如今CPU的核数从单核,到双核,再到4核、8核、甚至10核。但是我们知道Android使用的多核架构都是分大小核,或者现在最新的,除了大小核以外,还有一个超大核。
区分大小核,是因为它们之间的性能(算力),功耗是不同的,而且它们又以cluster来区分(小核在一个cluster,大核在另一个cluster),而目前由于同cluster内的cpu freq是同步调节的。
所以,在对CPU的任务调度中,需要对其同样进行区分,来确保性能和功耗的平衡。
因此,针对CPU的拓扑结构,内核中会建立不同的调度域、调度组来体现。如下图,以某8核cpu为例:
- 在DIE level,cpu 0-7
- 在MC level,cpu 0-3在一组,而cpu4-7在另一组
- *SMT超线程技术,会在MC level以下,再进行一次区分:01、23、45、67(这里可以暂不考虑,因为当前ARM平台并未支持SMT)
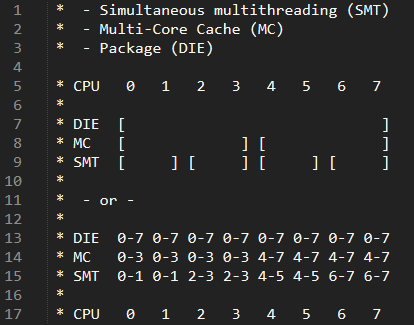
CPU Topology建立
在kernel中,有CPU Topology的相关代码来形成这样的结构,结构的定义在dts文件中,根据不同平台会不同。我当前这个mtk平台的DTS相关信息如下(至于这里为什么没有用qcom平台,因为现在公司暂时貌似只有mtk平台,所以可能略微有点差别):
cpu0: cpu@000 { device_type = "cpu"; compatible = "arm,cortex-a53"; reg = <0x000>; enable-method = "psci"; clock-frequency = <2301000000>; operating-points-v2 = <&cluster0_opp>; dynamic-power-coefficient = <275>; capacity-dmips-mhz = <1024>; cpu-idle-states = <&STANDBY &MCDI_CPU &MCDI_CLUSTER>, <&SODI &SODI3 &DPIDLE &SUSPEND>; }; cpu1: cpu@001 { device_type = "cpu"; compatible = "arm,cortex-a53"; reg = <0x001>; enable-method = "psci"; clock-frequency = <2301000000>; operating-points-v2 = <&cluster0_opp>; dynamic-power-coefficient = <275>; capacity-dmips-mhz = <1024>; cpu-idle-states = <&STANDBY &MCDI_CPU &MCDI_CLUSTER>, <&SODI &SODI3 &DPIDLE &SUSPEND>; }; cpu2: cpu@002 { device_type = "cpu"; compatible = "arm,cortex-a53"; reg = <0x002>; enable-method = "psci"; clock-frequency = <2301000000>; operating-points-v2 = <&cluster0_opp>; dynamic-power-coefficient = <275>; capacity-dmips-mhz = <1024>; cpu-idle-states = <&STANDBY &MCDI_CPU &MCDI_CLUSTER>, <&SODI &SODI3 &DPIDLE &SUSPEND>; }; cpu3: cpu@003 { device_type = "cpu"; compatible = "arm,cortex-a53"; reg = <0x003>; enable-method = "psci"; clock-frequency = <2301000000>; operating-points-v2 = <&cluster0_opp>; dynamic-power-coefficient = <275>; capacity-dmips-mhz = <1024>; cpu-idle-states = <&STANDBY &MCDI_CPU &MCDI_CLUSTER>, <&SODI &SODI3 &DPIDLE &SUSPEND>; }; cpu4: cpu@100 { device_type = "cpu"; compatible = "arm,cortex-a53"; reg = <0x100>; enable-method = "psci"; clock-frequency = <1800000000>; operating-points-v2 = <&cluster1_opp>; dynamic-power-coefficient = <85>; capacity-dmips-mhz = <801>; cpu-idle-states = <&STANDBY &MCDI_CPU &MCDI_CLUSTER>, <&SODI &SODI3 &DPIDLE &SUSPEND>; }; cpu5: cpu@101 { device_type = "cpu"; compatible = "arm,cortex-a53"; reg = <0x101>; enable-method = "psci"; clock-frequency = <1800000000>; operating-points-v2 = <&cluster1_opp>; dynamic-power-coefficient = <85>; capacity-dmips-mhz = <801>; cpu-idle-states = <&STANDBY &MCDI_CPU &MCDI_CLUSTER>, <&SODI &SODI3 &DPIDLE &SUSPEND>; }; cpu6: cpu@102 { device_type = "cpu"; compatible = "arm,cortex-a53"; reg = <0x102>; enable-method = "psci"; clock-frequency = <1800000000>; operating-points-v2 = <&cluster1_opp>; dynamic-power-coefficient = <85>; capacity-dmips-mhz = <801>; cpu-idle-states = <&STANDBY &MCDI_CPU &MCDI_CLUSTER>, <&SODI &SODI3 &DPIDLE &SUSPEND>; }; cpu7: cpu@103 { device_type = "cpu"; compatible = "arm,cortex-a53"; reg = <0x103>; enable-method = "psci"; clock-frequency = <1800000000>; operating-points-v2 = <&cluster1_opp>; dynamic-power-coefficient = <85>; capacity-dmips-mhz = <801>; cpu-idle-states = <&STANDBY &MCDI_CPU &MCDI_CLUSTER>, <&SODI &SODI3 &DPIDLE &SUSPEND>; }; cpu-map { cluster0 { core0 { cpu = <&cpu0>; }; core1 { cpu = <&cpu1>; }; core2 { cpu = <&cpu2>; }; core3 { cpu = <&cpu3>; }; }; cluster1 { core0 { cpu = <&cpu4>; }; core1 { cpu = <&cpu5>; }; core2 { cpu = <&cpu6>; }; core3 { cpu = <&cpu7>; }; }; };
代码路径:drivers/base/arch_topology.c、arch/arm64/kernel/topology.c,本文代码以CAF Kernel msm-5.4为例。
第一部分,这里解析DTS,并保存cpu_topology的package_id,core_id,cpu_sclae(cpu_capacity_orig)
kernel_init() -> kernel_init_freeable() -> smp_prepare_cpus() -> init_cpu_topology() -> parse_dt_topology()
针对dts中,依次解析"cpus"节点,以及其中的"cpu-map"节点;
- 先解析了其中cluster节点的内容结构。
- 在对cpu capacity进行归一化
static int __init parse_dt_topology(void) { struct device_node *cn, *map; int ret = 0; int cpu; cn = of_find_node_by_path("/cpus"); //查找dts中 /cpus的节点 if (!cn) { pr_err("No CPU information found in DT\n"); return 0; } /* * When topology is provided cpu-map is essentially a root * cluster with restricted subnodes. */ map = of_get_child_by_name(cn, "cpu-map"); //查找/cpus节点下,cpu-map节点 if (!map) goto out; ret = parse_cluster(map, 0); //(1)解析cluster结构 if (ret != 0) goto out_map; topology_normalize_cpu_scale(); //(2)将cpu capacity归一化 /* * Check that all cores are in the topology; the SMP code will * only mark cores described in the DT as possible. */ for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) if (cpu_topology[cpu].package_id == -1) ret = -EINVAL; out_map: of_node_put(map); out: of_node_put(cn); return ret; }
(1)解析cluster结构
- 通过第一个do-while循环,进行"cluster+序号"节点的解析:当前平台分别解析cluster0、1。然后仍然调用自身函数,这样代码复用,进一步解析其中的“core”结构
- 在进一步解析core结构时,同样通过第二个do-while循环,进行"core+序号"节点的解析:当前平台支持core0,1...7,共8个核,通过parse_core函数进一步解析
- 所以实际解析执行顺序应该是:cluster0,core0,1,2,3;cluster1,core4,5,6,7。
- 最后在每个cluster中的所有core都解析完,跳出其do-while循环时,package_id就是递增。说明package_id就对应了cluster的id
static int __init parse_cluster(struct device_node *cluster, int depth) { char name[20]; bool leaf = true; bool has_cores = false; struct device_node *c; static int package_id __initdata; int core_id = 0; int i, ret; /* * First check for child clusters; we currently ignore any * information about the nesting of clusters and present the * scheduler with a flat list of them. */ i = 0; do { snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "cluster%d", i); //依次解析cluster0,1... 当前平台只有cluster0/1 c = of_get_child_by_name(cluster, name); //检查cpu-map下,是否有cluster结构 if (c) { leaf = false; ret = parse_cluster(c, depth + 1); //如果有cluster结构,会继续解析更深层次的core结构。(这里通过代码复用,接着解析core结构) of_node_put(c); if (ret != 0) return ret; } i++; } while (c); /* Now check for cores */ i = 0; do { snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "core%d", i); //依次解析core0,1... 当前平台有8个core c = of_get_child_by_name(cluster, name); //检查cluster下,是否有core结构 if (c) { has_cores = true; if (depth == 0) { //这里要注意,是因为上面depth+1的调用才会走下去 pr_err("%pOF: cpu-map children should be clusters\n", //如果cpu-map下没有cluster结构的(depth==0),就会报错 c); of_node_put(c); return -EINVAL; } if (leaf) { //在depth+1的情况下,leaf == true,说明是core level了 ret = parse_core(c, package_id, core_id++); //(1-1)解析core结构 } else { pr_err("%pOF: Non-leaf cluster with core %s\n", cluster, name); ret = -EINVAL; } of_node_put(c); if (ret != 0) return ret; } i++; } while (c); if (leaf && !has_cores) pr_warn("%pOF: empty cluster\n", cluster); if (leaf) //在core level遍历完成:说明1个cluster解析完成,要解析下一个cluster了,package id要递增了 package_id++; //所以package id就对应了cluster id return 0; }
(1-1)解析core结构
- 因为当前平台不支持超线程,所以core+序号节点下面,没有thread+序号的节点了
- 解析cpu节点中的所有信息
- 更新cpu_topology[cpu].package_id、core_id,分别对应了哪个cluster的哪个core
static int __init parse_core(struct device_node *core, int package_id, int core_id) { char name[20]; bool leaf = true; int i = 0; int cpu; struct device_node *t; do { snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "thread%d", i); //不支持SMT,所以dts没有在core下面配置超线程 t = of_get_child_by_name(core, name); if (t) { leaf = false; cpu = get_cpu_for_node(t); if (cpu >= 0) { cpu_topology[cpu].package_id = package_id; cpu_topology[cpu].core_id = core_id; cpu_topology[cpu].thread_id = i; } else { pr_err("%pOF: Can't get CPU for thread\n", t); of_node_put(t); return -EINVAL; } of_node_put(t); } i++; } while (t); cpu = get_cpu_for_node(core); //(1-1-1)从core中解析cpu节点 if (cpu >= 0) { if (!leaf) { pr_err("%pOF: Core has both threads and CPU\n", core); return -EINVAL; } cpu_topology[cpu].package_id = package_id; //保存package id(cluster id)到cpu_topology结构体的数组 cpu_topology[cpu].core_id = core_id; //保存core id到cpu_topology结构体的数组; core id对应cpu号:0,1...7 } else if (leaf) { pr_err("%pOF: Can't get CPU for leaf core\n", core); return -EINVAL; } return 0; }
(1-1-1)从core中解析cpu节点
- 从core节点中查找cpu节点,并对应好cpu id
- 再解析cpu core的capacity
static int __init get_cpu_for_node(struct device_node *node) { struct device_node *cpu_node; int cpu; cpu_node = of_parse_phandle(node, "cpu", 0); //获取core节点中cpu节点信息 if (!cpu_node) return -1; cpu = of_cpu_node_to_id(cpu_node); //获取cpu节点对应的cpu core id:cpu-0,1... if (cpu >= 0) topology_parse_cpu_capacity(cpu_node, cpu); //(1-1-1-1)解析每个cpu core的capacity else pr_crit("Unable to find CPU node for %pOF\n", cpu_node); of_node_put(cpu_node); return cpu; }
(1-1-1-1)解析每个cpu core的capacity
- 先解析capacity-dmips-mhz值作为cpu raw_capacity,这个参数就是对应了cpu的算力,数字越大,算力越强(可以对照上面mtk平台dts,明显是大小核架构;但不同的是,它cpu0-3都是大核,cpu4-7是小核,这个与一般的配置不太一样,一般qcom平台是反过来,cpu0-3是小核,4-7是大核)
- 当前raw_capcity是cpu 0-3:1024,cpu4-7:801
bool __init topology_parse_cpu_capacity(struct device_node *cpu_node, int cpu) { static bool cap_parsing_failed; int ret; u32 cpu_capacity; if (cap_parsing_failed) return false; ret = of_property_read_u32(cpu_node, "capacity-dmips-mhz", //解析cpu core算力,kernel4.19后配置该参数 &cpu_capacity); if (!ret) { if (!raw_capacity) { raw_capacity = kcalloc(num_possible_cpus(), //为所有cpu raw_capacity变量都申请空间 sizeof(*raw_capacity), GFP_KERNEL); if (!raw_capacity) { cap_parsing_failed = true; return false; } } capacity_scale = max(cpu_capacity, capacity_scale); //记录最大cpu capacity值作为scale raw_capacity[cpu] = cpu_capacity; //raw capacity就是dts中dmips值 pr_debug("cpu_capacity: %pOF cpu_capacity=%u (raw)\n", cpu_node, raw_capacity[cpu]); } else { if (raw_capacity) { pr_err("cpu_capacity: missing %pOF raw capacity\n", cpu_node); pr_err("cpu_capacity: partial information: fallback to 1024 for all CPUs\n"); } cap_parsing_failed = true; free_raw_capacity(); } return !ret; }
(2)将cpu raw_capacity进行归一化
- 遍历每个cpu core进行归一化,其实就是将最大值映射为1024,小的值,按照原先比例n,归一化为n*1024。
- 归一化步骤:将当前raw_capacity *1024 /capacity_scale,capacity_scale其实就是raw_capacity的最大值,其实就是1024
- 将cpu raw capacity保存到per_cpu变量:cpu_scale中,在内核调度中经常使用的cpu_capacity_orig、cpu_capacity参数的计算都依赖它。
void topology_normalize_cpu_scale(void) { u64 capacity; int cpu; if (!raw_capacity) return; pr_debug("cpu_capacity: capacity_scale=%u\n", capacity_scale); for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) { pr_debug("cpu_capacity: cpu=%d raw_capacity=%u\n", cpu, raw_capacity[cpu]); capacity = (raw_capacity[cpu] << SCHED_CAPACITY_SHIFT) //就是按照max cpu capacity的100% = 1024的方式归一化capacity / capacity_scale; topology_set_cpu_scale(cpu, capacity); //更新per_cpu变量cpu_scale(cpu_capacity_orig)为各自的cpu raw capacity pr_debug("cpu_capacity: CPU%d cpu_capacity=%lu\n", cpu, topology_get_cpu_scale(cpu)); } }
第二部分更新sibling_mask
cpu0的调用路径如下:
kernel_init -> kernel_init_freeable -> smp_prepare_cpus -> store_cpu_topology
cpu1-7的调用路径如下:
secondary_start_kernel
-> store_cpu_topology
void store_cpu_topology(unsigned int cpuid) { struct cpu_topology *cpuid_topo = &cpu_topology[cpuid]; u64 mpidr; if (cpuid_topo->package_id != -1) //这里因为已经解析过package_id了,所以直接就不会走读协处理器寄存器等相关步骤了 goto topology_populated; mpidr = read_cpuid_mpidr(); /* Uniprocessor systems can rely on default topology values */ if (mpidr & MPIDR_UP_BITMASK) return; /* * This would be the place to create cpu topology based on MPIDR. * * However, it cannot be trusted to depict the actual topology; some * pieces of the architecture enforce an artificial cap on Aff0 values * (e.g. GICv3's ICC_SGI1R_EL1 limits it to 15), leading to an * artificial cycling of Aff1, Aff2 and Aff3 values. IOW, these end up * having absolutely no relationship to the actual underlying system * topology, and cannot be reasonably used as core / package ID. * * If the MT bit is set, Aff0 *could* be used to define a thread ID, but * we still wouldn't be able to obtain a sane core ID. This means we * need to entirely ignore MPIDR for any topology deduction. */ cpuid_topo->thread_id = -1; cpuid_topo->core_id = cpuid; cpuid_topo->package_id = cpu_to_node(cpuid); pr_debug("CPU%u: cluster %d core %d thread %d mpidr %#016llx\n", cpuid, cpuid_topo->package_id, cpuid_topo->core_id, cpuid_topo->thread_id, mpidr); topology_populated: update_siblings_masks(cpuid); //(1)更新当前cpu的sibling_mask }
(1)更新当前cpu的sibling_mask
- 匹配规则就是如果是同一个package id(同一个cluster内),那么就互为sibling,并设置core_sibling的mask
- 当前平台不支持超线程,所以没有thread_sibling
void update_siblings_masks(unsigned int cpuid) { struct cpu_topology *cpu_topo, *cpuid_topo = &cpu_topology[cpuid]; int cpu; /* update core and thread sibling masks */ for_each_online_cpu(cpu) { cpu_topo = &cpu_topology[cpu]; if (cpuid_topo->llc_id == cpu_topo->llc_id) { //当前平台不支持acpi,所以所有cpu的llc_id都是-1。这里都会满足 cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, &cpuid_topo->llc_sibling); cpumask_set_cpu(cpuid, &cpu_topo->llc_sibling); } if (cpuid_topo->package_id != cpu_topo->package_id) //只有当在同一个cluster内时,才可能成为core_sibling/thread_sibling(当前平台不支持线程sibling) continue; cpumask_set_cpu(cpuid, &cpu_topo->core_sibling); //互相设置各自cpu topo结构体的core_sibling mask中添加对方的cpu bit cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, &cpuid_topo->core_sibling); if (cpuid_topo->core_id != cpu_topo->core_id) //只有在同一个core内时,才有可能成为thread_sibling continue; cpumask_set_cpu(cpuid, &cpu_topo->thread_sibling); //互相设置thread_sibling mask中的thread bit cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, &cpuid_topo->thread_sibling); } }
最终我们可以通过adb查看cpu相关节点信息来确认上面的cpu topology信息:
TECNO-KF6p:/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology # ls
core_id core_siblings core_siblings_list physical_package_id thread_siblings thread_siblings_list
cpu0:
TECNO-KF6p:/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology # cat core_id 0 TECNO-KF6p:/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology # cat core_siblings 0f TECNO-KF6p:/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology # cat core_siblings_list 0-3 TECNO-KF6p:/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology # cat physical_package_id 0 TECNO-KF6p:/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology # cat thread_siblings 01 TECNO-KF6p:/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology # cat thread_siblings_list 0
cpu1:
TECNO-KF6p:/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu1/topology # cat * 1 0f 0-3 0 02 //thread_siblings 1 //thread_siblings_list
cpu7:
TECNO-KF6p:/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu7/topology # cat * 3 //core_id(cpu4-7的core id分别为0,1,2,3。相当于另一个cluster内重新开始计数) f0 //core_siblings 4-7 //core_siblings_list(兄弟姐妹core列表) 1 //physical_package_id(就是cluster id) 80 //thread_siblings 7 //thread_siblings_list
以上就是CPU topology建立的相关流程了,还是比较清晰的。
sd调度域和sg调度组建立
CPU MASK
* cpu_possible_mask- has bit 'cpu' set iff cpu is populatable //系统所有cpu * cpu_present_mask - has bit 'cpu' set iff cpu is populated //存在的所有cpu,根据hotplug变化, <= possible * cpu_online_mask - has bit 'cpu' set iff cpu available to scheduler //处于online的cpu,即active cpu + idle cpu * cpu_active_mask - has bit 'cpu' set iff cpu available to migration //处于active的cpu,区别与idle cpu * cpu_isolated_mask- has bit 'cpu' set iff cpu isolated //处于isolate的cpu,隔离的cpu不会被分配task运行,但是没有下电 * 1、如果没有CONFIG_HOTPLUG_CPU,那么 present == possible, active == online。 2、配置了cpu hotplug的情况下,present会根据hotplug状态,动态变化。
调度域和调度组是在kernel初始化时开始建立的,调用路径如下:
kernel_init() -> kernel_init_freeable() -> sched_init_smp() -> sched_init_domains()
传入的cpu_map是cpu_active_mask,即活动状态的cpu,建立调度域:
/* Current sched domains: */ static cpumask_var_t *doms_cur; /* Number of sched domains in 'doms_cur': */ static int ndoms_cur;
/* * Set up scheduler domains and groups. For now this just excludes isolated * CPUs, but could be used to exclude other special cases in the future. */ int sched_init_domains(const struct cpumask *cpu_map) { int err; zalloc_cpumask_var(&sched_domains_tmpmask, GFP_KERNEL); zalloc_cpumask_var(&sched_domains_tmpmask2, GFP_KERNEL); zalloc_cpumask_var(&fallback_doms, GFP_KERNEL); arch_update_cpu_topology(); //(1)填充cpu_core_map数组 ndoms_cur = 1; //记录调度域数量的变量,当前初始化为1 doms_cur = alloc_sched_domains(ndoms_cur); //alloc调度域相关结构体内存空间 if (!doms_cur) doms_cur = &fallback_doms; cpumask_and(doms_cur[0], cpu_map, housekeeping_cpumask(HK_FLAG_DOMAIN)); //这里会从cpu_map中挑选没有isolate的cpu,初始化时没有isolate cpu? err = build_sched_domains(doms_cur[0], NULL); //(2)根据提供的一组cpu,建立调度域 register_sched_domain_sysctl(); //(3)注册proc/sys/kernel/sched_domain目录,并完善其中相关sysctl控制参数 return err; }
(1)用cpu_possiable_mask填充cpu_core_map数组
int arch_update_cpu_topology(void) { unsigned int cpu; for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) //遍历每个cpu cpu_core_map[cpu] = cpu_coregroup_map(cpu); //利用cpu_possiable_mask,也就是物理上所有的cpu core return 0; }
(2)根据提供的可用cpu(active的cpu中去掉isolate cpu),建立调度域
- (2-1)根据配置的default topology建立其CPU拓扑结构(MC、DIE);alloc sched_domain以及per_cpu私有变量;alloc root domain空间并初始化
- (2-2)判断当前平台类型:大小核;获取拥有不同cpu capacity的最浅level:DIE
- (2-3)根据平台cpu和topology结构,申请MC、DIE level调度域,并建立其child-parent关系;初始化调度域flag和load balance参数;使能MC、DIE的idle balance
- (2-4)申请sched group并初始化cpu mask以及capacity,建立sg在MC、DIE上的内部环形链表关系;建立sd、sg、sgc的关联;
- (2-5)针对出现一些错误(sa_sd_storage)的情况下,防止正在使用的sd_data在(2-8)中被free
- (2-6)更新MC level下每个sg(其实就是每个cpu)的cpu_orig_capacity/cpu_capacity等,再更新DIE level下每个sg(其实就是每个cluster内所有cpu)的cpu_orig_capacity/cpu_capacity
- 遍历cpu_map中每个cpu,
- 找到拥有最大/最小 cpu_orig_capacity(即cpu_scale)的cpu,并保存到walt root domain结构体中
- 将新建立的MC level的sd、root domain、cpu_rq三者绑定起来
- (2-7)将每个新的MC level的sd与对应cpu rq绑定,将每个新的rd与cpu rq绑定;旧的sd、旧的rd都进行销毁
- 遍历cpu_map,找到cpu_orig_capacity的中间值(适用于有3种不同cpu core类型的情况,当前平台只有大小核,没有超大核,所以这里不用考虑);上一步中找到的最大/最小 cpu_orig_capacity(即cpu_scale)以及其对应的cpu,都将更新到rd中
- 使用static-key机制来修改当前调度域是否有不同cpu capacity的代码路径;
- 根据上述建立cpu拓扑、申请root domain的正常/异常情况,进行错误处理(释放必要结构体等)
/* * Build sched domains for a given set of CPUs and attach the sched domains * to the individual CPUs */ static int build_sched_domains(const struct cpumask *cpu_map, struct sched_domain_attr *attr) { enum s_alloc alloc_state = sa_none; struct sched_domain *sd; struct s_data d; int i, ret = -ENOMEM; struct sched_domain_topology_level *tl_asym; bool has_asym = false; if (WARN_ON(cpumask_empty(cpu_map))) //过滤cpu_map为空的情况 goto error; alloc_state = __visit_domain_allocation_hell(&d, cpu_map); //(2-1)建立MC、DIE的拓扑结构;初始化root domain if (alloc_state != sa_rootdomain) goto error; tl_asym = asym_cpu_capacity_level(cpu_map); //(2-2)获取包含max cpu capacity的最浅level:DIE level /* Set up domains for CPUs specified by the cpu_map: */ //根据cpu map建立调度域 for_each_cpu(i, cpu_map) { //遍历每个cpu map中的cpu:0-7 struct sched_domain_topology_level *tl; sd = NULL; for_each_sd_topology(tl) { //遍历MC、DIE level int dflags = 0; if (tl == tl_asym) { //DIE level会带有:SD_ASYM_CPUCAPACITY flag,并设has_asym = true dflags |= SD_ASYM_CPUCAPACITY; has_asym = true; } if (WARN_ON(!topology_span_sane(tl, cpu_map, i))) goto error; sd = build_sched_domain(tl, cpu_map, attr, sd, dflags, i); //(2-3)建立MC、DIE level的调度域 if (tl == sched_domain_topology) //将最低层级的sd保存到s_data.sd的per_cpu变量中,当前平台为MC level的sd *per_cpu_ptr(d.sd, i) = sd; if (tl->flags & SDTL_OVERLAP) //判断是否sd有重叠,当前平台没有重叠 sd->flags |= SD_OVERLAP; if (cpumask_equal(cpu_map, sched_domain_span(sd))) //判断cpu map和当前sd->span是否一致,一致则表示当前cpu_map中的所有cpu都在这个sd->span内。就会停止下一层tl的sd建立,可能用当前这一层的sd就已经足够了? break; } } /* Build the groups for the domains */ for_each_cpu(i, cpu_map) { //遍历cpu_map中每个cpu for (sd = *per_cpu_ptr(d.sd, i); sd; sd = sd->parent) { //从cpu的最低层级sd开始向上遍历,当前平台遍历顺序是:MC->DIE sd->span_weight = cpumask_weight(sched_domain_span(sd)); //获取当前sd范围内的cpu数量 if (sd->flags & SD_OVERLAP) { //根据是否有重叠的sd,建立调度组sg(NUMA架构才会有这个flag) if (build_overlap_sched_groups(sd, i)) //重叠sd情况下,建立sg(非当前平台,暂不展开) goto error; } else { if (build_sched_groups(sd, i)) //(2-4)因为当前平台没有重叠sd,所以走这里建立调度组sg goto error; } } } /* Calculate CPU capacity for physical packages and nodes */ for (i = nr_cpumask_bits-1; i >= 0; i--) { //遍历所有cpu,当前平台遍历顺序是cpu7,6...0 if (!cpumask_test_cpu(i, cpu_map)) //如果cpu不在cpu map中,应该是hotplug的情况 continue; for (sd = *per_cpu_ptr(d.sd, i); sd; sd = sd->parent) { //依次遍历MC level和DIE level claim_allocations(i, sd); //(2-5)将用于建立sd、sg的per_cpu指针(sdd),防止随后的__free_domain_allocs()将其free init_sched_groups_capacity(i, sd); //(2-6)初始化sg的cpu_capacity } } /* Attach the domains */ rcu_read_lock(); for_each_cpu(i, cpu_map) { //遍历cpu map中所有cpu #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_WALT int max_cpu = READ_ONCE(d.rd->wrd.max_cap_orig_cpu); //获取walt_root_domain中保存最大orig_capacity cpu的变量 int min_cpu = READ_ONCE(d.rd->wrd.min_cap_orig_cpu); //获取walt_root_domain中保存最小orig_capacity cpu的变量 #endif sd = *per_cpu_ptr(d.sd, i); //最低层级的sd在上面的流程中被保存到per_cpu变量中,当前平台为MC level #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_WALT //通过遍历循环,找除最大和最小orig_capacity的cpu if ((max_cpu < 0) || (arch_scale_cpu_capacity(i) > arch_scale_cpu_capacity(max_cpu))) WRITE_ONCE(d.rd->wrd.max_cap_orig_cpu, i); if ((min_cpu < 0) || (arch_scale_cpu_capacity(i) < arch_scale_cpu_capacity(min_cpu))) WRITE_ONCE(d.rd->wrd.min_cap_orig_cpu, i); #endif cpu_attach_domain(sd, d.rd, i); //(2-7)将sd、rd与cpu rq绑定起来 } #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_WALT /* set the mid capacity cpu (assumes only 3 capacities) */ for_each_cpu(i, cpu_map) { int max_cpu = READ_ONCE(d.rd->wrd.max_cap_orig_cpu); //获取拥有最大orig cpu capacity的第一个cpu int min_cpu = READ_ONCE(d.rd->wrd.min_cap_orig_cpu); //获取拥有最小orig cpu capacity的第一个cpu if ((arch_scale_cpu_capacity(i) //找到orig cpu capacity在最大和最小之间的cpu != arch_scale_cpu_capacity(min_cpu)) && (arch_scale_cpu_capacity(i) != arch_scale_cpu_capacity(max_cpu))) { WRITE_ONCE(d.rd->wrd.mid_cap_orig_cpu, i); //当前平台只有2个值orig cpu capacity,所以这里找不到mid值的cpu break; } } /* * The max_cpu_capacity reflect the original capacity which does not * change dynamically. So update the max cap CPU and its capacity * here. */ if (d.rd->wrd.max_cap_orig_cpu != -1) { d.rd->max_cpu_capacity.cpu = d.rd->wrd.max_cap_orig_cpu; //更新rd中的拥有最大orig cpu capacity的cpu(注意变量与max_cap_orig_cpu不同) d.rd->max_cpu_capacity.val = arch_scale_cpu_capacity( //并更新该cpu的orig cpu capacity值 d.rd->wrd.max_cap_orig_cpu); } #endif rcu_read_unlock(); if (has_asym) //当前平台为大小核架构,所以为true static_branch_inc_cpuslocked(&sched_asym_cpucapacity); //针对sched_asym_cpucapacity的变量判断分支做更改(static key机制用来优化指令预取,类似likely/unlikely) ret = 0; error: __free_domain_allocs(&d, alloc_state, cpu_map); //(2-8)根据函数最上面建立拓扑、以及申请root domain结果,释放相应的空间 return ret; }
(2-1)建立MC、DIE的拓扑结构;初始化root domain
static enum s_alloc __visit_domain_allocation_hell(struct s_data *d, const struct cpumask *cpu_map) { memset(d, 0, sizeof(*d)); if (__sdt_alloc(cpu_map)) //(2-1-1)初始化MC、DIE的拓扑结构 return sa_sd_storage; d->sd = alloc_percpu(struct sched_domain *); //申请d->sd空间 if (!d->sd) return sa_sd_storage; d->rd = alloc_rootdomain(); //(2-1-2)申请root domain并初始化 if (!d->rd) return sa_sd; return sa_rootdomain; }
(2-1-1)初始化MC、DIE的拓扑结构
CPU topology结构如下,因为当前平台不支持SMT,所以从下到上,分别是MC level、DIE level。在sdt_alloc()中的循环中会使用到。
/* * Topology list, bottom-up. */ static struct sched_domain_topology_level default_topology[] = { #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_SMT { cpu_smt_mask, cpu_smt_flags, SD_INIT_NAME(SMT) }, #endif #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_MC { cpu_coregroup_mask, cpu_core_flags, SD_INIT_NAME(MC) }, #endif { cpu_cpu_mask, SD_INIT_NAME(DIE) }, { NULL, }, };
- 首先建立MC level
- alloc了sd_data结构体(&tl->data)的4个指针:sdd->sd,sdd->sds,sdd->sg,sdd->sgc;
- 在遍历CPU时,从cpu0-7,分别创建了每个per_cpu变量保存:sd、sds、sg、sgc
- 再建立DIE level
- alloc了sd_data结构体(&tl->data)的4个指针:sdd->sd,sdd->sds,sdd->sg,sdd->sgc;
- 在遍历CPU时,从cpu0-7,分别创建了每个per_cpu变量保存:sd、sds、sg、sgc
static int __sdt_alloc(const struct cpumask *cpu_map) { struct sched_domain_topology_level *tl; int j; for_each_sd_topology(tl) { //依次遍历MC、DIE结构 struct sd_data *sdd = &tl->data; //如下是为MC、DIE level的percpu变量sd_data,申请空间 sdd->sd = alloc_percpu(struct sched_domain *); //sched_domain if (!sdd->sd) return -ENOMEM; sdd->sds = alloc_percpu(struct sched_domain_shared *); //sched_domain_shared if (!sdd->sds) return -ENOMEM; sdd->sg = alloc_percpu(struct sched_group *); //sched_group if (!sdd->sg) return -ENOMEM; sdd->sgc = alloc_percpu(struct sched_group_capacity *); //sched_group_capacity if (!sdd->sgc) return -ENOMEM; for_each_cpu(j, cpu_map) { //遍历了cpu_map中所有cpu,当前平台为8核:cpu0-7 struct sched_domain *sd; struct sched_domain_shared *sds; struct sched_group *sg; struct sched_group_capacity *sgc; sd = kzalloc_node(sizeof(struct sched_domain) + cpumask_size(), //申请sd + cpumask的空间 GFP_KERNEL, cpu_to_node(j)); //cpu_to_node应该是选择cpu所在本地的内存node,UMA架构仅有一个node if (!sd) return -ENOMEM; *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sd, j) = sd; //将cpu[j]的调度域sd绑定到sdd->sd上 sds = kzalloc_node(sizeof(struct sched_domain_shared), //类似申请sds空间,并绑定到sdd->sds GFP_KERNEL, cpu_to_node(j)); if (!sds) return -ENOMEM; *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sds, j) = sds; sg = kzalloc_node(sizeof(struct sched_group) + cpumask_size(), //类似申请sg + cpumask空间,并绑定到sdd->sg GFP_KERNEL, cpu_to_node(j)); if (!sg) return -ENOMEM; sg->next = sg; //初始化时,sg的链表并未真正建立 *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sg, j) = sg; sgc = kzalloc_node(sizeof(struct sched_group_capacity) + cpumask_size(),//类似申请sgc + cpumask空间,并绑定到sdd->sgc GFP_KERNEL, cpu_to_node(j)); if (!sgc) return -ENOMEM; #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_DEBUG sgc->id = j; //将cpu编号绑定到sgc->id #endif *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sgc, j) = sgc; } } return 0; }
(2-1-2) 申请root domain并初始化
static struct root_domain *alloc_rootdomain(void) { struct root_domain *rd; rd = kzalloc(sizeof(*rd), GFP_KERNEL); if (!rd) return NULL; if (init_rootdomain(rd) != 0) { //(2-1-2-1)初始化root domain kfree(rd); return NULL; } return rd; }
(2-1-2-1)初始化root domain
static int init_rootdomain(struct root_domain *rd) { if (!zalloc_cpumask_var(&rd->span, GFP_KERNEL)) //申请4个cpu mask的空间 goto out; if (!zalloc_cpumask_var(&rd->online, GFP_KERNEL)) goto free_span; if (!zalloc_cpumask_var(&rd->dlo_mask, GFP_KERNEL)) goto free_online; if (!zalloc_cpumask_var(&rd->rto_mask, GFP_KERNEL)) goto free_dlo_mask; #ifdef HAVE_RT_PUSH_IPI rd->rto_cpu = -1; //初始化rto相关参数和队列,针对IPI pull的请求,在rto_mask中loop,暂时没理解? raw_spin_lock_init(&rd->rto_lock); init_irq_work(&rd->rto_push_work, rto_push_irq_work_func); #endif init_dl_bw(&rd->dl_bw); //初始化deadline bandwidth if (cpudl_init(&rd->cpudl) != 0) //初始化cpudl结构体 goto free_rto_mask; if (cpupri_init(&rd->cpupri) != 0) //初始化cpupri结构体 goto free_cpudl; #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_WALT rd->wrd.max_cap_orig_cpu = rd->wrd.min_cap_orig_cpu = -1; //初始化walt_root_domain rd->wrd.mid_cap_orig_cpu = -1; #endif init_max_cpu_capacity(&rd->max_cpu_capacity); //初始化max_cpu_capacity ->val=0、->cpu=-1 return 0; free_cpudl: cpudl_cleanup(&rd->cpudl); free_rto_mask: free_cpumask_var(rd->rto_mask); free_dlo_mask: free_cpumask_var(rd->dlo_mask); free_online: free_cpumask_var(rd->online); free_span: free_cpumask_var(rd->span); out: return -ENOMEM; }
(2-2)获取包含max cpu capacity的最浅level:DIE level
- 判断当前是否是大小核架构:
- 遍历cpu map和cpu toplology,找到最大cpu capacity
- 找到有不同cpu capacity的level:DIE level
/* * Find the sched_domain_topology_level where all CPU capacities are visible * for all CPUs. */ static struct sched_domain_topology_level *asym_cpu_capacity_level(const struct cpumask *cpu_map) { int i, j, asym_level = 0; bool asym = false; struct sched_domain_topology_level *tl, *asym_tl = NULL; unsigned long cap; /* Is there any asymmetry? */ cap = arch_scale_cpu_capacity(cpumask_first(cpu_map)); //获取cpu_map中第一个cpu,cpu0的capacity for_each_cpu(i, cpu_map) { //判断是否有不同capacity的cpu,决定是否是大小核架构 if (arch_scale_cpu_capacity(i) != cap) { //当前平台是大小核有不同capacity asym = true; break; } } if (!asym) return NULL; /* * Examine topology from all CPU's point of views to detect the lowest * sched_domain_topology_level where a highest capacity CPU is visible * to everyone. */ for_each_cpu(i, cpu_map) { //遍历cpu map中的每个cpu,cpu 0-7 unsigned long max_capacity = arch_scale_cpu_capacity(i); int tl_id = 0; for_each_sd_topology(tl) { //依次遍历MC、DIE level if (tl_id < asym_level) goto next_level; for_each_cpu_and(j, tl->mask(i), cpu_map) { //(2-2-1)在MC level时分别遍历cpu0-3、cpu4-7;DIE level时遍历cpu0-7 unsigned long capacity; capacity = arch_scale_cpu_capacity(j); //获取cpu_capacity_orig if (capacity <= max_capacity) continue; max_capacity = capacity; //在所有cpu中找到最大的cpu capacity asym_level = tl_id; //记录level id:1 asym_tl = tl; //记录有不同cpu capacity的cpu topology level: DIE } next_level: tl_id++; } } return asym_tl; }
(2-2-1)单独分析下tl->mask(i)
- 因为tl实际就是default_topology的指针,所以tl->mask:在MC level下,就是cpu_coregroup_mask;在DIE level下,就是cpu_cpu_mask
- 所以MC level下,获取的mask就是core_siblings mask;DIE level下,获取的就是所有物理cpu的mask
const struct cpumask *cpu_coregroup_mask(int cpu) { const cpumask_t *core_mask = cpumask_of_node(cpu_to_node(cpu)); /* Find the smaller of NUMA, core or LLC siblings */ if (cpumask_subset(&cpu_topology[cpu].core_sibling, core_mask)) { /* not numa in package, lets use the package siblings */ core_mask = &cpu_topology[cpu].core_sibling; } if (cpu_topology[cpu].llc_id != -1) { if (cpumask_subset(&cpu_topology[cpu].llc_sibling, core_mask)) core_mask = &cpu_topology[cpu].llc_sibling; } return core_mask; }
static inline const struct cpumask *cpu_cpu_mask(int cpu) { return cpumask_of_node(cpu_to_node(cpu)); } /* Returns a pointer to the cpumask of CPUs on Node 'node'. */ static inline const struct cpumask *cpumask_of_node(int node) { if (node == NUMA_NO_NODE) //当前平台是UMA架构,非NUMA结构,所以只有一个node return cpu_all_mask; return node_to_cpumask_map[node]; }
(2-3)建立MC、DIE level的调度域
static struct sched_domain *build_sched_domain(struct sched_domain_topology_level *tl, const struct cpumask *cpu_map, struct sched_domain_attr *attr, struct sched_domain *child, int dflags, int cpu) { struct sched_domain *sd = sd_init(tl, cpu_map, child, dflags, cpu); //(2-3-1)初始化sched_domain,填充sd结构体,根据tl level构建sd父子关系等 if (child) { //MC level的child为NULL;所以下面只针对DIE level sd->level = child->level + 1; //DIE level值为child level+1 sched_domain_level_max = max(sched_domain_level_max, sd->level);//记录sd最大level child->parent = sd; //将MC level sd的parent设置为DIE level的sd if (!cpumask_subset(sched_domain_span(child), sched_domain_span(sd))) { pr_err("BUG: arch topology borken\n"); #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_DEBUG pr_err(" the %s domain not a subset of the %s domain\n", child->name, sd->name); #endif /* Fixup, ensure @sd has at least @child CPUs. */ cpumask_or(sched_domain_span(sd), sched_domain_span(sd), sched_domain_span(child)); } } set_domain_attribute(sd, attr); //(2-3-2)这里attr为NULL,打开idle balance return sd; }
(2-3-1)初始化sched_domain
-
初始化sd.flags,最后 MC、DIE level的flags 如下:

- 初始化sd结构体中其他重要参数:

3. 设置cpu mask:sched_domain_span(sd) 。在MC level,就是cluster的范围;在DIE level,就是所有物理cpu
4. 通过外面的遍历循环,将MC、DIE建立child-parent的链接关系
5. 打开MC、DIE level的idle load balance功能
static struct sched_domain * sd_init(struct sched_domain_topology_level *tl, const struct cpumask *cpu_map, struct sched_domain *child, int dflags, int cpu) { struct sd_data *sdd = &tl->data; struct sched_domain *sd = *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sd, cpu); //获取当前cpu的sd结构体 int sd_id, sd_weight, sd_flags = 0; #ifdef CONFIG_NUMA /* * Ugly hack to pass state to sd_numa_mask()... */ sched_domains_curr_level = tl->numa_level; #endif sd_weight = cpumask_weight(tl->mask(cpu)); //获取MC/DIE level下的sd_weight(就是topology level下的cpu个数,当前平台:MC为4,DIE为8) if (tl->sd_flags) //只有MC level有配置 sd_flags = (*tl->sd_flags)(); // MC level的sd_flags:SD_SHARE_PKG_RESOURCES;DIE level则没有 if (WARN_ONCE(sd_flags & ~TOPOLOGY_SD_FLAGS, //仅仅是判断下是否有相关bit位是否越界 "wrong sd_flags in topology description\n")) sd_flags &= TOPOLOGY_SD_FLAGS; //然后越界的话,清零下 /* Apply detected topology flags */ sd_flags |= dflags; //DIE level会传入 SD_ASYM_CPUCAPACITY flag *sd = (struct sched_domain){ //初始化sd结构体 .min_interval = sd_weight, //MC:4,DIE:8 .max_interval = 2*sd_weight, //MC:8,DIE:16 .busy_factor = 32, .imbalance_pct = 125, //用于load balance .cache_nice_tries = 0, .flags = 1*SD_LOAD_BALANCE | 1*SD_BALANCE_NEWIDLE | 1*SD_BALANCE_EXEC | 1*SD_BALANCE_FORK | 0*SD_BALANCE_WAKE | 1*SD_WAKE_AFFINE | 0*SD_SHARE_CPUCAPACITY | 0*SD_SHARE_PKG_RESOURCES | 0*SD_SERIALIZE | 1*SD_PREFER_SIBLING | 0*SD_NUMA | sd_flags //MC:SD_SHARE_PKG_RESOURCES,DIE:SD_ASYM_CPUCAPACITY , .last_balance = jiffies, //初始化load balance的时间戳 .balance_interval = sd_weight, //load balance的间隔,MC:4,DIE:8 .max_newidle_lb_cost = 0, //newidle load balance的cost .next_decay_max_lb_cost = jiffies, //idle balance中用到,暂时还不清楚什么cost .child = child, //MC level:sd的child为NULL;而DIE level:sd的child是MC level的sd #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_DEBUG .name = tl->name, #endif }; cpumask_and(sched_domain_span(sd), cpu_map, tl->mask(cpu)); //将对应tl mask(MC:core_siblings, DIE:所有物理cpu),与cpu map进行“位与”,作为sd的范围 sd_id = cpumask_first(sched_domain_span(sd)); //拿取sd范围内的第一个cpu,作为sd_id /* * Convert topological properties into behaviour. */ /* Don't attempt to spread across CPUs of different capacities. */ if ((sd->flags & SD_ASYM_CPUCAPACITY) && sd->child) //当前平台只有DIE level满足条件 sd->child->flags &= ~SD_PREFER_SIBLING; //所以DIE level的child,就是MC level的sd,其flags会去掉清掉SD_PREFER_SIBLING //所以,DIE sd的flag有SD_PREFER_SIBLING;而MC sd没有此flag if (sd->flags & SD_SHARE_CPUCAPACITY) { //这个flag应该是超线程sd支持的flag sd->imbalance_pct = 110; } else if (sd->flags & SD_SHARE_PKG_RESOURCES) { //从上面*tl->sd_flags()调用了MC level函数:cpu_core_flags(),所有这个flag在MC level是为1的 sd->imbalance_pct = 117; //修改MC level的sd不平衡百分比 sd->cache_nice_tries = 1; //修改MC level的cache_nice_tries = 2,暂时不清楚变量用途? #ifdef CONFIG_NUMA //当前平台不支持NUMA(平台为UMA架构) } else if (sd->flags & SD_NUMA) { sd->cache_nice_tries = 2; sd->flags &= ~SD_PREFER_SIBLING; sd->flags |= SD_SERIALIZE; if (sched_domains_numa_distance[tl->numa_level] > node_reclaim_distance) { sd->flags &= ~(SD_BALANCE_EXEC | SD_BALANCE_FORK | SD_WAKE_AFFINE); } #endif } else { //DIE level的cache_nice_tries = 1 sd->cache_nice_tries = 1; } sd->shared = *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sds, sd_id); //MC level是每个cpu各自的sds;而DIE level:是cpu0、cpu4的sds atomic_inc(&sd->shared->ref); //对sd->shared的引用计数+1 if (sd->flags & SD_SHARE_PKG_RESOURCES) //MC leve满足 atomic_set(&sd->shared->nr_busy_cpus, sd_weight); //设置sd->shared->nr_busy_cpus = 4 sd->private = sdd; //sd->private指向&tl->data,MC/DIE level的cpu sd都指向对应level的tl->data的结构 return sd; }
(2-3-2)传参attr =NULL,所以这里是判断sd是否要打开idle balance。实际是当前平台MC、DIE level都打开了idle balance
static void set_domain_attribute(struct sched_domain *sd, struct sched_domain_attr *attr) { int request; if (!attr || attr->relax_domain_level < 0) { if (default_relax_domain_level < 0) return; else request = default_relax_domain_level; } else request = attr->relax_domain_level; if (request < sd->level) { /* Turn off idle balance on this domain: */ sd->flags &= ~(SD_BALANCE_WAKE|SD_BALANCE_NEWIDLE); } else { /* Turn on idle balance on this domain: */ sd->flags |= (SD_BALANCE_WAKE|SD_BALANCE_NEWIDLE); } }
(2-4)当前平台没有重叠sd,所以会调用函数build_sched_groups逐步建立调度组sg
- 外部有2层循环,第一层为cpu_map:cpu0-7,第二层为sd:MC、DIE;函数内部有1层循环:从当前cpu开始,在sd内遍历所有cpu--------感觉有点多余:比如DIE level时,cpu0/cpu4各是child sd中的第一个cpu,就会进行初始化;而cpu1-3/cpu5-7时,就会在get_group中直接过滤return。
- 通过get_group进行sg初始化:sg/sgc->cpumask,sgc->capacity;并把sd、sg、sgc 3者关联起来
- MC、DIE level下将每个sg用环形链表关联起来
/* * build_sched_groups will build a circular linked list of the groups * covered by the given span, will set each group's ->cpumask correctly, * and will initialize their ->sgc. * * Assumes the sched_domain tree is fully constructed */ static int build_sched_groups(struct sched_domain *sd, int cpu) { struct sched_group *first = NULL, *last = NULL; struct sd_data *sdd = sd->private; const struct cpumask *span = sched_domain_span(sd); //获取当前sd的范围,MC是core_siblings,DIE是所有物理cpu struct cpumask *covered; int i; lockdep_assert_held(&sched_domains_mutex); covered = sched_domains_tmpmask; cpumask_clear(covered); //每次外面大循环新的sd或者cpu,就会清空covered mask for_each_cpu_wrap(i, span, cpu) { //从当前cpu开始遍历整个sd span struct sched_group *sg; if (cpumask_test_cpu(i, covered)) //已经在covered mask中的cpu,不需要再进行下面工作 continue; sg = get_group(i, sdd); //(2-4-1)初始化cpu i的调度组sg cpumask_or(covered, covered, sched_group_span(sg)); //将covered = covered | sg的span if (!first) //每个cpu、每个level进来记录第一个sg first = sg; if (last) last->next = sg; //每个sg的next都指向下一个sg last = sg; } last->next = first; //将所有sg->next形成环形链表 sd->groups = first; //sd->groups只指向第一个sg return 0; }
(2-4-1)初始化cpu i的调度组sg
- 如果sd是DIE level的,那么就会只初始化并返回cluster中的第1个cpu-----非常重要!!!
- 将sd与sg、sg与sgc关联起来
- 初始化sg->cpumask和sg->sgc->cpumask:DIE level,为child sd的范围;MC level,为单个cpu。----------这里区别于sched_domain_span(sd),sg的范围会比sd的范围降一级!!!用一句话说就是:每个sched domain的第一个sched group就是sd对应的child sched domain。
- 初始化sgc->capacity(等于child sd中cpu个数 * 1024),最大和最小capacity都是1024---------这个当前还不准确,仅仅是初始化,后面还会再修改
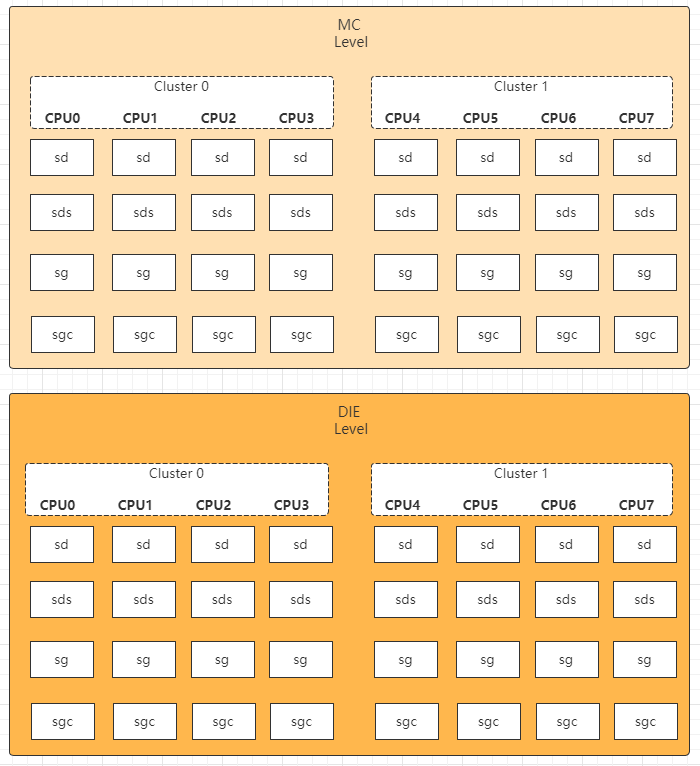
通过上述sd和sg的初始化建立,最终形成如下图关系。而其中DIE level上,只会初始化每个cluster的第一个cpu的sched group调度组(图中虚线表示的都没有关联到per_cpu变量中)

/* * Package topology (also see the load-balance blurb in fair.c) * * The scheduler builds a tree structure to represent a number of important * topology features. By default (default_topology[]) these include: * * - Simultaneous multithreading (SMT) * - Multi-Core Cache (MC) * - Package (DIE) * * Where the last one more or less denotes everything up to a NUMA node. * * The tree consists of 3 primary data structures: * * sched_domain -> sched_group -> sched_group_capacity * ^ ^ ^ ^ * `-' `-' * * The sched_domains are per-CPU and have a two way link (parent & child) and * denote the ever growing mask of CPUs belonging to that level of topology. * * Each sched_domain has a circular (double) linked list of sched_group's, each * denoting the domains of the level below (or individual CPUs in case of the * first domain level). The sched_group linked by a sched_domain includes the * CPU of that sched_domain [*]. * * Take for instance a 2 threaded, 2 core, 2 cache cluster part: * * CPU 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 * * DIE [ ] * MC [ ] [ ] * SMT [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] * * - or - * * DIE 0-7 0-7 0-7 0-7 0-7 0-7 0-7 0-7 * MC 0-3 0-3 0-3 0-3 4-7 4-7 4-7 4-7 * SMT 0-1 0-1 2-3 2-3 4-5 4-5 6-7 6-7 * * CPU 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 * * One way to think about it is: sched_domain moves you up and down among these * topology levels, while sched_group moves you sideways through it, at child * domain granularity. * * sched_group_capacity ensures each unique sched_group has shared storage. * * There are two related construction problems, both require a CPU that * uniquely identify each group (for a given domain): * * - The first is the balance_cpu (see should_we_balance() and the * load-balance blub in fair.c); for each group we only want 1 CPU to * continue balancing at a higher domain. * * - The second is the sched_group_capacity; we want all identical groups * to share a single sched_group_capacity. * * Since these topologies are exclusive by construction. That is, its * impossible for an SMT thread to belong to multiple cores, and cores to * be part of multiple caches. There is a very clear and unique location * for each CPU in the hierarchy. * * Therefore computing a unique CPU for each group is trivial (the iteration * mask is redundant and set all 1s; all CPUs in a group will end up at _that_ * group), we can simply pick the first CPU in each group. * * * [*] in other words, the first group of each domain is its child domain. */ static struct sched_group *get_group(int cpu, struct sd_data *sdd) { struct sched_domain *sd = *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sd, cpu); struct sched_domain *child = sd->child; struct sched_group *sg; bool already_visited; if (child) //child sd存在,说明当前是DIE level的sd cpu = cpumask_first(sched_domain_span(child)); //那么取出MC level中child sd的第一个cpu;DIE level时,下面用的sg都是每个cluster的第一个cpu的sg sg = *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sg, cpu); //绑定sd和sg sg->sgc = *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sgc, cpu); //绑定sg和sgc /* Increase refcounts for claim_allocations: */ //计算sg的引用计数 already_visited = atomic_inc_return(&sg->ref) > 1; /* sgc visits should follow a similar trend as sg */ WARN_ON(already_visited != (atomic_inc_return(&sg->sgc->ref) > 1)); /* If we have already visited that group, it's already initialized. */ //过滤已经初始化过的sg:在DIE level时,build_sched_groups函数遍历所有物理cpu,但是当前函数仅初始化child sd中的第一个cpu。所以当遍历cpu0/4,会实际执行下去,而cpu1-3/cpu5-7时,就会在这里过滤 if (already_visited) return sg; if (child) { //如果是DIE level cpumask_copy(sched_group_span(sg), sched_domain_span(child)); //sg的范围(sg->cpumask)是child sd的范围 cpumask_copy(group_balance_mask(sg), sched_group_span(sg)); //sg->sgc->cpumask也是child sd的范围 } else { //如果是MC level cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, sched_group_span(sg)); //那么sg的范围(sg->cpumask)就是自己对应的单个cpu cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, group_balance_mask(sg)); //sg->sgc->cpumask也是自己对应的单个cpu } sg->sgc->capacity = SCHED_CAPACITY_SCALE * cpumask_weight(sched_group_span(sg)); //根据sg范围内有几个cpu,来简单计算总capacity sg->sgc->min_capacity = SCHED_CAPACITY_SCALE; //初始化最小capacity sg->sgc->max_capacity = SCHED_CAPACITY_SCALE; //初始化最大capacity return sg; }
(2-5)将用于建立sd、sg的per_cpu指针(sdd)置NULL,防止随后的__free_domain_allocs()将其free-----结合(2-8)看来下,应该是出现一些错误(sa_sd_storage)的情况下,防止正在使用的sd_data被free
/* * NULL the sd_data elements we've used to build the sched_domain and * sched_group structure so that the subsequent __free_domain_allocs() * will not free the data we're using. */ static void claim_allocations(int cpu, struct sched_domain *sd) { struct sd_data *sdd = sd->private; WARN_ON_ONCE(*per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sd, cpu) != sd); //依次判断sd、sds、sg、sgc的per_cpu指针,并置为NULL *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sd, cpu) = NULL; if (atomic_read(&(*per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sds, cpu))->ref)) *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sds, cpu) = NULL; if (atomic_read(&(*per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sg, cpu))->ref)) *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sg, cpu) = NULL; if (atomic_read(&(*per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sgc, cpu))->ref)) *per_cpu_ptr(sdd->sgc, cpu) = NULL; }
(2-6)初始化sg的cpu_capacity
- do-while循环中对每个sg->group_weight进行初始化:MC level,sg范围是对应cpu;DIE level,sg范围是cluster的范围(如果支持WALT,还要去掉isolate cpu)
- 对sg中的第一个cpu(MC level,cpumask为sg对应cpu;DIE level,cpumask为cluster中第一个cpu),更新group capacity;
/* * Initialize sched groups cpu_capacity. * * cpu_capacity indicates the capacity of sched group, which is used while * distributing the load between different sched groups in a sched domain. * Typically cpu_capacity for all the groups in a sched domain will be same * unless there are asymmetries in the topology. If there are asymmetries, * group having more cpu_capacity will pickup more load compared to the * group having less cpu_capacity. */ void init_sched_groups_capacity(int cpu, struct sched_domain *sd) { struct sched_group *sg = sd->groups; //获取sd对应的sg #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_WALT cpumask_t avail_mask; #endif WARN_ON(!sg); do { //do-while循环中,对sg环形链表中的所有sg的->group_weight进行初始化 int cpu, max_cpu = -1; #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_WALT cpumask_andnot(&avail_mask, sched_group_span(sg), //如果支持WALT,那么group_weight = sg的范围中去掉isolate cpu;MC level,sg范围是对应cpu;DIE level,sg范围是cluster的范围 cpu_isolated_mask); sg->group_weight = cpumask_weight(&avail_mask); #else sg->group_weight = cpumask_weight(sched_group_span(sg)); //如果不支持WALT,那么group_weight = sg的范围;MC level,sg范围是对应cpu;DIE level,sg范围是cluster的范围 #endif if (!(sd->flags & SD_ASYM_PACKING)) //当前平台没有这个flag。这个flag应该表示支持非对称SMT调度 goto next; for_each_cpu(cpu, sched_group_span(sg)) { if (max_cpu < 0) max_cpu = cpu; else if (sched_asym_prefer(cpu, max_cpu)) max_cpu = cpu; } sg->asym_prefer_cpu = max_cpu; next: sg = sg->next; } while (sg != sd->groups); if (cpu != group_balance_cpu(sg)) //仅对sg->sgc->cpumask中第一个cpu,进行下一步更新group capacity。MC level,cpumask为sg对应cpu;DIE level,cpumask为cluster中第一个cpu return; update_group_capacity(sd, cpu); //(2-6-1)更新对应group的capacity }
(2-6-1)更新对应group的capacity-----这个函数在load balance的流程中也会被调用到
- 更新group capacity有时间间隔要求,间隔限制在[1,25]个tick之间
- 当sd为MC level时,因为其对应sg只有自身一个cpu,所以仅仅只需更新cpu capacity;而如果是DIE level,则需要进一步更新和计算
- 当sd为MC level,更新rq->cpu_orig_capacity/cpu_capacity、sgc->capacity/min_capacity/max_capcity
- 当sd为DIE level,那么通过child sd->groups指针,以及通过MC level的sg环形链表,依次遍历每个sgc->capcity(但会排除isolate状态cpu):遍历时,其中最大cpu max_capacity和最小cpu min_capacity分别作为DIE level sd->sg->sgc->max_capacity/min_capacity,最后把所有非isolate cpu的sgc->capacity累加起来,作为这个DIE level sd->sg->sgc->capacity;
void update_group_capacity(struct sched_domain *sd, int cpu) { struct sched_domain *child = sd->child; struct sched_group *group, *sdg = sd->groups; unsigned long capacity, min_capacity, max_capacity; unsigned long interval; interval = msecs_to_jiffies(sd->balance_interval); //sgc的更新有间隔限制:1 ~ HZ/10 interval = clamp(interval, 1UL, max_load_balance_interval); sdg->sgc->next_update = jiffies + interval; if (!child) { //如果是MC level的sd更新sgc,那么就只要更新cpu capacity,因为MC level的sg只有单个cpu在内 update_cpu_capacity(sd, cpu); //(2-6-1-1)更新cpu capacity return; } capacity = 0; min_capacity = ULONG_MAX; max_capacity = 0; if (child->flags & SD_OVERLAP) { //这个是sd有重叠的情况,当前平台没有sd重叠 /* * SD_OVERLAP domains cannot assume that child groups * span the current group. */ for_each_cpu(cpu, sched_group_span(sdg)) { struct sched_group_capacity *sgc; struct rq *rq = cpu_rq(cpu); if (cpu_isolated(cpu)) continue; /* * build_sched_domains() -> init_sched_groups_capacity() * gets here before we've attached the domains to the * runqueues. * * Use capacity_of(), which is set irrespective of domains * in update_cpu_capacity(). * * This avoids capacity from being 0 and * causing divide-by-zero issues on boot. */ if (unlikely(!rq->sd)) { capacity += capacity_of(cpu); } else { sgc = rq->sd->groups->sgc; capacity += sgc->capacity; } min_capacity = min(capacity, min_capacity); max_capacity = max(capacity, max_capacity); } } else { /* * !SD_OVERLAP domains can assume that child groups 因为没有sd重叠,那么所有child sd的groups合在一起,就是当前的group * span the current group. */ group = child->groups; do { //do-while遍历child sd的sg环形链表;当前平台为例,走到这里是DIE level,那么child sd就是MC level的groups struct sched_group_capacity *sgc = group->sgc; //获取对应sgc __maybe_unused cpumask_t *cpus = sched_group_span(group); //因为group是处于MC level,所以范围就是sg对应的cpu if (!cpu_isolated(cpumask_first(cpus))) { //排除isolate状态的cpu capacity += sgc->capacity; //将每个sgc(cpu)的capacity累加起来 min_capacity = min(sgc->min_capacity, //保存最小的sgc->capacity min_capacity); max_capacity = max(sgc->max_capacity, //保存最大的sgc->capacity max_capacity); } group = group->next; } while (group != child->groups); } sdg->sgc->capacity = capacity; //将MC level中每个sgc->capacity累加起来,其总和作为DIE level中group capacity sdg->sgc->min_capacity = min_capacity; //并保存最大、最小capacity sdg->sgc->max_capacity = max_capacity; }
(2-6-1-1)更新cpu capacity
- 获取cpu的orig_capacity(也就是cpu_scale),并获取max_freq_scale(每次在cpufreq调频中通过不同policy会变化,每次调频更新的公式如下)
policy_max_freq * 1024 max_freq_scale = ———————————————————————————————— ,在cpufreq中会根据policy设置policy_max_freq;max_freq_scale在开机初始化为1024,并作为per_cpu保存起来 原max_freq_scale
- 再通过cpu_scale和max_freq_scale计算,并考虑thermal限制,最终计算结果更新为当前cpu rq的cpu_capacity_orig,公式如下:
rq->cpu_orig_capacity = min(cpu_scale * max_freq_scale /1024, thermal限制的最大cpu capacity) - 通过特定的计算公式,计算得出去掉irq、rt进程、dl进程util之后的剩余cpu capacity。之后将其更新为rq->cpu_capacity、sgc->capacity/min_capacity/max_capacity
static void update_cpu_capacity(struct sched_domain *sd, int cpu) { unsigned long capacity = arch_scale_cpu_capacity(cpu); //获取per_cpu变量cpu_scale struct sched_group *sdg = sd->groups; capacity *= arch_scale_max_freq_capacity(sd, cpu); //获取per_cpu变量max_freq_scale,参与计算 capacity >>= SCHED_CAPACITY_SHIFT; //这2步计算为:cpu_scale * max_freq_scale / 1024 capacity = min(capacity, thermal_cap(cpu)); //计算得出的capacity不能超过thermal限制中的cpu的capacity cpu_rq(cpu)->cpu_capacity_orig = capacity; //将计算得出的capacity作为当前cpu rq的cpu_capacity_orig capacity = scale_rt_capacity(cpu, capacity); //(2-6-1-1-1)计算cfs rq剩余的cpu capacity if (!capacity) //如果没有剩余cpu capacity给cfs了,那么就强制写为1 capacity = 1; cpu_rq(cpu)->cpu_capacity = capacity; //更新相关sgc capacity:cpu rq的cpu_capacity、sgc的最大/最小的capacity sdg->sgc->capacity = capacity; sdg->sgc->min_capacity = capacity; sdg->sgc->max_capacity = capacity; }
(2-6-1-1-1)计算cfs rq剩余的cpu capacity
- 获取irq util,如果irq util超过orig cpu capacity,则说明已经没有剩余CPU算力了
- 获取rt进程的util,和dl进程的util,并求和。如果结果超过orig cpu capacity,则说明也已经没有剩余CPU算力了
- 如果上面2步,计算都还有剩余算力,那么就计算剩余cpu算力,如下:
(max - avg_rt.util_avg - avg_dl.util_avg) * (max - avg_irq.util_avg) 剩余cpu capacity = ————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————, 其中 max = rq->cpu_orig_capacity(上面计算出的结果) max
static unsigned long scale_rt_capacity(int cpu, unsigned long max) { struct rq *rq = cpu_rq(cpu); unsigned long used, free; unsigned long irq; irq = cpu_util_irq(rq); //获取cpu rq的avg_irq.util_avg if (unlikely(irq >= max)) //如果util_avg超过max,则说明util满了? return 1; used = READ_ONCE(rq->avg_rt.util_avg); //获取rt task rq的util_avg used += READ_ONCE(rq->avg_dl.util_avg); //获取并累加dl task rq的util_avg if (unlikely(used >= max)) //如果util_avg超过max,则说明util满了? return 1; free = max - used; //计算free util = 最大capacity - rt的util_avg - dl的util_avg return scale_irq_capacity(free, irq, max); //(max - rt的util_avg - dl的util_avg) * (max - irq) /max }
(2-7)将sd、rd与cpu rq绑定起来
- for循环从当前sd向parent遍历,但是会过滤DIE level sd----------当前平台也就是只判断MC level的sd
- 首先判断是否要对parent sd销毁?其中有2层判断是否需要销毁parent sd:一层是判断parent sd本身是否已满足销毁条件,另一层是判断与child sd对比,是否有必要对parent sd进行销毁
- 先取出parent(链表中先断开连接,将parent->parent和child链接),根据parent sd如有flag:SD_PREFER_SIBLING,将其传递到child sd。-------这2步,在当前平台都不满足。所以仅仅指挥断开parent sd、child sd的链接
- 销毁parent sd,参考(2-7-2)
- 再对child sd也同样进行销毁判断,以及进行销毁
前面这些都是将新的sd进行”修剪“,去掉一些不影响调度的sd层级,之后就会将新的sd绑定到rd上:
- (2-7-3)将新root domain与cpu_rq绑定起来,旧rd会被free
- 更新rq->sd为新的sd;将当前cpu更新进sd_sysctl_cpus的cpu mask中
- (2-7-5)将原先的tmp sd给销毁
- 最后更新per_cpu相关的sd变量
/* * Attach the domain 'sd' to 'cpu' as its base domain. Callers must * hold the hotplug lock. */ static void cpu_attach_domain(struct sched_domain *sd, struct root_domain *rd, int cpu) { struct rq *rq = cpu_rq(cpu); struct sched_domain *tmp; /* Remove the sched domains which do not contribute to scheduling. */ for (tmp = sd; tmp; ) { struct sched_domain *parent = tmp->parent; //过滤没有parent sd的sd,即过滤DIE level sd if (!parent) break; if (sd_parent_degenerate(tmp, parent)) { //(2-7-1)判断是否要对parent sd进行degenerate操作 tmp->parent = parent->parent; //首先断开parent' sd的链表关系 if (parent->parent) //根据parent->parent是否存在,将parnet->parent的child链接到tmp sd parent->parent->child = tmp; /* * Transfer SD_PREFER_SIBLING down in case of a * degenerate parent; the spans match for this * so the property transfers. */ if (parent->flags & SD_PREFER_SIBLING) //因为当前平台只有DIE level有这个flag,又因为DIE level没有parent sd,所以在上面已经过滤了,这里的条件不会满足 tmp->flags |= SD_PREFER_SIBLING; destroy_sched_domain(parent); //(2-7-2)销毁'parent' sd } else //如果不需要degenerate操作 tmp = tmp->parent; //则直接更新tmp,准备遍历下一层level } if (sd && sd_degenerate(sd)) { //判断sd是否需要进行degenerate tmp = sd; sd = sd->parent; destroy_sched_domain(tmp); //销毁sd,同上 if (sd) //如果被销毁的sd有parent sd,那么就将parent sd的->child置为NULL sd->child = NULL; } sched_domain_debug(sd, cpu); //打印sd attach的debug信息 rq_attach_root(rq, rd); //(2-7-3) 将新的root doamin与cpu rq绑定在一起 tmp = rq->sd; rcu_assign_pointer(rq->sd, sd); //将新sd与rq->sd绑定起来 dirty_sched_domain_sysctl(cpu); //(2-7-4)更新sd_sysctl_cpus的cpu mask destroy_sched_domains(tmp); //(2-7-5)将tmp sd销毁 update_top_cache_domain(cpu); //(2-7-6)更新cpu的sd相关的per_cpu变量 }
(2-7-1)判断是否要对parent sd进行degenerate操作?sd_parent_degenerate函数:return 1,则表示要进行销毁;return 0,则不需要进行销毁
- 先针对sd本身是否可以进行销毁进行判断,标准参考(2-7-1-1)如果sd_degenerate函数return 1,则说明这个parent sd需要销毁;反之则不需要销毁
- 如果child sd和parent sd的范围不相同,则return 0;反之,则继续进行判断
- 如果parent sd level下只有一个sg,那么就先清空一些flags。再判断child sd和parent sd的flag是否一致?如果一致,则return 1;不一致,则return 0
static int sd_parent_degenerate(struct sched_domain *sd, struct sched_domain *parent) { unsigned long cflags = sd->flags, pflags = parent->flags; if (sd_degenerate(parent)) //(2-7-1-1) 判断parent sd是否有必要做下面的步骤来degenerate判断 return 1; if (!cpumask_equal(sched_domain_span(sd), sched_domain_span(parent))) //判断MC和DIE level是否sd范围一样?当前平台不一样 return 0; //所以,一般这里就会return 0 /* Flags needing groups don't count if only 1 group in parent */ if (parent->groups == parent->groups->next) { //如果parent sg只有一个了,那么下面这些flag,就不需要了 pflags &= ~(SD_LOAD_BALANCE | SD_BALANCE_NEWIDLE | SD_BALANCE_FORK | SD_BALANCE_EXEC | SD_ASYM_CPUCAPACITY | SD_SHARE_CPUCAPACITY | SD_SHARE_PKG_RESOURCES | SD_PREFER_SIBLING | SD_SHARE_POWERDOMAIN); if (nr_node_ids == 1) pflags &= ~SD_SERIALIZE; } if (~cflags & pflags) //判断MC level的flag与DIE level修改后的flag是否一致? return 0; //如果一致,则return 1;不一致,则return 0 return 1; }
(2-7-1-1) 判断parent sd是否有必要做下面的步骤来degenerate判断
- 如果DIE level sd的范围内只有1个cpu,则表示需要销毁sd-------这么理解:DIE leve都只有一个cpu了,那也就没有MC level sd存在的必要了
- 如果sd中包含一些flag,并且sd至少有2个sg,这种情况下不能销毁sd。-------实际当前平台DIE level,会有2个sg,所以这里就会return 0(暂只考虑全核都开的情况)
- 如果sd包含SD_WAKE_AFFINE(flag意义:任务唤醒时,放置到临近的cpu),则return 0。-------目前平台所有sd都有这个flag
- 如果上面3个条件都不满足,则return 1
return 0表示不需要进行sd销毁;return 1表示要进行sd销毁。
static int sd_degenerate(struct sched_domain *sd) { if (cpumask_weight(sched_domain_span(sd)) == 1) //如果DIE level sd中,只有一个cpu(当前平台有8个cpu),就return 1 return 1; /* Following flags need at least 2 groups */ if (sd->flags & (SD_LOAD_BALANCE | //当前DIE level中会由部分flag,但同时sg有2个,所以会return 0 SD_BALANCE_NEWIDLE | SD_BALANCE_FORK | SD_BALANCE_EXEC | SD_SHARE_CPUCAPACITY | SD_ASYM_CPUCAPACITY | SD_SHARE_PKG_RESOURCES | SD_SHARE_POWERDOMAIN)) { if (sd->groups != sd->groups->next) return 0; } /* Following flags don't use groups */ if (sd->flags & (SD_WAKE_AFFINE)) //所有sd都这个flag,所以这里都会return 0 return 0; return 1; }
(2-7-2)销毁'parent' sd:主要就是依次释放申请的空间:sd->groups、sd->shared、sd本身。
static void destroy_sched_domain(struct sched_domain *sd) { /* * A normal sched domain may have multiple group references, an * overlapping domain, having private groups, only one. Iterate, * dropping group/capacity references, freeing where none remain. */ free_sched_groups(sd->groups, 1); //(2-7-2-1)free sd对应的sg结构体 if (sd->shared && atomic_dec_and_test(&sd->shared->ref)) //判断是否有sds结构,并且sds的引用==1时。就free掉sds kfree(sd->shared); kfree(sd); //free sd结构体 }
(2-7-2-1)free sd对应的sg结构体:do-while循环中会遍历sg循环链表,将sd->sgc也会释放掉,最后再释放sg本身
static void free_sched_groups(struct sched_group *sg, int free_sgc) { struct sched_group *tmp, *first; if (!sg) return; first = sg; do { //do-while循环,完整遍历sg循环链表元素一次 tmp = sg->next; if (free_sgc && atomic_dec_and_test(&sg->sgc->ref)) //检查引用数是否为1,判断是否要free sgc结构 kfree(sg->sgc); //free sgc结构体 if (atomic_dec_and_test(&sg->ref)) //检查sg结构应用数是否为1 kfree(sg); //free sg结构体 sg = tmp; } while (sg != first); }
(2-7-3) 将新的root doamin与cpu rq绑定在一起
- 如果cpu rq上原先绑定过roo domain,那么就将其作为old rd
- 通过old rd判断rq还处于online,那就先将rq offline
- 清空old rd中对应的当前rq的cpu;当old rd不在被使用时,将old rd置为NULL;如果old rd引用不为0,则后面要对其进行free-------这一步是对old rd的剥离
- 将新的rd,赋给rq->rd,并将rq对应的cpu添加到rd的span范围中。--------这里完成root domain的更新
- 判断如果rq->cpu是active的状态,那么就要将rq online
- 最后根据所需,对old rd进行free
void rq_attach_root(struct rq *rq, struct root_domain *rd) { struct root_domain *old_rd = NULL; unsigned long flags; raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&rq->lock, flags); if (rq->rd) { old_rd = rq->rd; //暂存原先的rd if (cpumask_test_cpu(rq->cpu, old_rd->online)) //如果原先的rd还处于online set_rq_offline(rq); //(2-7-3-1)则先让rq offline cpumask_clear_cpu(rq->cpu, old_rd->span); //在old rd中去掉offline rq对应的cpu /* * If we dont want to free the old_rd yet then * set old_rd to NULL to skip the freeing later * in this function: */ if (!atomic_dec_and_test(&old_rd->refcount)) //判断old rd的引用是否为0(代表是否需要free old rd) old_rd = NULL; //设置为NULL后,后面流程就不会free old rd } atomic_inc(&rd->refcount); //将rd引用+1 rq->rd = rd; //更新rq->rd为新的rd cpumask_set_cpu(rq->cpu, rd->span); //将rq->cpu为新rd的范围 if (cpumask_test_cpu(rq->cpu, cpu_active_mask)) //如果rq->cpu都是active的 set_rq_online(rq); //(2-7-3-2)那么就将rq set为online raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&rq->lock, flags); if (old_rd) //根据上面是否设置old rd为NULL,确定是否free old rd call_rcu(&old_rd->rcu, free_rootdomain); //(2-7-3-3)free old rd }
(2-7-3-1)让rq offline:依次对rq中的所有class调用rq_offline接口,并对,再置rq->online为0
void set_rq_offline(struct rq *rq) { if (rq->online) { //确认rq online const struct sched_class *class; for_each_class(class) { //遍历所有调度class if (class->rq_offline) //判断对应class rq_offline是否存在 class->rq_offline(rq); //(2-3-7-1-1)调用class对应的rq_offline,这里以cfs rq为例 } cpumask_clear_cpu(rq->cpu, rq->rd->online); //将rq的rq online mask中去掉当前rq对应的cpu rq->online = 0; //将rq online置为0 } }
(2-3-7-1-1)调用class对应的rq_offline,这里以cfs rq为例
static void rq_offline_fair(struct rq *rq) { update_sysctl(); //更新sysctl参数 /* Ensure any throttled groups are reachable by pick_next_task */ unthrottle_offline_cfs_rqs(rq); //(2-3-7-1-1-1)把rq中的所有cfs_rq都解除带宽限制 }
(2-3-7-1-1-1)把rq中的所有cfs_rq都解除带宽限制(这部分其实属于cfs带宽限制的范畴,不深入分析。之前有看过代码,但是没有记录下来。以后有时间再整理)
/* cpu offline callback */ static void __maybe_unused unthrottle_offline_cfs_rqs(struct rq *rq) { struct task_group *tg; lockdep_assert_held(&rq->lock); rcu_read_lock(); list_for_each_entry_rcu(tg, &task_groups, list) { //遍历所有task group struct cfs_rq *cfs_rq = tg->cfs_rq[cpu_of(rq)]; //取出tg中对应cpu的cfs_rq if (!cfs_rq->runtime_enabled) //过滤已关闭带宽限制功能的cfs_rq continue; /* * clock_task is not advancing so we just need to make sure * there's some valid quota amount */ cfs_rq->runtime_remaining = 1; //确保有有效的配额值 /* * Offline rq is schedulable till CPU is completely disabled //offline rq在take_cpu_down()中完全disable CPU前,仍然可以被调度 * in take_cpu_down(), so we prevent new cfs throttling here. //所以,我们把新的cfs限制在这里。 */ cfs_rq->runtime_enabled = 0; //关闭cfs rq的带宽限制功能 if (cfs_rq_throttled(cfs_rq)) //判断cfs_rq的是否处于带宽被限制状态 unthrottle_cfs_rq(cfs_rq); //解除带宽限制 } rcu_read_unlock(); }
(2-7-3-2)将rq set为online,其实就是做set offline的相反操作
void set_rq_online(struct rq *rq) { if (!rq->online) { const struct sched_class *class; cpumask_set_cpu(rq->cpu, rq->rd->online); //将rq->cpu设置到rq->rd->online的cpu mask中,表示对应rd中的online cpu增加了 rq->online = 1; //将rq设为online for_each_class(class) { //遍历所有调度class if (class->rq_online) //判断对应class rq_offline是否存在 class->rq_online(rq); //(2-3-7-2-1)调用class对应的rq_offline,这里以cfs rq为例 } } }
(2-3-7-2-1)调用class对应的rq_offline,这里以cfs rq为例
static void rq_online_fair(struct rq *rq) { update_sysctl(); //更新sysctl参数 update_runtime_enabled(rq); //(2-3-7-2-1-1)更新cfs带宽限制的开关和配置 }
(2-3-7-2-1-1)更新cfs带宽限制的开关和配置
/* * Both these CPU hotplug callbacks race against unregister_fair_sched_group() * * The race is harmless, since modifying bandwidth settings of unhooked group * bits doesn't do much. */ /* cpu online calback */ static void __maybe_unused update_runtime_enabled(struct rq *rq) { struct task_group *tg; lockdep_assert_held(&rq->lock); rcu_read_lock(); list_for_each_entry_rcu(tg, &task_groups, list) { //遍历所有task group struct cfs_bandwidth *cfs_b = &tg->cfs_bandwidth; //获取tg对应的cfs带宽限制结构体 struct cfs_rq *cfs_rq = tg->cfs_rq[cpu_of(rq)]; //取出tg中对应cpu的cfs_rq raw_spin_lock(&cfs_b->lock); cfs_rq->runtime_enabled = cfs_b->quota != RUNTIME_INF; //根据cfs带宽限制的配额有没有限制,设置cfs_rq带宽限制是否打开 raw_spin_unlock(&cfs_b->lock); } rcu_read_unlock(); }
(2-7-3-3)free old rd:主要对rd结构提的各个成员依次free,最后free rd自身
static void free_rootdomain(struct rcu_head *rcu) { struct root_domain *rd = container_of(rcu, struct root_domain, rcu); //通过rcu获取要free的rd cpupri_cleanup(&rd->cpupri); //free rd结构体中的相关成员 cpudl_cleanup(&rd->cpudl); free_cpumask_var(rd->dlo_mask); free_cpumask_var(rd->rto_mask); free_cpumask_var(rd->online); free_cpumask_var(rd->span); free_pd(rd->pd); kfree(rd); //最后free rd本身 }
(2-7-4)更新sd_sysctl_cpus的cpu mask:将cpu添加进去(暂不清楚这个cpu mask有什么用处?)
void dirty_sched_domain_sysctl(int cpu) { if (cpumask_available(sd_sysctl_cpus)) __cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, sd_sysctl_cpus); }
(2-7-5)将tmp sd销毁:从sd向其parent遍历,进行逐层销毁
static void destroy_sched_domains(struct sched_domain *sd) { if (sd) call_rcu(&sd->rcu, destroy_sched_domains_rcu); //如果sd是否存在,则进行销毁 }
static void destroy_sched_domains_rcu(struct rcu_head *rcu) { struct sched_domain *sd = container_of(rcu, struct sched_domain, rcu); while (sd) { struct sched_domain *parent = sd->parent; //从MC->DIE遍历sd destroy_sched_domain(sd); //并销毁sd,参照(2-7-2) sd = parent; } }
(2-7-6)更新cpu的sd相关的per_cpu变量
static void update_top_cache_domain(int cpu) { struct sched_domain_shared *sds = NULL; struct sched_domain *sd; int id = cpu; int size = 1; sd = highest_flag_domain(cpu, SD_SHARE_PKG_RESOURCES); //找到该cpu所在的最高的、包含这个flag的domain。即 MC level if (sd) { id = cpumask_first(sched_domain_span(sd)); //取出该sd中第一个cpu size = cpumask_weight(sched_domain_span(sd)); //获取该sd中cpu的数量 sds = sd->shared; //获取sd的sds } rcu_assign_pointer(per_cpu(sd_llc, cpu), sd); //更新sd_lcc = sd per_cpu(sd_llc_size, cpu) = size; //更新sd_lcc_size = sd中cpu数量 per_cpu(sd_llc_id, cpu) = id; //更新sd_lcc_id = sd中第一个cpu rcu_assign_pointer(per_cpu(sd_llc_shared, cpu), sds); //更新sd_llc_shared = sd->sds sd = lowest_flag_domain(cpu, SD_NUMA); //当前平台不支持NUMA rcu_assign_pointer(per_cpu(sd_numa, cpu), sd); //所以最后这个sd是DIE level,但是其本身也没有什么意义 sd = highest_flag_domain(cpu, SD_ASYM_PACKING); //当前平台不支持SMT rcu_assign_pointer(per_cpu(sd_asym_packing, cpu), sd); //所以最后这个sd是DIE level,但是其本身也没有什么意义 sd = lowest_flag_domain(cpu, SD_ASYM_CPUCAPACITY); //获取cpu最低的、包含这个flag的domain。即 DIE level rcu_assign_pointer(per_cpu(sd_asym_cpucapacity, cpu), sd); }
(2-8)根据函数最上面建立拓扑、以及申请root domain结果,释放相应的空间
static void __free_domain_allocs(struct s_data *d, enum s_alloc what, const struct cpumask *cpu_map) { switch (what) { case sa_rootdomain: //一切正常情况下是这个分支 if (!atomic_read(&d->rd->refcount)) //根据rd的引用,决定是否还需要保留root domain free_rootdomain(&d->rd->rcu); //如不需要,则进行free /* Fall through */ case sa_sd: //申请root domain失败的情况 free_percpu(d->sd); //free d->sd /* Fall through */ case sa_sd_storage: //建立拓扑结构失败、或者申请d->sd 失败的情况 __sdt_free(cpu_map); //free整个cpu_map中所有cpu的拓扑结构,并遍历free所有per_cpu的sdd->* /* Fall through */ case sa_none: break; } }
register_sched_domain_sysctl(); //(3)注册proc/sys/kernel/sched_domain目录,并完善其中相关sysctl控制参数
-----这部分暂不准备解析了,都是一些sysfs接口。有兴趣的可以参考这位大佬博主的blog:https://blog.csdn.net/wukongmingjing/article/details/100043644
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wukongmingjing/article/details/82426568