阅读目录

进程: 进程就是一个正在执行的过程,或者说一个软件的运行过程 进程是一个虚拟的概念 进程的概念起源:操作系统 操作系统发展史 批处理操作系统:(串行) 把程序员的程序攒成一堆 然后批处理系统读一道程序到内存然后执行 执行完毕后输出,然后才能读入下一道程序 多道技术: 产生背景:在单核下实现并发 两大核心点: 1、空间的复用 多道程序同时读入内存中。等到被 CPU执行,即产生了多个进程 强调:进程之间的内存空间是互相隔离的,而且这种隔离栅物理级别 2、时间的复用 复用CPU的时间 切: 1、正在执行的进程遇到I/O操作(提升效率) 2、正在执行的进程,占用时间过长, 或优先级更高的进程抢走的CPU执行权限(降低效率) 并发:本质是切换+保存状态 并行 串行:一个进程正在使用CPU,其他进程均在等待(区别于阻塞) 阻塞:正在运行的进程,遇到I/O,被剥夺了CPU的使用权限 非阻塞
开启进程的目的:开启一个子进程,和主进程并发执行任务,同时子进程不影响主进程。
进程,操作系统(win,unix)里管理的单位:
win:父、子进程是各自不同的地址空间
unix:每开启一个子进程,子进程的初始数据,是主进程的一个副本
注意:在windows中Process()必须放到# if __name__ == '__main__':下

Since Windows has no fork, the multiprocessing module starts a new Python process and imports the calling module. If Process() gets called upon import, then this sets off an infinite succession of new processes (or until your machine runs out of resources). This is the reason for hiding calls to Process() inside if __name__ == "__main__" since statements inside this if-statement will not get called upon import. 由于Windows没有fork,多处理模块启动一个新的Python进程并导入调用模块。 如果在导入时调用Process(),那么这将启动无限继承的新进程(或直到机器耗尽资源)。 这是隐藏对Process()内部调用的原,使用if __name__ == “__main __”,这个if语句中的语句将不会在导入时被调用。
开启(申请)进程的两种方式:

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # @Time : 2018/04/24 10:29 4 # @Author : MJay_Lee 5 # @File : 02开启进程.py 6 # @Contact : limengjiejj@hotmail.com 7 8 import time 9 from multiprocessing import Process 10 11 def task(name): 12 print('%s is running' % name) 13 time.sleep(3) 14 print('%s is done' % name) 15 16 if __name__ == '__main__': 17 # 在windows系统上,开启子进程的操作一定要放到此步骤下面,unix则不用 18 # Process(target=task,kwargs={'name':'egon'}) 方式一 关键字赋值 19 p = Process(target=task,args=('egon',)) # 方式二,args传值是元组,勿忘逗号 20 p.start() # 想操作系统发送请求,操作系统会申请内存空进啊,然后把父进程的数据拷贝给子进程,作为子进程的初始状态 21 print('========主')

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # @Time : 2018/04/24 10:48 4 # @Author : MJay_Lee 5 # @File : 03开启进程方式二.py 6 # @Contact : limengjiejj@hotmail.com 7 8 import time 9 from multiprocessing import Process 10 11 class MyProcess(Process): 12 def __init__(self,name): 13 super(MyProcess,self).__init__() 14 self.name = name 15 def run(self): 16 print('%s is running' % self.name) 17 time.sleep(3) 18 print('%s is done' % self.name) 19 20 if __name__ == '__main__': 21 p = MyProcess('lmj') 22 p.start() 23 print('====>主')
父进程等待子进程结束:

1 import time 2 from multiprocessing import Process 3 4 def task(n): 5 print('%s is running' % n) 6 time.sleep(n) 7 8 if __name__ == '__main__': 9 p_list = [] 10 for i in range(1,4): 11 p = Process(target=task,args=(i,)) 12 p_list.append(p) 13 p.start() 14 15 for p in p_list: 16 p.join() 17 18 print('====>主') 19 20 """ 21 3 is running 22 2 is running 23 1 is running 24 ====>主 25 """
子进程ppid方法的认识:
https://segmentfault.com/q/1010000014562902?_ea=3668830

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # @Time : 2018/04/24 12:02 4 # @Author : MJay_Lee 5 # @File : 05进程对象????.py 6 # @Contact : limengjiejj@hotmail.com 7 8 # import time,os 9 # from multiprocessing import Process 10 # 11 # def task(): 12 # print('self:%s parent:%s' %(os.getpid(),os.getppid())) 13 # time.sleep(3) 14 # 15 # if __name__ == '__main__': 16 # p1 = Process(target=task,) 17 # p1.start() 18 # 19 # print(p1.pid) 20 # # print(p1.ppid) 21 # print('====>主',os.getpid()) 22 23 24 import time,os 25 from multiprocessing import Process 26 27 class Myprocess(Process): 28 def __init__(self,name): 29 super(Myprocess,self).__init__() 30 self.name = name 31 32 def run(self): 33 print('子进程:�33[1;32;40m%s�33[0m 父进程:�33[1;31;40m%s�33[0m' %(os.getpid(),os.getppid())) 34 print('系统调用执行子进程,等待3秒') 35 time.sleep(3) 36 37 @property 38 def ppid(self): 39 return os.getpid() 40 41 42 if __name__ == '__main__': 43 p1 = Myprocess('进程对象') 44 p1.start() 45 print('%s,的pid:�33[1;32;40m%s�33[0m' % (p1.name,p1.pid)) 46 print('%s,的ppid:�33[1;31;40m%s�33[0m' % (p1.name,p1.ppid)) 47 print('【主进程】:',os.getpid()) 48 time.sleep(5)
基于多进程实现并发的套接字通信
提示:需要在server.bind(('127.0.0.1',8080))之前添加一行
server.setsockopt(SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,1)

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # @Time : 2018/04/24 19:05 4 # @Author : MJay_Lee 5 # @File : server.py 6 # @Contact : limengjiejj@hotmail.com 7 8 import socket 9 import os 10 from multiprocessing import Process 11 12 server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) 13 server.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET,socket.SO_REUSEADDR,1) 14 server.bind(('127.0.0.1',8080)) 15 server.listen(5) 16 print('服务端已启动,子进程:[%s],父进程:[%s]'%(os.getpid(),os.getppid())) 17 18 def communication(conn,client_addr): 19 while True: 20 try: 21 msg = conn.recv(1024) 22 print(client_addr,'客户端消息:',msg.decode('utf-8')) 23 conn.send(msg.upper()) 24 except ConnectionResetError: 25 print(client_addr,'断开连接') 26 conn.close() 27 break 28 29 30 if __name__ == '__main__': 31 while True: 32 conn, client_addr = server.accept() 33 p = Process(target=communication,args=(conn,client_addr)) 34 p.start()

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # @Time : 2018/04/24 19:05 4 # @Author : MJay_Lee 5 # @File : client.py 6 # @Contact : limengjiejj@hotmail.com 7 8 import socket 9 import os 10 11 client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) 12 client.connect(('127.0.0.1',8080)) 13 print('客户端已启动,子进程:[%s],父进程:[%s]'%(os.getpid(),os.getppid())) 14 15 while True: 16 17 cmd = input('>>>:').strip() 18 if not cmd:continue 19 client.send(cmd.encode('utf-8')) 20 msg = client.recv(1024) 21 print('回复消息:',msg.decode('utf-8')) 22 23 client.close()
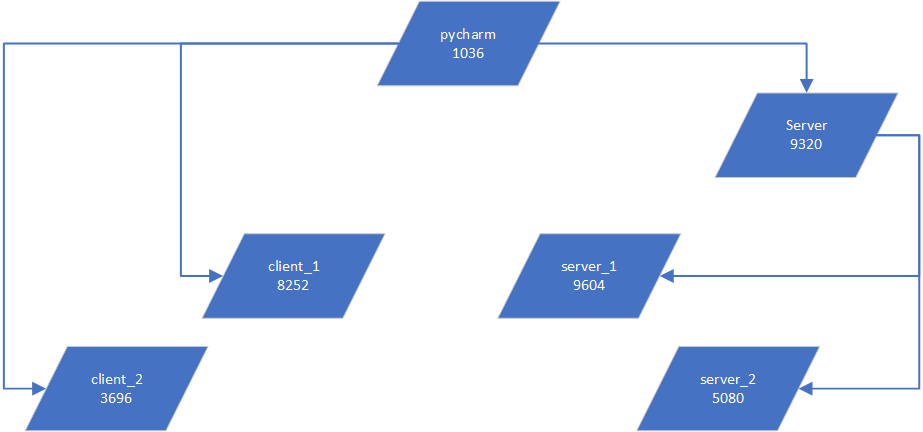
如下图:

整理pid图如下:

1 import time,random 2 from multiprocessing import Process,Lock 3 4 def task1(): 5 print('task_1 is running') 6 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) 7 print('task_1: work_1') 8 time.sleep(random.randint(1, 3)) 9 print('task_1 is done') 10 11 def task2(): 12 print('task_2 is running') 13 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) 14 print('task_2: work_2') 15 time.sleep(random.randint(1, 3)) 16 print('task_2 is done') 17 18 def task3(): 19 print('task_3 is running') 20 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) 21 print('task_3: work_3') 22 time.sleep(random.randint(1, 3)) 23 print('task_3 is done') 24 25 if __name__ == '__main__': 26 p1 = Process(target=task1) 27 p2 = Process(target=task2) 28 p3 = Process(target=task3) 29 30 p1.start() 31 p1.join() 32 p2.start() 33 p2.join() 34 p3.start() 35 p3.join() 36 37 print('主进程 running')

1 import time,random 2 from multiprocessing import Process,Lock 3 4 mutex = Lock() 5 6 def task1(lock): 7 lock.acquire() 8 print('task_1 is running') 9 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) 10 print('task_1: work_1') 11 time.sleep(random.randint(1, 3)) 12 print('task_1 is done') 13 lock.release() 14 15 def task2(lock): 16 lock.acquire() 17 print('task_2 is running') 18 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) 19 print('task_2: work_2') 20 time.sleep(random.randint(1, 3)) 21 print('task_2 is done') 22 lock.release() 23 24 def task3(lock): 25 lock.acquire() 26 print('task_3 is running') 27 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) 28 print('task_3: work_3') 29 time.sleep(random.randint(1, 3)) 30 print('task_3 is done') 31 lock.release() 32 33 34 if __name__ == '__main__': 35 p1 = Process(target=task1,args=(mutex,)) 36 p2 = Process(target=task2,args=(mutex,)) 37 p3 = Process(target=task3,args=(mutex,)) 38 39 p1.start() 40 p2.start() 41 p3.start() 42 43 print('主进程 running')
强调:必须是lock.acquire()一次,然后lock.release()释放一次,才能继续lock.acquire()
互斥锁 vs join 的区别之一:
大前提:二者的原理都是一样,都是将并发变成串行,从而保证有序
区别:join是按照人为指定的顺序执行,而互斥锁是进程平等竞争,谁先抢到谁执行

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # @Time : 2018/04/25 10:02 4 # @Author : MJay_Lee 5 # @File : 03抢票.py 6 # @Contact : limengjiejj@hotmail.com 7 8 import json 9 import time 10 import random 11 import os 12 from multiprocessing import Process,Lock 13 14 mutex = Lock() 15 16 def search(): 17 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) # 模拟网络延迟 18 with open('db.json','r',encoding='utf-8') as f: 19 dic = json.load(f) 20 print('%s当前票数:%s' % (os.getpid(),dic['count'])) 21 22 def get(): 23 with open('db.json','r',encoding='utf-8') as f: 24 dic = json.load(f) 25 if dic['count'] > 0: 26 dic['count'] -= 1 27 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) # 模拟“票数-1”结果写入数据库 28 with open('db.json','w',encoding='utf-8') as f: 29 json.dump(dic,f) 30 print('%s购票成功' % os.getpid()) 31 32 def task(lock): 33 search() # 查询功能是随时都可以进行,不需要约束于互斥锁,并行 34 lock.acquire() 35 get() # 购票过程取决于谁先抢到锁,串行 36 lock.release() 37 38 if __name__ == '__main__': 39 for i in range(10): 40 p = Process(target=task,args=(mutex,)) # 采用互斥锁,保证了公正性 41 p.start() 42 # p.join() # 此方法是人为指定顺序,此方法不合理

1 db.json的内容 2 {“count”:1} 3 4 运行结果: 5 "C:Program Filespythonanacondapython.exe" C:/my_python/classOn/classOn/0425/03抢票.py 6 500当前票数:1 7 7640当前票数:1 8 7780当前票数:1 9 8100当前票数:1 10 7664当前票数:1 11 7764当前票数:1 12 7564当前票数:1 13 7980当前票数:1 14 6316当前票数:1 15 3016当前票数:1 16 500购票成功 17 18 Process finished with exit code 0
进程之间通信,必须找到一种介质,该介质必须满足
1、是所有进程共享的
2、必须是内存空间

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # @Time : 2018/04/25 11:04 4 # @Author : MJay_Lee 5 # @File : 04IPC通信.py 6 # @Contact : limengjiejj@hotmail.com 7 8 import time 9 from multiprocessing import Process,Manager,Lock 10 11 mutex = Lock() 12 13 def task(dic,lock): 14 lock.acquire() 15 temp = dic['num'] 16 time.sleep(0.1) 17 dic['num'] -= 1 18 lock.release() 19 20 if __name__ == '__main__': 21 m = Manager() 22 dic = m.dict({'num':10}) # 造一个共享的内存地址 23 24 l = [] 25 for i in range(10): 26 p = Process(target=task,args=(dic,mutex)) 27 l.append(p) 28 p.start() 29 30 for p in l: 31 p.join() 32 33 print(dic)
附加:IPC机制要帮我们自动处理锁问题

1 from multiprocessing import Queue 2 3 # 队列 4 # 1、共享的空间 5 # 2、内存空间 6 # 3、自动帮我们处理锁定问题 7 q = Queue(3) 8 q.put('first') 9 q.put({'first':None}) 10 q.put('三') 11 12 # q.put(4) #阻塞 13 14 print(q.get()) 15 print(q.get()) 16 print(q.get())
强调:
1、队列用来存成进程之间沟通的消息,不应该过大
2、maxsize的值超过内存限制就变得毫无意义
该模型中包含两类重要的角色,三要素:
# 生产者:将负责造数据的任务比喻为生产者
# 消费者:接受生产者造出的数据来做进一步的处理,该类任务被比喻成消费者
# 队列:不一定是队列,只要是共享的空间,内存空间即可,但队列的好处是可以自动解决锁问题
#生产者消费者模型总结 #程序中有两类角色 一类负责生产数据(生产者) 一类负责处理数据(消费者) #引入生产者消费者模型为了解决的问题是: 平衡生产者与消费者之间的工作能力,从而提高程序整体处理数据的速度 #如何实现: 生产者<-->队列<——>消费者 #生产者消费者模型实现类程序的解耦和
什么时候用该模型:
# 程序中,出现明显的两类任务,一类任务是负责生产数据,另一类任务是负责处理生产产生的数据,如爬虫。
该模型的好处:
# 1 、实现了生产力与消费力解耦和
# 2、平衡消费者和生产者的工作能力,从而提高程序整体处理数据的能力

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # @Time : 2018/04/25 10:55 4 # @Author : MJay_Lee 5 # @File : 生产者消费者模型.py 6 # @Contact : limengjiejj@hotmail.com 7 8 import time 9 import random 10 from multiprocessing import Process,Queue 11 12 13 def consumer(name,q): 14 while True: 15 res = q.get() 16 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) 17 print('�33[1;32;40m%s 吃了 %s�33[0m' % (name,res)) 18 19 def producer(name,q): 20 for i in range(5): 21 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) 22 res = '包子%s' % i 23 q.put(res) 24 print('�33[1;31;40m%s 生产了 %s�33[0m' % (name, res)) 25 26 if __name__ == '__main__': 27 # 1、共享的介质 28 q = Queue() 29 30 # 2、生产者 31 p1 = Process(target=producer,args=('lmj',q)) 32 33 # 3、消费者 34 c1 = Process(target=consumer,args=('cly',q)) 35 36 p1.start() 37 c1.start() 38 39 print('�33[1;36;40m主进程�33[0m')
注意:此示例中,无法正常结束程序
解决方案:导入JoinableQueue模块,q = JoinableQueue()
consumer()每个进程的函数体代码末尾加上,q.task_done(),此方法是起到监控队列是否为None
在主进程运行完毕后,此模型中,生产者生产完毕被回收,队列取空,那么是时候自动回收消费者,故将消费者设为守护程序

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # @Time : 2018/04/25 10:55 4 # @Author : MJay_Lee 5 # @File : 生产者消费者模型.py 6 # @Contact : limengjiejj@hotmail.com 7 8 ''' 9 模型是指一种解决问题的套路 10 该模型下具备两类角色: 11 生产者:生产数据 12 消费者:处理数据 13 14 该模型的运作方式: 15 生产者生产数据,放到一个共享的空间(容器),然后消费者取走进行处理 16 17 该模式的实现方式一: 18 生产者进程 + 队列 + 消费者进程 19 强调:队列中,存放的使一些消息(通知,指令),不应存具体工作程序 20 21 该模式的应用场景: 22 如果程序中有明显的两类任务,一类人物是负责生产数据,另外一类是处理数据 23 就可以考虑用该模型 24 25 该模型的优点: 26 1、解耦合 27 2、平衡两者的工作能力,提升程序处理速率 28 29 ''' 30 31 import time 32 import random 33 from multiprocessing import Process,JoinableQueue 34 35 36 def consumer(name,q): 37 while True: 38 res = q.get() 39 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) 40 print('�33[41m%s 吃了 %s�33[0m' % (name,res)) 41 q.task_done() 42 43 def producer(name,q,food): 44 for i in range(5): 45 time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) 46 res = '%s:%s' % (food,i) 47 q.put(res) 48 print('�33[42m%s 生产了 %s�33[0m' % (name, res)) 49 50 if __name__ == '__main__': 51 # 1、共享的介质 52 q = JoinableQueue() 53 54 # 2、生产者 55 p1 = Process(target=producer,args=('李梦杰',q,'骨头')) 56 p2 = Process(target=producer,args=('朱志伟',q,'米饭')) 57 p3 = Process(target=producer,args=('程灵燕',q,'鸡汤')) 58 59 # 3、消费者 60 c1 = Process(target=consumer,args=('陈杰1号',q)) 61 c2 = Process(target=consumer,args=('陈杰2号',q)) 62 # 关键:在主进程运行完毕后,此模型中,生产者生产完毕被回收,队列取空,那么是时候自动回收消费者,故将消费者设为守护程序 63 c1.daemon = True 64 c2.daemon = True 65 66 p1.start() 67 p2.start() 68 p3.start() 69 c1.start() 70 c2.start() 71 72 # 确定生产者确确实实已经生产完毕 73 p1.join() 74 p2.join() 75 p3.join() 76 # p1~x.join()在所有生产者1~x生产完毕后,拿到队列中元素的总个数,然后直到元素总数变为0,q.join()这一行代码才算运行完毕 77 q.join() 78 # q.join()一旦结束就意味着队列确实被取空,消费者已经确确实实把数据取干净 79 print('�33[1;31;40m主进程结束�33[0m')
