一、Synchornized锁重入

例子程序:
package com.lhy.thread01; public class SyncDouble1 { public synchronized void method1(){ System.err.println("method-1...."); method2(); } public synchronized void method2(){ System.err.println("method-2...."); method3(); } public synchronized void method3(){ System.err.println("method-3...."); } public static void main(String[] args) { final SyncDouble1 sd = new SyncDouble1(); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { sd.method1(); } }); t1.start(); } }
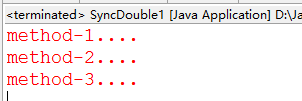
二、父子类
有父类、子类继承关系的,父类和子类都加上synchronized关键字,也是线程安全的,可以放心去用。
例子程序:
package com.lhy.thread02; public class SyncDouble2 { static class Main{ public int i=10; public synchronized void operationSup(){ try { i--; System.err.println("Main print i ="+i); Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } static class Sub extends Main{ public synchronized void operationSub(){ try { while(i > 0){ i--; System.err.println("Sub print i = "+i); Thread.sleep(100); this.operationSup();//调用父类的方法 } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Sub sub = new Sub(); sub.operationSub(); } }); t1.start(); } }
打印结果;
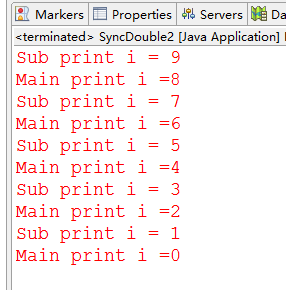
三、出现异常,锁自动释放
例子程序:
package com.lhy.thread02; /** * 模拟synchronized加锁的方法,发生异常时,怎么处理 * @author dev * */ public class SyncException { private int i = 0; boolean flag = true; //传过来多个任务,taskSize模拟任务个数 public synchronized void operation(int taskSize){ while(flag){ try { i++; Thread.sleep(200); System.err.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ,i =" +i); if(i == (taskSize/2)){//模拟任务执行了一半 Integer.parseInt("a"); //发生异常 //throw new RuntimeException(); } //任务执行完了停止 if(i == taskSize){ shutdown(); } } catch (Exception e) { //catch到InterruptedException,不再往下执行 e.printStackTrace(); //情况一:所有任务不是一个整体,一个有问题不影响其他,只把出错的记录日志,下次执行,此时catch应该捕捉Exception。/continue; System.err.println("这里可以记录到日志,i= "+i); //情况二:所有任务是一个整体,一个有问题影响其他,此时可以通过捕捉InterruptedException、catch里抛出RuntimeException();来终止线程继续执行 //throw new RuntimeException(); //continue; } } } //终止 public void shutdown(){ this.flag = false; } public static void main(String[] args) { final SyncException se = new SyncException(); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { se.operation(10); } },"t1"); t1.start(); } }
打印结果;
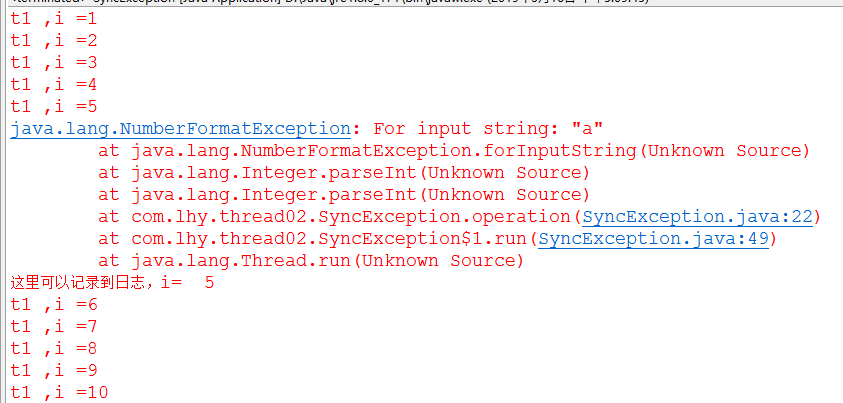
如果整个任务是一个整体,1,可以 catch InterruptedException

运行结果:
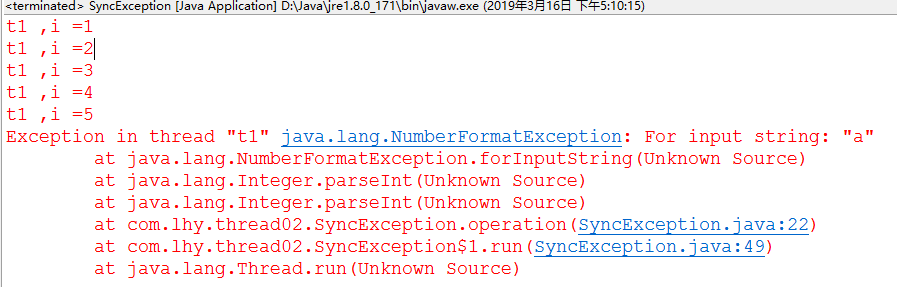
2,中断线程的执行,也可以在catch里抛出运行时异常:

执行结果:

