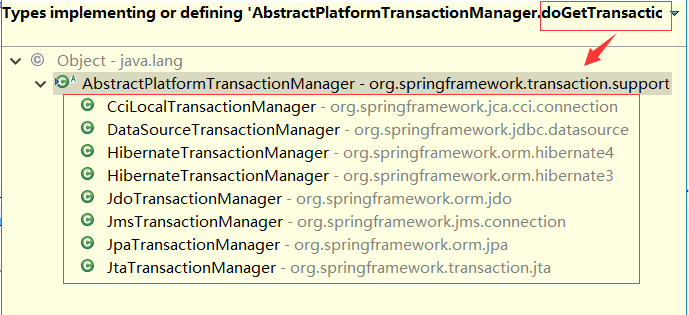
一、Spring事务
TranscationProxyFactoryBean
代理工厂bean,用于简化声明性的事务处理
1、类的位置:在spring-tx jar 中

配置的示例代码

2、TranscationProxyFactoryBean的代码如下

AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean类

代理对象proxy代理目标对象target
3、TransactionInterceptor实现了AOP联盟定义的一个接口MethodInterceptor
4、设置事务管理器
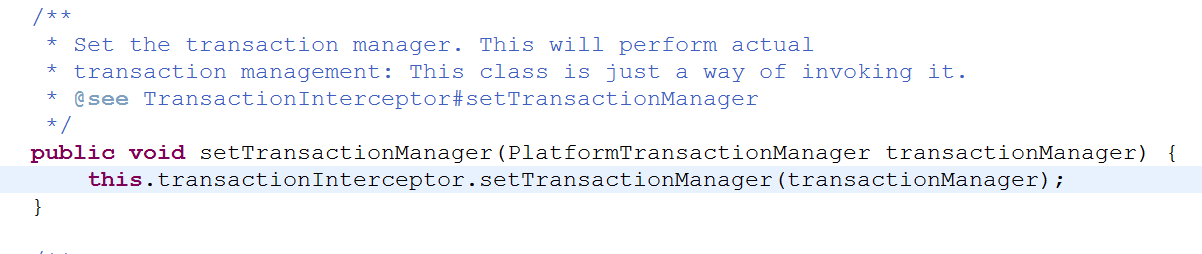
参数类型为PlatformTransactionManager接口,这个接口有很多实现类
5、设置事务属性

6、设置事务属性源
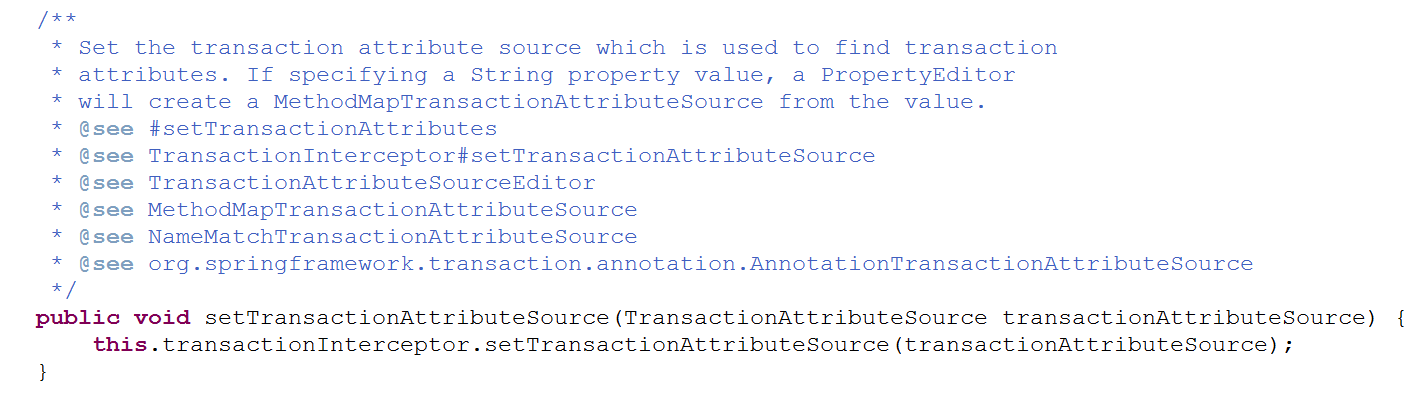
7、 AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean类获得对象

发现proxy赋值的地方不在这个方法里
真正赋值的地方在afterPropertiesSet这个方法里,这个方法被触发的时机是属性设置完成后。
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (this.target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'target' is required");
}
if (this.target instanceof String) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("'target' needs to be a bean reference, not a bean name as value");
}
if (this.proxyClassLoader == null) {
this.proxyClassLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
if (this.preInterceptors != null) {
for (Object interceptor : this.preInterceptors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(interceptor));
}
}
// Add the main interceptor (typically an Advisor).
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(createMainInterceptor()));
if (this.postInterceptors != null) {
for (Object interceptor : this.postInterceptors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(interceptor));
}
}
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
TargetSource targetSource = createTargetSource(this.target);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
if (this.proxyInterfaces != null) {
proxyFactory.setInterfaces(this.proxyInterfaces);
}
else if (!isProxyTargetClass()) {
// Rely on AOP infrastructure to tell us what interfaces to proxy.
proxyFactory.setInterfaces(
ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(targetSource.getTargetClass(), this.proxyClassLoader));
}
this.proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy(this.proxyClassLoader);
}
8、进入ProxyFactory
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();

以编程的方式实现AOP代理的工厂,。而不是通过bean工厂方式。提供简单的方式获取和配置Aop代理
9、AdvisorAdapterRegistry接口
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(createMainInterceptor()));
AdvisorAdapterRegistry接口的实现类GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry

进入GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry

里面使用的是DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry类,进入DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry类

registerAdvisorAdapter(new MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter()); //方法执行之前拦截适配器
registerAdvisorAdapter(new AfterReturningAdviceAdapter()); //返回之后拦截适配器
registerAdvisorAdapter(new ThrowsAdviceAdapter()); //抛出异常拦截适配器
这里使用了适配器模式
10、createMainInterceptor方法

11、TransactionInterceptor类的invoke方法
invoke方法的调用时机: 当代理对象去代理目标对象的时候,尝试去调用目标对象的时候,这时候就拦截到了,调用invoke方法
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be <code>null</code>.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
final TransactionAttribute txAttr =
getTransactionAttributeSource().getTransactionAttribute(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr,
new TransactionCallback<Object>() {
public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
return invocation.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
return new ThrowableHolder(ex);
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
}
});
// Check result: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (result instanceof ThrowableHolder) {
throw ((ThrowableHolder) result).getThrowable();
}
else {
return result;
}
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
}
}
二、Spring事务的底层实现
TransactionInterceptor类的invoke方法中
1、获得目标类
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
进入获得目标类

result = (isCglibProxy(candidate) ? candidate.getClass().getSuperclass() : candidate.getClass());
如果是cglib代理,则目标类代理类的父类(根据cglib的实现原理)
2、设置事务属性
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional. final TransactionAttribute txAttr = getTransactionAttributeSource().getTransactionAttribute(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
事务属性的设置

进入tas.setProperties(transactionAttributes);
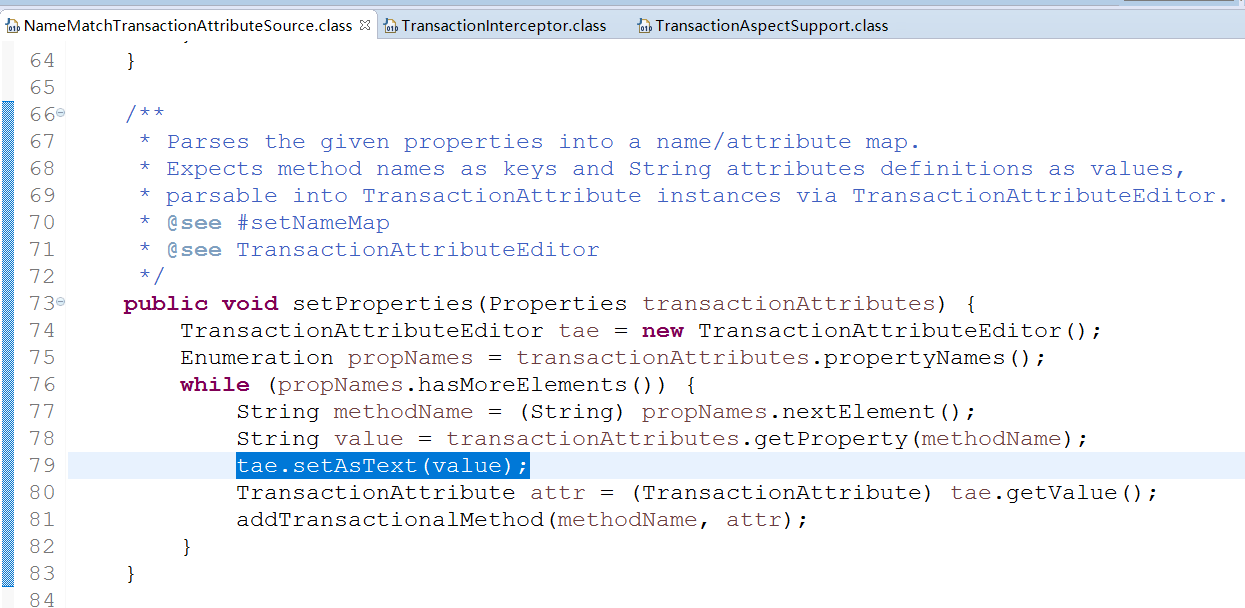
进入tae.setAsText(value)方法, TransactionAttributeEditor类的setAsText方法
@Override
public void setAsText(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(text)) {
// tokenize it with ","
String[] tokens = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(text);
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute attr = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++) {
// Trim leading and trailing whitespace.
String token = StringUtils.trimWhitespace(tokens[i].trim());
// Check whether token contains illegal whitespace within text.
if (StringUtils.containsWhitespace(token)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Transaction attribute token contains illegal whitespace: [" + token + "]");
}
// Check token type.
if (token.startsWith(RuleBasedTransactionAttribute.PREFIX_PROPAGATION)) {
attr.setPropagationBehaviorName(token);
}
else if (token.startsWith(RuleBasedTransactionAttribute.PREFIX_ISOLATION)) {
attr.setIsolationLevelName(token);
}
else if (token.startsWith(RuleBasedTransactionAttribute.PREFIX_TIMEOUT)) {
String value = token.substring(DefaultTransactionAttribute.PREFIX_TIMEOUT.length());
attr.setTimeout(Integer.parseInt(value));
}
else if (token.equals(RuleBasedTransactionAttribute.READ_ONLY_MARKER)) {
attr.setReadOnly(true);
}
else if (token.startsWith(RuleBasedTransactionAttribute.PREFIX_COMMIT_RULE)) {
attr.getRollbackRules().add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(token.substring(1)));
}
else if (token.startsWith(RuleBasedTransactionAttribute.PREFIX_ROLLBACK_RULE)) {
attr.getRollbackRules().add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(token.substring(1)));
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid transaction attribute token: [" + token + "]");
}
}
setValue(attr);
}
else {
setValue(null);
}
}
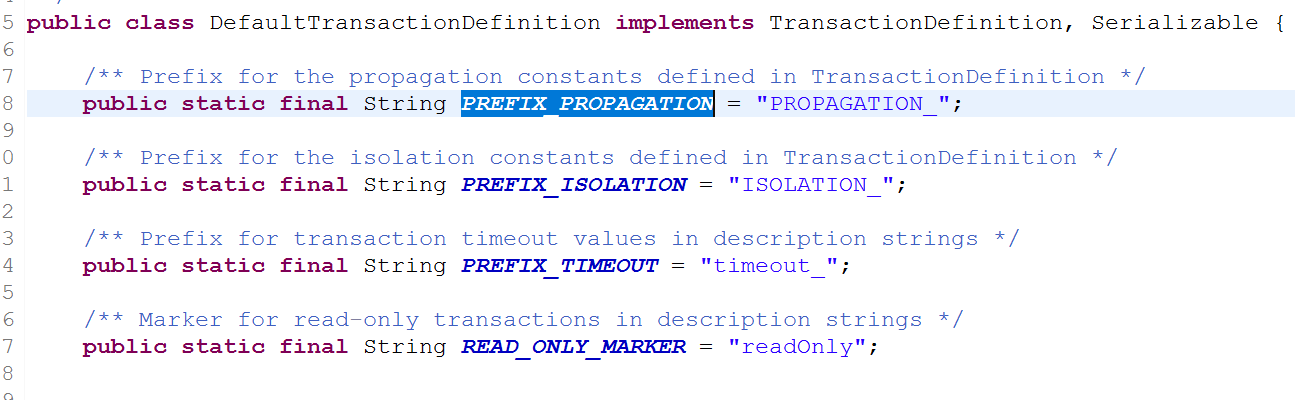
对应xml的配置的地方如下图:

属性字符的前缀与DefaultTransactionDefinition定义的字符相同
3、determineTransactionManager方法
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
进入determineTransactionManager方法
/**
* Determine the specific transaction manager to use for the given transaction.
*/
protected PlatformTransactionManager determineTransactionManager(TransactionAttribute txAttr) {
if (this.transactionManager != null || this.beanFactory == null || txAttr == null) {
return this.transactionManager;
}
String qualifier = txAttr.getQualifier();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(qualifier)) {
return BeanFactoryAnnotationUtils.qualifiedBeanOfType(this.beanFactory, PlatformTransactionManager.class, qualifier);
}
else if (this.transactionManagerBeanName != null) {
return this.beanFactory.getBean(this.transactionManagerBeanName, PlatformTransactionManager.class);
}
else if (this.beanFactory instanceof ListableBeanFactory) {
return BeanFactoryUtils.beanOfTypeIncludingAncestors(((ListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory), PlatformTransactionManager.class);
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot retrieve PlatformTransactionManager beans from non-listable BeanFactory: " + this.beanFactory);
}
}
对应Xml的配置

4、事务的方式
如果属性为空(txAtrr为空或者事务管理器(tm)不是CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager),采用正常的方式: 开启事务,提交事务。
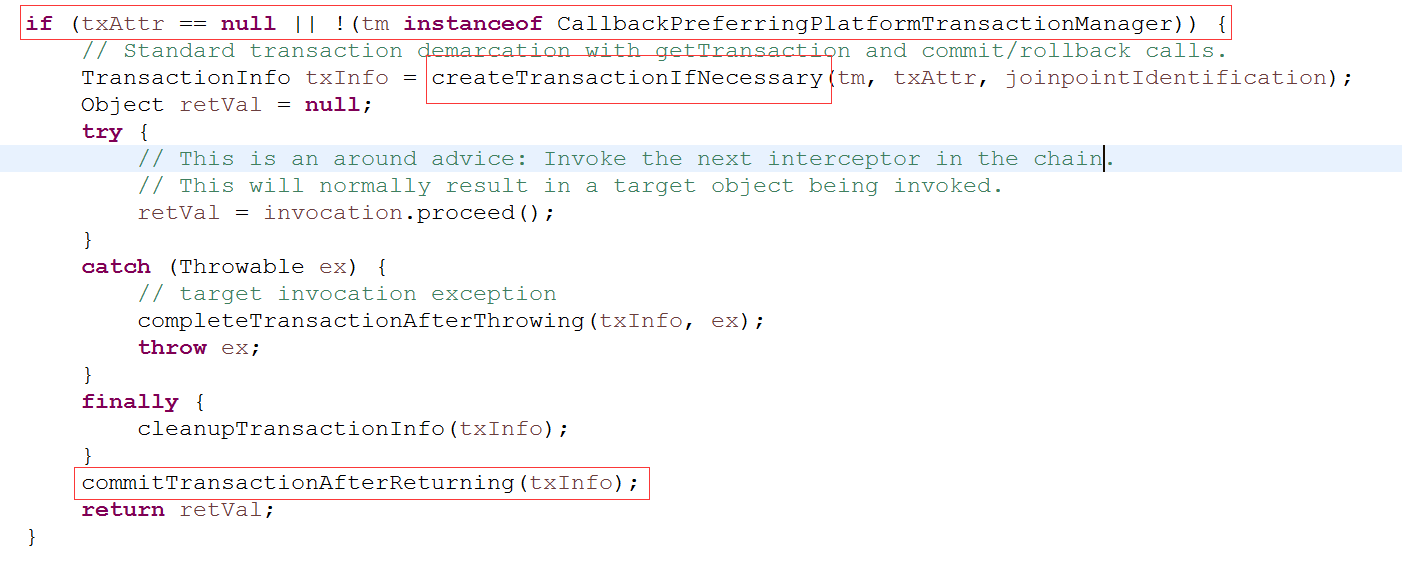
否则,采用回调的方式
try {
Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr,
new TransactionCallback<Object>() {
public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
return invocation.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
return new ThrowableHolder(ex);
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
}
});
// Check result: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (result instanceof ThrowableHolder) {
throw ((ThrowableHolder) result).getThrowable();
}
else {
return result;
}
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
三、Spring事务处理流程详解
1、createTransactionIfNecessary方法
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
进入createTransactionIfNecessary方法
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(
PlatformTransactionManager tm, TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
2、getTransaction获得事务状态
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
进入getTransaction方法
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException {
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
// Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks.
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (definition == null) {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
}
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout());
}
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition);
}
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
doBegin(transaction, definition);
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw err;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
3、doGetTransaction方法

有很多子类实现了doGetTransaction方法