Description
如今的道路收费发展很快。道路的密度越来越大,因此选择最佳路径是很现实的问题。城市的道路是双向的,每条道路有固定的旅行时间以及需要支付的费用。
路径是连续经过的道路组成的。总时间是各条道路旅行时间的和,总费用是各条道路所支付费用的总和。一条路径越快,或者费用越低,该路径就越好。严格地说,如果一条路径比别的路径更快,而且不需要支付更多费用,它就比较好。反过来也如此理解。如果没有一条路径比某路径更好,则该路径被称为最小路径。
这样的最小的路径有可能不止一条,或者根本不存在路径。
问题:读入网络,计算最小路径的总数。费用时间都相同的两条最小路径只算作一条。你只要输出不同种类的最小路径数即可。
Input
第一行有四个整数,城市总数 (n),道路总数 (m),起点和终点城市 (s),(e);
接下来的 (m) 行每行描述了一条道路的信息,包括四个整数,两个端点 (p),(r),费用 (c),以及时间 (t);
两个城市之间可能有多条路径连接。
Output
仅一个数,表示最小路径的总数。
Sample Input
4 5 1 4
2 1 2 1
3 4 3 1
2 3 1 2
3 1 1 4
2 4 2 4
Sample Output
2
HINT
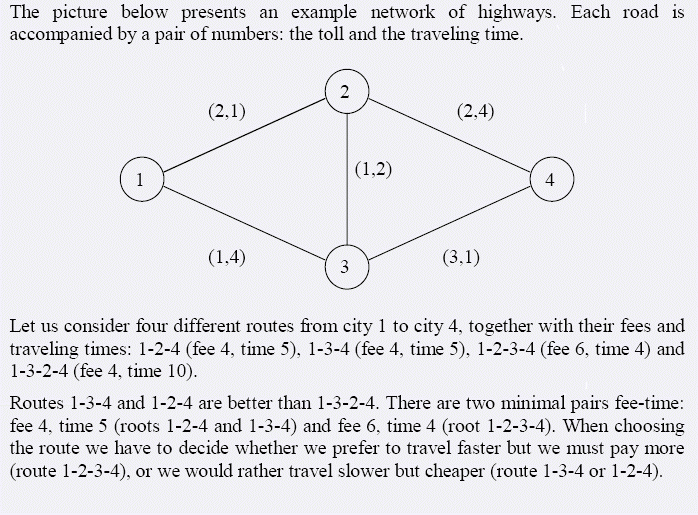
题解
首先,题目中对最小路径的描述有些歧义,实际上最小路径 (u) 应满足不存在路径 (v) 使 (cost[v] leq cost[u]),(len[v] leq len[u])
这可以说是一道 (DP) 题,也可以说是一道分层图 (SPFA)(本质是一样的)
分层图 (SPFA) 要好写一些。
设 (f[i][j]) 表示走到第 (i) 个结点,费用为 (j) 时的最短路
“转移”就是 (f[k][j+cost]=min(f[k][j+cost],f[i][j]+len)) ,不断更新
之后类似二维偏序,用树状数组就行了。
代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 105;
typedef pair<int,int> P;
struct node {
int v,len,cost;
node *next;
}pool[N*6],*h[N];
int cnt;
void addedge(int u,int v,int len,int cost){
node *p=&pool[++cnt],*q=&pool[++cnt];
p->v=v;p->next=h[u];h[u]=p;p->len=len;p->cost=cost;
q->v=u;q->next=h[v];h[v]=q;q->len=len;q->cost=cost;
}
int n,m,s1,s2,S,T;
int f[N][N*N],vis[N][N*N];
queue<P> que;
void spfa(){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<=s1;j++) f[i][j]=1e8;
f[S][0]=0; vis[S][0]=1; que.push(P(S,0));
while(!que.empty()){
int u=que.front().first,c=que.front().second,v;
que.pop();
vis[u][c]=0;
s2=max(s2,f[u][c]);
if(u==T) continue;
for(node *p=h[u];p;p=p->next)
if(c+p->cost<=s1 && f[v=p->v][c+p->cost]>f[u][c]+p->len){
f[v][c+p->cost]=f[u][c]+p->len;
if(!vis[v][c+p->cost]){
vis[v][c+p->cost]=1;
que.push(P(v,c+p->cost));
}
}
}
}
int d[N*N];
int lowbit(int x) { return x&(-x); }
int add(int x,int y){
while(x<=s2){
d[x]+=y;
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int sum(int x){
int ret=0;
while(x){
ret+=d[x];
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int x,y,len,c,ans=0;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&S,&T);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&c,&len);
addedge(x,y,len,c);
s1=max(s1,c);
}
s1*=(n-1);
spfa();
s2++;
for(int i=0;i<=s1;i++)
if(f[T][i]!=1e8){
if(sum(f[T][i]+1)==0) ans++;
add(f[T][i]+1,1);
}
printf("%d
",ans);
return 0;
}