在操作系统中,线程是有优先级划分的,优先级较高的线程会得到相对较多的资源。
也就是说CPU会优先执行优先级较高的线程对象中的任务。
设置线程优先级有助于帮“线程规划器”确定下次选择哪一个线程来优先执行。
设置线程的优先级使用setPriority()方法,此方法在JDK的源代码如下:
public final void setPriority(int newPriority) {
ThreadGroup g;
checkAccess();
if (newPriority > MAX_PRIORITY || newPriority < MIN_PRIORITY) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if((g = getThreadGroup()) != null) {
if (newPriority > g.getMaxPriority()) {
newPriority = g.getMaxPriority();
}
setPriority0(priority = newPriority);
}
}
在java中,线程的优先级分为1~10这10个优先级,如果小于1或者大于10,则JDK抛出异常IllegalArgumentException()。
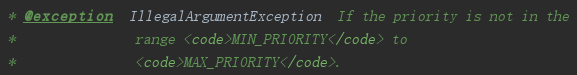
JDK常用下面三个量来预置定义优先级的值。

1.10.1线程优先级的继承特性
在java中线程的优先级具有继承性,比如A线程启动B线程,则B线程的优先级与A是一样的。
线程代码1:
public class Thread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread1 run priority = " + this.getPriority());
Thread2 thread = new Thread2();
thread.start();
}
}
线程代码2:
public class Thread2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread2 run priority = " + this.getPriority());
}
}
执行代码:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Main thread begin priority = " + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
//Thread.currentThread().setPriority(6);
System.out.println("main thread end priority = " + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1();
thread1.start();
}
}
执行结果(左为有注释,右为没注释):


1.10.2优先级具有规则性:
线程代码1:
public class Thread3 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long addResult = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 50000; j++){
Random random = new Random();
random.nextInt();
addResult = addResult + j;
}
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("thread 3 use time = " + (endTime - beginTime));
}
}
线程代码2:
public class Thread4 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long addResult = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 50000; j++){
Random random = new Random();
random.nextInt();
addResult = addResult + j;
}
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("thread 4 use time = " + (endTime - beginTime));
}
}
执行代码:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Thread3 thread3 = new Thread3();
thread3.setPriority(10);
thread3.start();
Thread4 thread4 = new Thread4();
thread4.setPriority(1);
thread4.start();
}
}
}
执行结果:
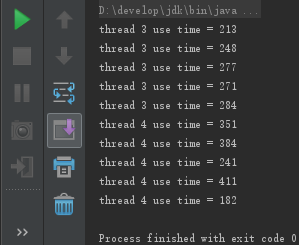

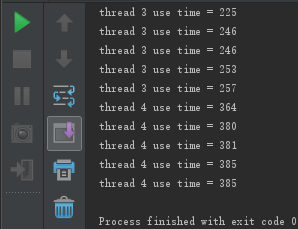
跑了多次后,会发现优先的线程会先执行完。
实际上线程的执行顺序与线程代码的执行顺序无关,与线程的优先级有关,优先级越高越先执行。
1.10.3优先级具有随机性:
随机性意味着优先级高的线程不一定总是能优先执行完。
线程代码1:
public class Thread5 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Random random = new Random();
random.nextInt();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("thread 5 use time = " + (endTime - beginTime));
}
}
线程代码2:
public class Thread6 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Random random = new Random();
random.nextInt();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("thread 6 use time = " + (endTime - beginTime));
}
}
执行代码:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Thread5 thread5 = new Thread5();
thread5.setPriority(5);
thread5.start();
Thread6 thread6 = new Thread6();
thread6.setPriority(6);
thread6.start();
}
}
}
执行结果:
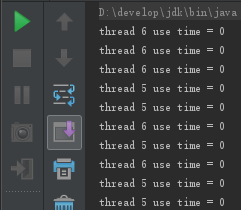
从这个结果来看线程的优先级具有随机性,不一定优先级高的就一定先执行完。
1.10.4看谁运行的快:
线程代码1:
public class ThreadA extends Thread {
private int count = 0;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
count++;
}
}
}
线程代码2:
public class ThreadB extends Thread {
private int count = 0;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
count++;
}
}
}
执行线程:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ThreadA a = new ThreadA();
a.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY - 3);
a.start();
ThreadB b = new ThreadB();
b.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY + 3);
b.start();
Thread.sleep(10000);
a.stop();
b.stop();
System.out.println("a = " + a.getCount());
System.out.println("b = " + b.getCount());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
执行结果:
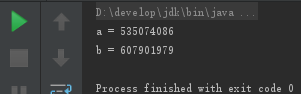
优先级高的线程,执行速度更快。
源码地址:https://github.com/lilinzhiyu/threadLearning