字串加密:
请编写一个程序,使用上述算法加密或解密用户输入的英文字串要求设计思想、程序流程图、源代码、结果截图。
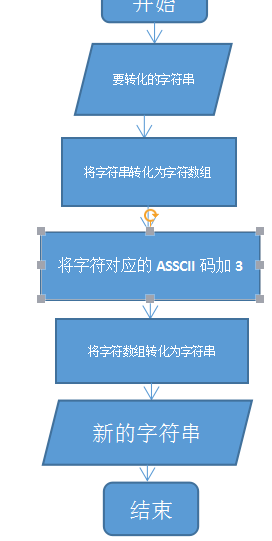
设计思想:先输入一个字符串,调用toCharArray()函数将它转化为字符数组,在利用while循环将每个字符对应的ASSCII码加3,最后再将字符数组转化为字符串输出。
程序流程图:
源代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class mima
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.print("请输入要加密的字符串:");
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
String s=scanner.nextLine();
char[] l=s.toCharArray();
System.out.print("加密后的字符串为:");
for(int i=0;i<l.length;i++)
{
int temp=l[i];
temp=temp+3;
l[i]=(char)temp;
System.out.print(l[i]);}
}
}
结果截图:

动手动脑:
1.请运行以下示例代码StringPool.java,查看其输出结果。如何解释这样的输出结果?从中你能总结出什么?

输出结果:
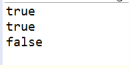
结论:s0,s1,s2都存储字符串Hello,存储地址相同,所以输出的前两个结果为true,而用new是创建了一个新的对象,即使存储的字符串相同,对象的地址不相同,用“==”比较时比较的是地址,所以输出为false。
2.为什么会有这样的输出结果,从中你又能总结什么?

结论:“==”判断两个对象的地址是否相同,s1与s2是两个不同的对象,所以第一个输出false。String对象的内容是只读的,使用“+”修改s1的值,是得到了一个信的字符串对象,变成“ab”,但它与原来s1所引用的对象a无关,所以s1==ab为false,equals函数是比较内容是否相同,s1的值为ab,所以最后输出为true。
3.请查看String.equals()方法的实现代码,注意学习其实现方法。
public boolean equals(Object anObject){
if(this==anObject){
return true;
}
if(anObject instanceof String){
String anotherString =(String)anObject;
int n=value.length;
if(n==anotherString.value.length){
char v1[]=value;
char v2[]=anotherString .value;
int i=0;
while(n-- !=0){
if(v1[i] !=v2[i])
return false;
i++
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
结论:首先判断是否为同一对象,再判断是否都为字符串,再判断字符串的长度是否相等,最后通过循环判断每个对应的字符是否相等,都符合即为相等。
4.String类的方法可以连续调用:
String str="abc"; String result=str.trim().toUpperCase().concat("defg");
请阅读JDK中String类上述方法的源码,模仿其编程方式,编写一个MyCounter类,它的方法也支持上述的“级联”调用特性,其调用示例为: MyCounter counter1=new MyCounter(1); MyCounter counter2=counter1.increase(100).decrease(2).increase(3);
public class MyCounter {
int i;
MyCounter(int n){
i=n;
}
public MyCounter increase(int n)
{
this.i=this.i+n;
return this;
}
public MyCounter decrease(int n)
{
this.i=this.i-n;
return this;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
MyCounter counter1=new MyCounter(1);
MyCounter counter2=counter1.increase(100).decrease(2).increase(3);
System.out.println("counter2.i="+counter2.i);
}
}
5.整理String类的Length()、charAt()、 getChars()、replace()、toLowerCase()、toCharArray()
Length():获取字符串长度,是针对数组说的。String a=”macaoyuan”; System.out.println(a.length());输出结果为9.
charAt():取字符串中指定位置的字符。String str=”abcdefg”; System.out.println(str.CharAt(3));输出结果为c。
getChars(int sourceStart,int sourceEnd,char target[],int targetStart): 将当前字符串从sourceStart到sourceEnd-1位置上的字符复制到字符数组target中,target的下标由targeStart指定。
class GetcharDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
String s=’This is a demo of getChar’;
int start=10;
int end=14;
char buf[]=new char[4];
s.getChars(start,end,buf,0);
System.out.println(buf);
}
}
输出demo.
replace(char oldChar,char newChar):替换后生成的新字符串。Admin=Trim(Replace(Request.Form(“admin”),””,””));即是将admin中的单引号替换为空,消除单引号。
toLowerCase():大写的换小写,小写的换大写。var str="Hello World!"
document.write(str.toLowerCase()) “Hello World!”将用小写字母来输出。
toCharArray():字符串转换为字符数组。 String s = "AaBbCcDd"; var chars = s.ToCharArray();
字符串的每个字符将被提取到数组中,将在字符数组中显示原始字符串和元素。