今日学习总结:
一、程序分支控制
1.单分支结构
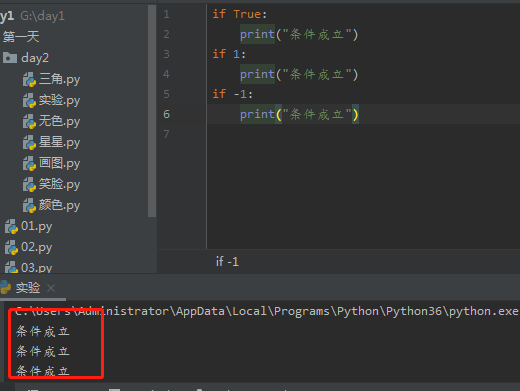
if True: #这是一个布尔值 print("条件成立") if 1: #这是一个布尔值 print("条件成立") if -1: #这是一个布尔值 print("条件成立")
2.二分支结构:if else 语句
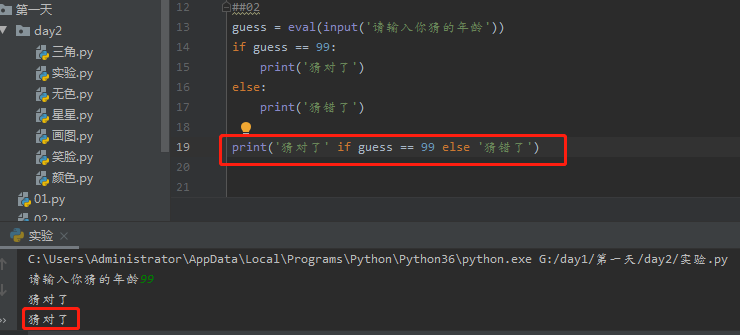
guess = eval(input('请输入你猜的年龄')) if guess == 99: print('猜对了') else: print('猜错了')
print('猜对了' if guess == 99 else '猜错了') #if else语句合并写
.
3.多支结构
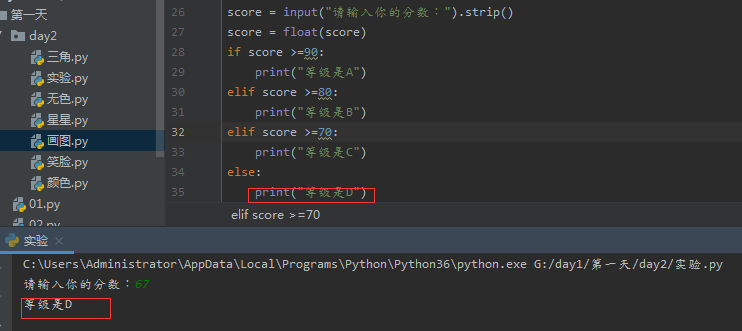
score = input("请输入你的分数:").strip() score = float(score) if score >=90: print("等级是A") elif score >=80: print("等级是B") elif score >=70: print("等级是C") else: print("等级是D")
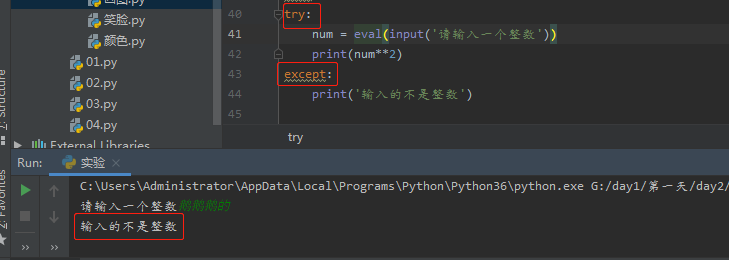
4.异常处理结构:try except
num = eval(input('请输入一个整数')) print(num**2)

用try except 来去除错误
try: num = eval(input('请输入一个整数')) print(num**2) except: print('输入的不是整数')
二、案例:国内身体质量指标数BMI
公式:bmi=体重/身高^2
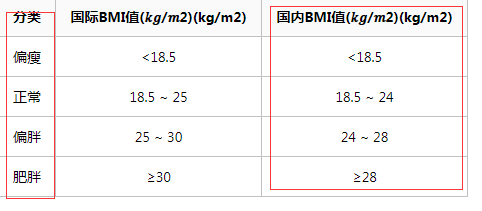
#hight,weight = eval(input('请输入您的身高/米 体重/kg'))
hight = eval(input('请输入您的身高/米:')) weight = eval(input('请输入您的体重/kg:')) bmi = weight/pow(hight, 2) print('BMI 数值为:{:.2f}'.format(bmi)) if bmi<18.5: print('BMI国内指标为:偏瘦') elif bmi <24: print('BMI国内指标为:正常') elif 24 <= bmi <28: print('BMI国内指标为:偏胖') else: print('BMI国内指标为:肥胖')
三、程序的循环结构
1.遍历循环结构:
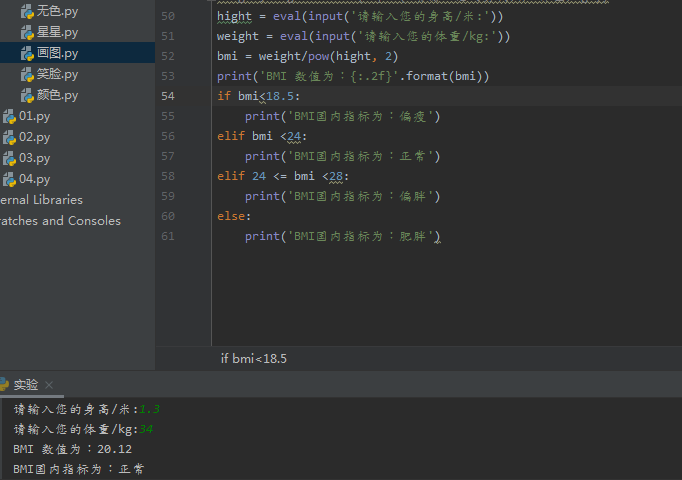
01.整数遍历循环: for i in range 结构的遍历循环,是指从遍历结构中逐一提取元素
for i in range(5): #for in 遍历结构 print(i) print('hello',i) for i in range(1,6): #for in 遍历结构,遍历1,2,3,4,5 因为不顾尾。 print(i) print('hello', i)
for i in range(1,6,2): #for in 遍历结构,2表示是步长
print('hello',i)
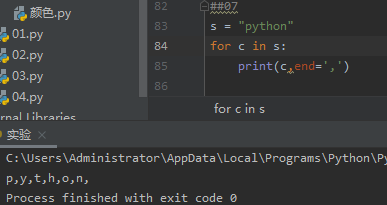
02. 字符串遍历循环:for c in s 遍历字符串的每个字符,产生循环
s = "python" for c in s: print(c,end=',') #end='' 是去掉print自带的换行
或者
for c in ('python'):
print(c,end=',')
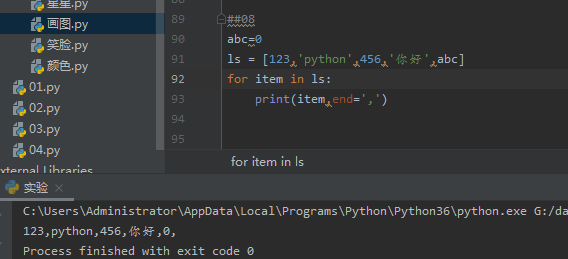
03.列表遍历循环:for item in ls ls是一个列表,遍历其里面的每个元素,产生循环
abc=0 ls = [123,'python',456,'你好',abc] for item in ls: print(item,end=',')
2.循环语句
01.无限循环,是指有条件控制的。如果条件无限,则循环无限。while语句。
a=3 while a>0: a=a-1 print(a) 输出结果: 2 1 0 a=3 while a>0: a=a+1 print(a) #出现死循环,因为条件永远成立
02.循环控制的break 语句 :跳出并结束当前整个循环 和 continue语句 :结束当初循环,继续执行后续次数循环
与for 循环连用
for c in "prthon": if c=='t': break print(c,end=",") 输出结果:p,r, for c in "prthon": if c=='t': continue print(c,end=",") 输出结果:p,r,h,o,n,
与while 循环连用
s = 'python' while s !="": for c in s: print(c,end=',') s=s[:-1] #因为[:-1]不顾尾,所以s字符串的长度在不断减少 #输出结果为:p,y,t,h,o,n,p,y,t,h,o,p,y,t,h,p,y,t,p,y,p, s = 'python' while s !="": for c in s: if c =='t': break #break结束的是离它最近的for循环 结束的不是while循环。if是条件语句 print(c,end=',') s=s[:-1] 输出结果为:p,y,p,y,p,y,p,y,p,y,p,
四、函数:一系列功能的集合体,类似于工具。
1.无参数函数
def index(): print("你好") index()
2.有参数函数
usename = "sean" password = "123" def login(usename, password): name = input("请输入您的名字:") pwd = input("请输入您的密码:") if name == usename and pwd == password: print('登录成功') else: print('登录s失败') login(usename, password)
3.空函数
def login(): 登录
pass
def register(): 注册
pass
def check_balance(): 查看银行账户
pass
def check_user(): 查看用户
pass
def logout(): 登出
pass
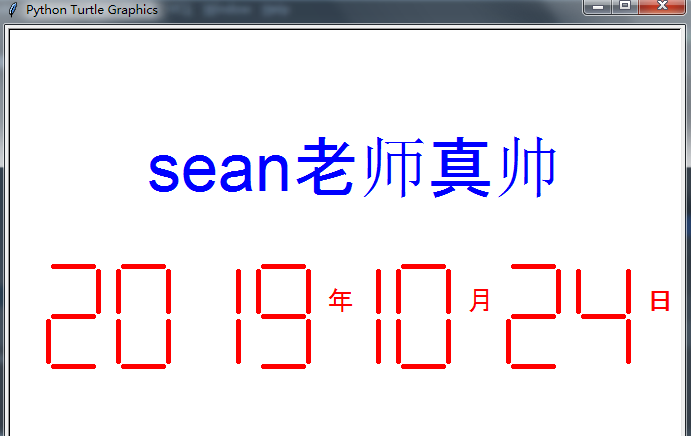
五、七段数码管绘制
函数的调用和嵌套的使用
import turtle import time t = turtle.Pen() def drawGap(): t.up() t.fd(5) def drawLine(flag): drawGap() if flag: t.down() else: t.up() t.fd(40) drawGap() t.right(90) def drawDight(num): drawLine(True) if num in [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9] else drawLine(False) drawLine(True) if num in [0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] else drawLine(False) drawLine(True) if num in [0, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9] else drawLine(False) drawLine(True) if num in [0, 2, 6, 8] else drawLine(False) t.left(90) drawLine(True) if num in [0, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9] else drawLine(False) drawLine(True) if num in [0, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] else drawLine(False) drawLine(True) if num in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 9] else drawLine(False) t.up() t.left(180) t.fd(20) def get_data(data): for i in data: if i=="/": t.write('年', font=("Arial", 20, "normal")) elif i=="-": t.write('月', font=("Arial", 20, "normal")) t.up() t.fd(40) t.down() elif i=="+": t.write('日', font=("Arial", 20, "normal")) else: drawDight(eval(i)) def mian(): t.up() t.backward(300) t.down() t.pencolor('red') t.pensize(5) get_data(time.strftime('%Y/%m-%d+', time.gmtime())) t.hideturtle() t.up() t.fd(-500) t.left(90) t.fd(110) t.right(90) t.pencolor('blue') t.write('sean老师真帅', font=("Arial", 50, "normal")) mian() turtle.mainloop()