串、bool值、整数、浮点数、时间、日期、null等)
None值可用null可 ~ 表示
二、安装yaml
pip命令: pip install PyYaml
引入:import yaml
用python读取yaml文件如下:
代码:
import yaml
from Common.dir_config import *
# 打开yaml文件
fs = open(os.path.join(caps_dir, "data.yaml"),encoding="UTF-8")
datas = yaml.load(fs)
print(datas)
备注:yaml版本5.1之后弃用,YAMLLoadWarning: calling yaml.load() without Loader=... is deprecated
代码改后:
import yaml
from Common.dir_config import *
# 打开yaml文件
fs = open(os.path.join(caps_dir, "data.yaml"),encoding="UTF-8")
datas = yaml.load(fs,Loader=yaml.FullLoader) #添加后就不警告了
print(datas)
三、python中读取yaml配置文件
1. 前提条件
python中读取yaml文件前需要安装pyyaml和导入yaml模块:
使用yaml需要安装的模块为pyyaml(pip3 install pyyaml);
导入的模块为yaml(import yaml)
2. 读取yaml文件数据
python通过open方式读取文件数据,再通过load函数将数据转化为列表或字典;
import yaml
import os
def get_yaml_data(yaml_file):
# 打开yaml文件
print("***获取yaml文件数据***")
file = open(yaml_file, 'r', encoding="utf-8")
file_data = file.read()
file.close()
print(file_data)
print("类型:", type(file_data))
# 将字符串转化为字典或列表
print("***转化yaml数据为字典或列表***")
data = yaml.load(file_data)
print(data)
print("类型:", type(data))
return data
current_path = os.path.abspath(".")
yaml_path = os.path.join(current_path, "config.yaml")
get_yaml_data(yaml_path)
"""
***获取yaml文件数据***
# yaml键值对:即python中字典
usr: my
psw: 123455
类型:<class 'str'>
***转化yaml数据为字典或列表***
{'usr': 'my', 'psw': 123455}
类型:<class 'dict'>
"""
3. yaml文件数据为键值对
(1)yaml文件中内容为键值对:
# yaml键值对:即python中字典
usr: my
psw: 123455
s: " abc
"
python解析yaml文件后获取的数据:
{'usr': 'my', 'psw': 123455, 's': ' abc
'}
(2)yaml文件中内容为“键值对'嵌套"键值对"
# yaml键值对嵌套:即python中字典嵌套字典
usr1:
name: a
psw: 123
usr2:
name: b
psw: 456
python解析yaml文件后获取的数据:
{'usr1': {'name': 'a', 'psw': 123}, 'usr2': {'name': 'b', 'psw': 456}}
(3)yaml文件中“键值对”中嵌套“数组”
# yaml键值对中嵌套数组
usr3:
- a
- b
- c
usr4:
- b
python解析yaml文件后获取的数据:
{'usr3': ['a', 'b', 'c'], 'usr4': ['b']}
4. yaml文件数据为数组
(1)yaml文件中内容为数组
# yaml数组
- a
- b
- 5
python解析yaml文件后获取的数据:
['a', 'b', 5]
(2)yaml文件“数组”中嵌套“键值对”
# yaml"数组"中嵌套"键值对"
- usr1: aaa
- psw1: 111
usr2: bbb
psw2: 222
python解析yaml文件后获取的数据:
[{'usr1': 'aaa'}, {'psw1': 111, 'usr2': 'bbb', 'psw2': 222}]
5. yaml文件中基本数据类型:
# 纯量
s_val: name # 字符串:{'s_val': 'name'}
spec_s_val: "name
" # 特殊字符串:{'spec_s_val': 'name
'
num_val: 31.14 # 数字:{'num_val': 31.14}
bol_val: true # 布尔值:{'bol_val': True}
nul_val: null # null值:{'nul_val': None}
nul_val1: ~ # null值:{'nul_val1': None}
time_val: 2018-03-01t11:33:22.55-06:00 # 时间值:{'time_val': datetime.datetime(2018, 3, 1, 17, 33, 22, 550000)}
date_val: 2019-01-10 # 日期值:{'date_val': datetime.date(2019, 1, 10)}
6. yaml文件中引用
yaml文件中内容
animal3: &animal3 fish
test: *animal3
python读取的数据
{'animal3': 'fish', 'test': 'fish'}
三、python中读取多个yaml文档
1. 多个文档在一个yaml文件,使用 --- 分隔方式来分段
如:yaml文件中数据
# 分段yaml文件中多个文档
---
animal1: dog
age: 2
---
animal2: cat
age: 3
2. python脚本读取一个yaml文件中多个文档方法
python获取yaml数据时需使用load_all函数来解析全部的文档,再从中读取对象中的数据
# yaml文件中含有多个文档时,分别获取文档中数据
def get_yaml_load_all(yaml_file):
# 打开yaml文件
file = open(yaml_file, 'r', encoding="utf-8")
file_data = file.read()
file.close()
all_data = yaml.load_all(file_data)
for data in all_data:
print(data)
current_path = os.path.abspath(".")
yaml_path = os.path.join(current_path, "config.yaml")
get_yaml_load_all(yaml_path)
"""结果
{'animal1': 'dog', 'age': 2}
{'animal2': 'cat', 'age': 3}
"""
四、python对象生成yaml文档
1. 直接导入yaml(即import yaml)生成的yaml文档
通过yaml.dump()方法不会将列表或字典数据进行转化yaml标准模式,只会将数据生成到yaml文档中
# 将python对象生成yaml文档
import yaml
def generate_yaml_doc(yaml_file):
py_object = {'school': 'zhang',
'students': ['a', 'b']}
file = open(yaml_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8')
yaml.dump(py_object, file)
file.close()
current_path = os.path.abspath(".")
yaml_path = os.path.join(current_path, "generate.yaml")
generate_yaml_doc(yaml_path)
"""结果
school: zhang
students: [a, b]
"""
2. 使用ruamel模块中的yaml方法生成标准的yaml文档
(1)使用ruamel模块中yaml前提条件
使用yaml需要安装的模块:ruamel.yaml(pip3 install ruamel.yaml);
导入的模块:from ruamel import yaml
(2)ruamel模块生成yaml文档
def generate_yaml_doc_ruamel(yaml_file):
from ruamel import yaml
py_object = {'school': 'zhang',
'students': ['a', 'b']}
file = open(yaml_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8')
yaml.dump(py_object, file, Dumper=yaml.RoundTripDumper)
file.close()
current_path = os.path.abspath(".")
yaml_path = os.path.join(current_path, "generate.yaml")
generate_yaml_doc_ruamel(yaml_path)
"""结果
school: zhang
students:
- a
- b
"""
(3)ruamel模块读取yaml文档
# 通过from ruamel import yaml读取yaml文件
def get_yaml_data_ruamel(yaml_file):
from ruamel import yaml
file = open(yaml_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8')
data = yaml.load(file.read(), Loader=yaml.Loader)
file.close()
print(data)
current_path = os.path.abspath(".")
yaml_path = os.path.join(current_path, "dict_config.yaml")
get_yaml_data_ruamel(yaml_path)
**************************************************
上代码
1 import yaml 2 import os 3 4 5 6 #单个文档 7 def get_yaml_data(yaml_file): 8 #打开yaml文件 9 print("***获取yam文件数据***") 10 file=open(yaml_file,'r',encoding='utf-8') 11 file_data=file.read() 12 file.close() 13 14 print(file_data) 15 print("类型",type(file_data)) 16 17 #将字符串转化为字典或列表 18 print("***转化yaml数据为字典或列表***") 19 data=yaml.safe_load(file_data) #safe_load,safe_load,unsafe_load 20 print(data) 21 print("类型",type(data)) 22 return data 23 24 current_path=os.path.abspath(".") 25 yaml_path=os.path.join(current_path,"config.yaml") 26 print('--------------------',yaml_path) 27 get_yaml_data(yaml_path) 28 29 30 #yaml文件中含多个文档时,分别获取文档中数据 31 def get_yaml_load_all(yaml_file): 32 #打开文件 33 file=open(yaml_file,'r',encoding='utf-8') 34 file_data=file.read() 35 file.close() 36 37 all_data=yaml.load_all(file_data,Loader=yaml.FullLoader) 38 for data in all_data: 39 print('data-----',data) 40 41 current_path=os.path.abspath(".") 42 yaml_path=os.path.join(current_path,"configall.yaml") 43 get_yaml_load_all(yaml_path) 44 45 46 #生成yaml文档 47 def generate_yaml_doc(yaml_file): 48 py_ob={"school":"zhang", 49 "students":['a','b']} 50 file=open(yaml_file,'w',encoding='utf-8') 51 yaml.dump(py_ob,file) 52 file.close() 53 54 current_path=os.path.abspath(".") 55 yaml_path=os.path.join(current_path,"generate.yaml") 56 generate_yaml_doc(yaml_path)
执行结果
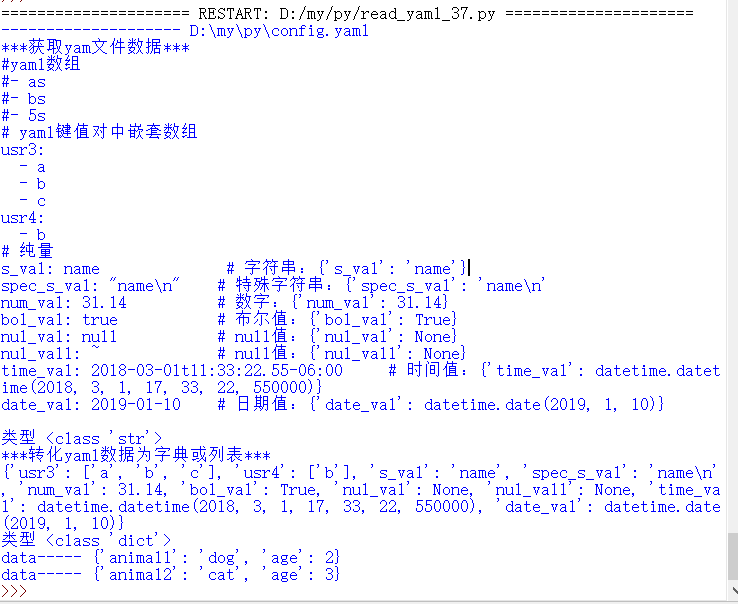
原文:https://www.jianshu.com/p/eaa1bf01b3a6