1、什么是链表?
数据存储在“节点”(Node)中
Class Node{
E e;
Node next;
}
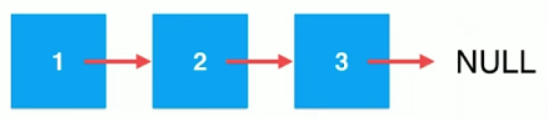
有点: 真正的动态,不需要处理固定容量的问题。
缺点: 和数组相比,丧失了随机访问的能力。
2、数组和链表的对比
数组最好用于索引有语义的情况,如scores[101], 学号为101的学生分数。
最大的优点: 支持快速查询
链表不适合用于索引有语义的情况
最大的优点: 动态
3、自定义链表
1) 添加链表头
把666节点添加到链表头
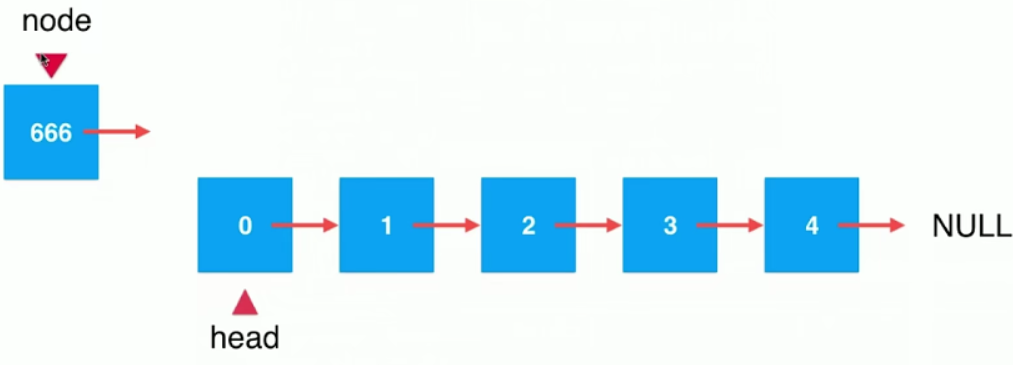
node.next = head; //将node的next指向head
head = node; // 将head执行node
上面两行执行后,效果如下图
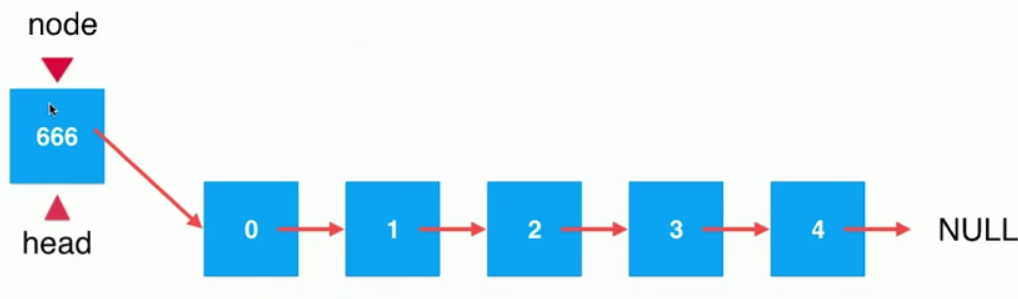
代码如下:
//在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e) {
Node node = new Node(e);
node.next = head;
head = node;
// 上面三行代码 等价于 head = new Node(e, head);
size++;
}
2) 在索引为2的地方添加元素666.
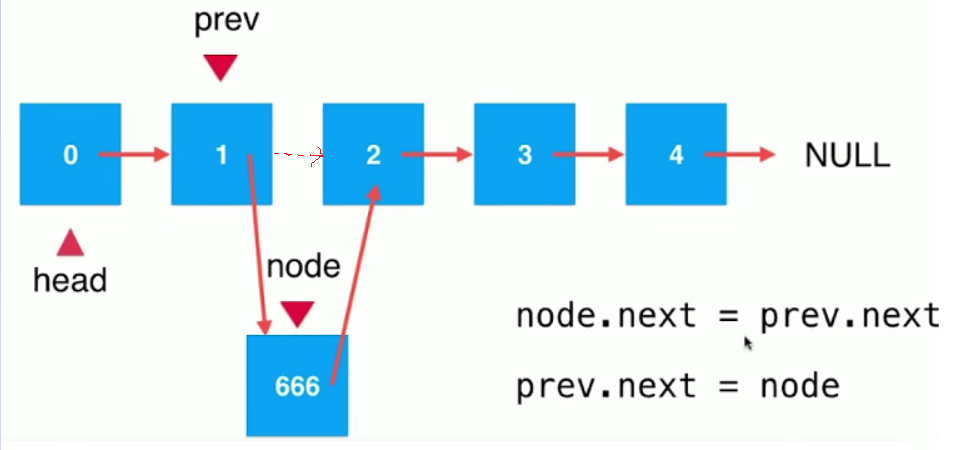
关键: 找到要添加的节点的前一个节点
//在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
//在链表中不是一个常用的操作
public void add(int index, E e) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add fial,illegal index.");
}
//在链表头中添加元素
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(e);
}else {
Node pre = head;
//寻找index前一个节点
for(int i = 0; i < index -1; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
Node node = new Node(e);
node.next = pre.next;
pre.next = node;
//上面三行 等价于 pre.next = new Node(e. prev.next);
size ++;
}
}
3) 向链表的末尾添加元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
完整的自定义链表代码
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node {
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next) {
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e) {
this(e, null);
}
public Node() {
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node head;
int size;
public LinkedList() {
head = null;
size = 0;
}
//获得链表元素个数
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
//返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
//在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e) {
Node node = new Node(e);
node.next = head;
head = node;
// 上面三行代码 等价于 head = new Node(e, head);
size++;
}
//在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
//在链表中不是一个常用的操作
public void add(int index, E e) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add fial,illegal index.");
}
//在链表头中添加元素
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(e);
}else {
Node pre = head;
//寻找index前一个节点
for(int i = 0; i < index -1; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
Node node = new Node(e);
node.next = pre.next;
pre.next = node;
//上面三行 等价于 pre.next = new Node(e. prev.next);
size ++;
}
}
//在链表末尾添加元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
}
4、使用链表的虚拟头节点
前面插入节点的时候,add方法每次都需要判断是否是头结点(index=0), 有没有办法移除这个判断,这里就引入了虚拟头节点?
所谓的虚拟头节点,就是引入一个空的节点dummyHead, 链表的第1个元素是dummyHead的下一个节点0
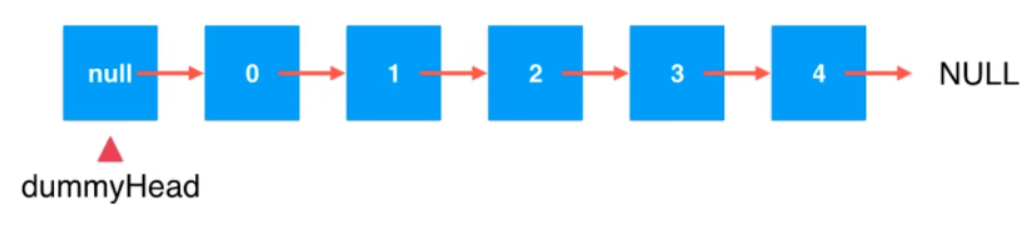
修改后的代码如下:
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node {
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next) {
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e) {
this(e, null);
}
public Node() {
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return e.toString();
}
}
//虚拟头结点
private Node dummyHead;
int size;
public LinkedList() {
dummyHead = new Node(null, null);
size = 0;
}
//获得链表元素个数
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
//返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
//在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e) {
add(0, e);
}
//在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
//在链表中不是一个常用的操作
public void add(int index, E e) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add fial,illegal index.");
}
Node pre = dummyHead;
//寻找index前一个节点
for(int i = 0; i < index ; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
Node node = new Node(e);
node.next = pre.next;
pre.next = node;
//上面三行 等价于 pre.next = new Node(e. prev.next);
size ++;
}
//在链表末尾添加元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
}
5、链表的变量,查询和修改操作
//获得链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素
//在链表中不是一个常用的操作
public E get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Gt fail,illegal index.");
}
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
//寻找index前一个节点
for(int i = 0; i < index ; i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.e;
}
//获得链表的第1个元素
public E getFirst(){
return get(0);
}
//获得链表的最后1个元素
public E getLast(){
return get(size -1);
}
//修改链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素e
//在链表中不是一个常用的操作
public void set(int index , E e){
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Gt fail,illegal index.");
}
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
//寻找index前一个节点
for(int i = 0; i < index ; i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.e = e;
}
//查找链表中是否存在e
public boolean contains(E e){
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
while (cur != null){
if(cur.e.equals(e)){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
/*Node cur = dummyHead.next;
while (cur != null){
res.append(cur + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}*/
res.append("链表头 ");
for(Node cur = dummyHead.next; cur != null; cur = cur.next){
res.append(cur + "->");
}
res.append("NULL");
return res.toString();
}
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
linkedList.addFirst(i);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
linkedList.add(2, 666);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
输出结果:
链表头 0->NULL 链表头 1->0->NULL 链表头 2->1->0->NULL 链表头 3->2->1->0->NULL 链表头 4->3->2->1->0->NULL 链表头 4->3->666->2->1->0->NULL
6、链表元素的删除
// 删除链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素e
public E remove(int index){
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Gt fail,illegal index.");
}
Node pre = dummyHead;
//寻找index前一个节点
for(int i = 0; i < index ; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
//要删除的节点
Node curDeleteNode = pre.next;
pre.next = curDeleteNode.next;
curDeleteNode.next = null;
size --;
return curDeleteNode.e;
}
// 删除链表的第index1个位置的元素e
public E removeFirst(){
return this.remove(0);
}
// 删除链表的最后1个位置的元素e
public E removeLast(){
return this.remove(size - 1);
}
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
linkedList.addFirst(i);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
linkedList.add(2, 666);
System.out.println(linkedList);
linkedList.remove(2);
System.out.println(linkedList);
System.out.print("移除第一个元素 ");
linkedList.removeFirst();
System.out.println(linkedList);
System.out.print("移除最后一个元素 ");
linkedList.removeLast();
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
输出结果:
链表头 0->NULL 链表头 1->0->NULL 链表头 2->1->0->NULL 链表头 3->2->1->0->NULL 链表头 4->3->2->1->0->NULL 链表头 4->3->666->2->1->0->NULL 链表头 4->3->2->1->0->NULL 移除第一个元素 链表头 3->2->1->0->NULL 移除最后一个元素 链表头 3->2->1->NULL
7、链表的时间复杂度分析
添加操作 总体来说是O(n)
addLast(e) O(n) 遍历所有节点
addFirst(e) O(1)
add(index,e) O(n/2) = O(n)
删除操作 总体来说是O(n)
removeLast(e) O(n) 遍历所有节点
removeFirst(e) O(1)
remove(index,e) O(n/2) = O(n)
修改操作 O(n)
set(index, e) O(n)
查找操作 O(n)
get(index) O(n)
contains(e) O(n)
总结: 链表的时间复杂度 增O(n), 删 O(n), 改O(n), 查O(n)
如果增删只对链表头操作O(1), 查找链表头元素O(1)