Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.
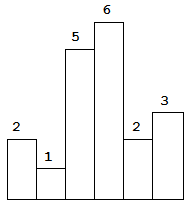
Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].
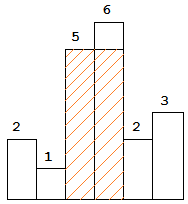
The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
For example,
Given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3],
return 10.
做不出来。完全的O(n^2)过不了。看了水中的鱼的解法,自己再把这两种算法重写了一次。
Method I
brute force+剪枝。O(n^2)。只有当前值比下一个值大的时候,才有必要往回计算它的面积。比如图中的height[2]=5,height[3]=6。假设height[2]往回找到一个区间[i...2]面积最大,那么一定会有一个[i...3]的面积比它还大。所以只需要从height[3]往回找就行了。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height) { 4 int n = height.size(); 5 if (n == 0) return 0; 6 7 int max = 0, min, area; 8 9 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 10 if (i < n - 1 && height[i] <= height[i + 1]) continue; 11 12 min = height[i]; 13 for (int j = i; j >= 0; --j) { 14 if (height[j] < min) min = height[j]; 15 area = min * (i - j + 1); 16 if (area > max) max = area; 17 } 18 } 19 20 return max; 21 } 22 };
Method II
用一个栈来实现。其实也是灵感来自于Method I。 对于一个呈上升趋势的多个点,只有最高的点需要往回扩展。假设height[i]>height[i+1],那么我们从i往回扩展,扩展到什么位置呢?
假设我们扩展到height[j]<=height[i+1],找到面积最大,那么我们一定能找到[j...i+1]比[j...i]的面积更大(高都为height[j],宽度[j...+1]更大)。
为了记录这个宽度,我们在stack中push的是index。这个算法有点类似于Longest Valid Parentheses.
这个j怎么求呢? 因为栈中元素是递增的,并且栈中元素的下标其实就对应于可以扩展的区间。height[i]>height[i+1]。对于栈中的元素,如果stack不为空,那么从stack中pop出height[i]后,[stack.top()+1...i-1]这一段就是可以扩展的区间。如果为空,那么说明[0...i-1]都是可以扩展的。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height) { 4 int n = height.size(); 5 if (n == 0) return 0; 6 7 int max = 0, last, area; 8 9 stack<int> indexes; 10 height.push_back(0); 11 12 for (int i = 0; i < height.size(); ) { 13 if (indexes.empty() || (height[i]>=height[indexes.top()])) { 14 indexes.push(i); 15 i++; 16 } else { 17 while (!indexes.empty() && height[indexes.top()] > height[i]) { 18 last = height[indexes.top()]; 19 indexes.pop(); 20 area = last * (indexes.empty() ? i : i - indexes.top() - 1); 21 if (area > max) max = area; 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 26 return max; 27 } 28 };
Line 10 push一个0是为了处理最后栈不为空的情况。
注意Line 21之后并没有i++,这是为了继续处理height[i]。
内循环是出栈,因为栈最大只可能为n,同时也不能重复入栈,所以整个时间复杂度为O(2*n),空间复杂度为栈大小O(n)。
水中的鱼提供了一个更简洁的实现代码。主要是将出栈的代码分摊到循环中了。于是我也重新实现一遍。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height) { 4 int n = height.size(); 5 if (n == 0) return 0; 6 7 int max = 0, last, area; 8 9 stack<int> indexes; 10 height.push_back(0); 11 12 for (int i = 0; i < height.size(); ) { 13 if (indexes.empty() || (height[i]>=height[indexes.top()])) { 14 indexes.push(i); 15 i++; 16 } else { 17 last = height[indexes.top()]; 18 indexes.pop(); 19 area = last * (indexes.empty() ? i : i - indexes.top() - 1); 20 if (area > max) max = area; 21 } 22 } 23 24 return max; 25 } 26 };
事后诸葛:
如果可以找到一个区间,这个区间符合一定的出栈入栈规律,就可以像此题或者Longest Valid Parentheses用一个栈来定位区间。