一、什么是循环链表?
将单链表中终端结点的指针端自空指针改为指向头结点,就使整个单链表形成一个环,这种头尾相接的单链表称为单循环链表,简称循环链表(circular linked
list)。
相比单链表,循环链表解决了一个很麻烦的问题。 即可以从任意一个结点出发,而不一定是要从头结点出发,就可访问到链表的全部结点。
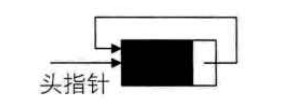
为了使空链表与非空链表处理一致,我们通常设一个头结点,当然, 这并不是说,循环链表一定要头结点,这需要注意。 循环链表带有头结点的空链表如下图所示:
对于非空的循环链表就如下图所示:
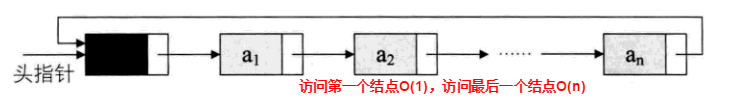
其实循环链表和单链表的主要差异就在于循环的判断条件上,原本是判断 p->next 是否为空,现在则是 p-> next 不等于头结点,则循环未结束。
二、循环链表的基本操作
2.1 初始化链表操作
// 初始化链表操作
void initList(LinkList **pList) // 必须使用双重指针,一重指针申请会出错
{
*pList = (LinkList *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!pList)
{
printf("malloc error!
");
return;
}
(*pList)->data = 0;
// 因为是循环链表,所以尾指针指向头节点
(*pList)->next = *pList;
}
循环链表的所有操作程序与单链表大致相同,只是修改了链表的结束判断条件,因为尾结点的 next 不再指向 NULL,而是指向头结点。
2.2 插入元素操作
// 插入元素操作
Status insertList(LinkList *pList, int i, const ElemType e)
{
Node *front; // 指向位置i所在的前一个结点
int j; // 计数器
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 只能在位置1以及后面插入,所以i至少为1
if (i < 1)
{
printf("i is invalid!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到i位置所在的前一个结点
front = pList;
if (i != 1) // 对i=1的情况特殊处理
{
front = pList->next; // 指向第2个结点的前一个结点,与j对应
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) // j为计数器,赋值为2,对应front指向的下一个结点
{
front = front->next;
if (front == pList)
{
printf("dont find front!
");
return false;
}
}
}
// 创建一个空节点,存放要插入的新元素
Node *temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!temp)
{
printf("malloc error!
");
return FALSE;
}
temp->data = e;
// 插入结点
temp->next = front->next;
front->next = temp;
return TRUE;
}
与单链表相比,找到 i 位置的前一个结点的结束判断更难处理,这里可以进一步改进。
2.3 删除元素操作
// 删除元素操作
Status deleteList(LinkList *pList, int i, ElemType *e)
{
Node *front; // 指向位置i所在的前一个结点
int j; // 计数器
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 只能删除位置1以及以后的结点
if (i < 1)
{
printf("i is invalid!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到i位置所在的前一个结点
front = pList;
if (i != 1) // 对i=1的情况特殊处理
{
front = pList->next; // 指向第2个结点的前一个结点,与j对应
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) // j为计数器,赋值为2,对应front指向的下一个结点
{
front = front->next;
if (front->next == pList)
{
printf("dont find front!
");
return false;
}
}
}
// 提前保存要删除的结点
Node *temp = front->next;
*e = temp->data; // 将要删除结点的数据赋给e
// 删除结点
front->next = front->next->next;
// 销毁结点
free(temp);
temp = NULL;
return TRUE;
}
三、完整程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef int Status; // Status是函数结果状态,成功返回TRUE,失败返回FALSE
typedef int ElemType;
/* 线性表的循环链表存储结构 */
typedef struct node
{
ElemType data;
struct node *next;
}Node, LinkList;
void initList(LinkList **pList); // 初始化链表操作
Status insertList(LinkList *pList, int i, const ElemType e); // 插入元素操作
Status deleteList(LinkList *pList, int i, ElemType *e); // 删除元素操作
Status getElem(LinkList *pList, int i, ElemType *e); // 获取元素操作
Status insertListHead(LinkList *pList, const ElemType e); // 头部后插入元素操作
Status insertListTail(LinkList *pList, const ElemType e); // 尾部后插入元素操作
Status clearList(LinkList *pList); // 清空链表操作
void traverseList(LinkList *pList); // 遍历链表操作
int getLength(LinkList *pList); // 获取链表长度操作
// 初始化链表操作
void initList(LinkList **pList) // 必须使用双重指针,一重指针申请会出错
{
*pList = (LinkList *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!pList)
{
printf("malloc error!
");
return;
}
(*pList)->data = 0;
// 因为是循环链表,所以尾指针指向头节点
(*pList)->next = *pList;
}
// 插入元素操作
Status insertList(LinkList *pList, int i, const ElemType e)
{
Node *front; // 指向位置i所在的前一个结点
int j; // 计数器
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 只能在位置1以及后面插入,所以i至少为1
if (i < 1)
{
printf("i is invalid!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到i位置所在的前一个结点
front = pList;
if (i != 1) // 对i=1的情况特殊处理
{
front = pList->next; // 指向第2个结点的前一个结点,与j对应
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) // j为计数器,赋值为2,对应front指向的下一个结点
{
front = front->next;
if (front == pList)
{
printf("dont find front!
");
return false;
}
}
}
// 创建一个空节点,存放要插入的新元素
Node *temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!temp)
{
printf("malloc error!
");
return FALSE;
}
temp->data = e;
// 插入结点
temp->next = front->next;
front->next = temp;
return TRUE;
}
// 删除元素操作
Status deleteList(LinkList *pList, int i, ElemType *e)
{
Node *front; // 指向位置i所在的前一个结点
int j; // 计数器
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 只能删除位置1以及以后的结点
if (i < 1)
{
printf("i is invalid!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到i位置所在的前一个结点
front = pList;
if (i != 1) // 对i=1的情况特殊处理
{
front = pList->next; // 指向第2个结点的前一个结点,与j对应
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) // j为计数器,赋值为2,对应front指向的下一个结点
{
front = front->next;
if (front->next == pList)
{
printf("dont find front!
");
return false;
}
}
}
// 提前保存要删除的结点
Node *temp = front->next;
*e = temp->data; // 将要删除结点的数据赋给e
// 删除结点
front->next = front->next->next;
// 销毁结点
free(temp);
temp = NULL;
return TRUE;
}
// 获取元素操作
Status getElem(LinkList *pList, int i, ElemType *e)
{
Node *cur;
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 只能获取位置1以及以后的元素
if (i < 1)
{
printf("i is invalid!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到i位置所在的结点
cur = pList->next; // 这里是让cur指向链表的第1个结点
int j = 1; // j为计数器,赋值为1,对应cur指向结点
while (cur != pList && j < i)
{
cur = cur->next;
j++;
}
// 未找到i位置所在的前一个结点
if (cur == pList)
{
printf("dont find front!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 取第i个结点的数据
*e = cur->data;
return TRUE;
}
// 头部后插入元素操作
Status insertListHead(LinkList *pList, const ElemType e)
{
Node *head;
Node *temp;
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 让head指向链表的头结点
head = pList;
// 创建存放插入元素的结点
temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!temp)
{
printf("malloc error!
");
return FALSE;
}
temp->data = e;
// 头结点后插入结点
temp->next = head->next;
head->next = temp;
return TRUE;
}
// 尾部后插入元素操作
Status insertListTail(LinkList *pList, const ElemType e)
{
Node *cur;
Node *temp;
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!
");
return FALSE;
}
// 找到链表尾节点
cur = pList;
while (cur->next != pList)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
// 创建存放插入元素的结点
temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!temp)
{
printf("malloc error!
");
return -1;
}
temp->data = e;
// 尾结点后插入结点
temp->next = cur->next;
cur->next = temp;
return TRUE;
}
// 清空链表操作
Status clearList(LinkList *pList)
{
Node *cur; // 当前结点
Node *temp; // 事先保存下一结点,防止释放当前结点后导致“掉链”
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!
");
return FALSE;
}
cur = pList->next; // 指向头结点后的第一个结点
while (cur != pList)
{
temp = cur->next; // 事先保存下一结点,防止释放当前结点后导致“掉链”
free(cur); // 释放当前结点
cur = NULL;
cur = temp; // 将下一结点赋给当前结点p
}
pList->next = NULL; // 头结点指针域指向空
return TRUE;
}
// 遍历链表操作
void traverseList(LinkList *pList)
{
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!pList)
{
printf("list not exist!
");
return;
}
Node *cur = pList->next;
while (cur != pList)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("
");
}
// 获取链表长度操作
int getLength(LinkList *pList)
{
Node *cur = pList;
int length = 0;
while (cur->next != pList)
{
cur = cur->next;
length++;
}
return length;
}
int main()
{
LinkList *pList;
// 初始化链表
initList(&pList);
printf("初始化链表!
");
// 尾部后插入结点
insertListTail(pList, 1);
printf("尾部后插入元素1
");
insertListTail(pList, 2);
printf("尾部后插入元素2
");
// 插入结点
insertList(pList, 1, 4);
printf("位置1插入元素4
");
// 删除结点
int val;
deleteList(pList, 3, &val);
printf("删除位置3的结点,删除结点的数据为: %d
", val);
printf("
");
// 遍历链表并显示元素操作
printf("遍历链表:");
traverseList(pList);
printf("
");
// 获得链表长度
printf("链表长度: %d
", getLength(pList));
// 销毁链表
clearList(pList);
printf("销毁链表
");
return 0;
}
参考:
《大话数据结构 - 第3章》 线性表