尽管在FPGA设计中,广泛使用芯片厂家集成的锁相环资源如altera的PLL,Xilinx的DLL来进行时钟的分频,倍频以及相移。但在对时钟要求 不高或资源有限的情况下,使用硬件描述语言设计电路来进行时钟的分频相移非常实用。因此分频器的设计仍然是FPGA中比较常用的一个设计,同时又被许多公司拿来作为面试题,称其为经典设计也不为过。本文所要讨论的是使用Verilog语言来设计等占空比任意整数分频器。为方便使用和比较,将不同分频倍数的分频器放在了一个模块中。
以下是设计的Verilog实现:freq_divide.v
`timescale 1ns / 100ps //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Company: hangzhou dianzi university // Engineer: D.H.j. // // Create Date: 2011.10.13 // Design Name: freq_divide // Module Name: freq_divide // Target Device: <target device> // Tool versions: QuartusII9.0 // Description: // 等占空比任意整数分频的verilog语言实现 //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// module freq_divide( clkin, rst_n, clkout1,//2分频 clkout2,//2的n次方分频 clkout3,//偶数倍(2J)分频 clkout4, clkout5, clkout6//奇数倍(2K+1)分频 ); input clkin;//50MHz input rst_n; output reg clkout1; output clkout2; output reg clkout3; output reg clkout4; output reg clkout5; output clkout6; //counter reg[7:0] cnt1; reg[7:0] cnt2; reg[7:0] cnt3; reg[7:0] cnt4; /* reg[7:0] cnt;//counter always@( posedge clkin or negedge rst_n ) begin if(!rst_n) cnt <= 0; else cnt <= cnt + 1'b1; end */ //*****************任意整数分频*****************//华丽的分割线 //最简单的2分频 always@( posedge clkin or negedge rst_n ) begin if(!rst_n) clkout1 <= 0; else clkout1 <= ~clkout1; end //2的n次方分频 /* 2 0010 4 0100 8 1000 ... */ parameter I = 2;//实现4分频 4=2^I I=2 always@( posedge clkin or negedge rst_n ) begin if(!rst_n) cnt1 <= 0; else cnt1 <= cnt1 + 1'b1; end assign clkout2 = cnt1[I-1]; //偶数倍(2J)分频 //计数器计到一半时,输出时钟翻转,计数器复位 parameter J = 3;//实现6分频 6=2M J=3 always@( posedge clkin or negedge rst_n ) begin if(!rst_n) begin clkout3 <= 0; cnt2 <= 0; end else begin if(cnt2==J-1) begin clkout3 <= ~clkout3; cnt2 <= 0;end else cnt2 <= cnt2 + 1'b1; end end //奇数倍(2K+1)分频 经典面试题 /* 分别利用上升沿和下降沿触发产生两个占空比为(K+1)/(2K+1)的时钟, 再将两个时钟进行逻辑与操作,得到奇数倍分频的时钟 */ parameter K = 5;//实现11分频 11=2K+1 K=5 //上升沿计数器 always@( posedge clkin or negedge rst_n ) begin if(!rst_n) begin cnt3 <= 0; end else begin if(cnt3==2*K) cnt3 <= 0; else cnt3 <= cnt3 + 1'b1; end end //一个周期内,正电平占(K+1)/(2K+1) always@( posedge clkin or negedge rst_n ) begin if(!rst_n) begin clkout4 <= 0; end else begin if(cnt3==K-1) clkout4 <= 1; else if(cnt3==2*K) clkout4 <= 0; end end //下降沿计数器 always@( negedge clkin or negedge rst_n ) begin if(!rst_n) begin cnt4 <= 0; end else begin if(cnt4==2*K) cnt4 <= 0; else cnt4 <= cnt4 + 1'b1; end end always@( negedge clkin or negedge rst_n ) begin if(!rst_n) begin clkout5 <= 0; end else begin if(cnt4==K-1) clkout5 <= 1; else if(cnt4==2*K) clkout5 <= 0; end end assign clkout6 = clkout4 & clkout5; endmodule
以下是testbench代码:freq_divide_tb.v
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Company: hangzhou dianzi university // Engineer: D.H.j. // // Create Date: 2011.10.13 // Design Name: freq_divide_tb // Module Name: freq_divide_tb // Target Device: <target device> // Tool versions: QuartusII9.0 // Description: // 等占空比任意整数分频的verilog语言实现testbench //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// module freq_divide_tb; reg clkin; reg rst_n; //counter reg[7:0] cnt1; reg[7:0] cnt2; reg[7:0] cnt3; reg[7:0] cnt4; always #10 clkin = ~clkin;//50MHz initial begin clkin = 0; rst_n = 0; #10 rst_n = 1; end freq_divide u( .clkin(clkin), .rst_n(rst_n), .clkout1(clkout1), .clkout2(clkout2), .clkout3(clkout3), .clkout4(clkout4), .clkout5(clkout5), .clkout6(clkout6) ); endmodule
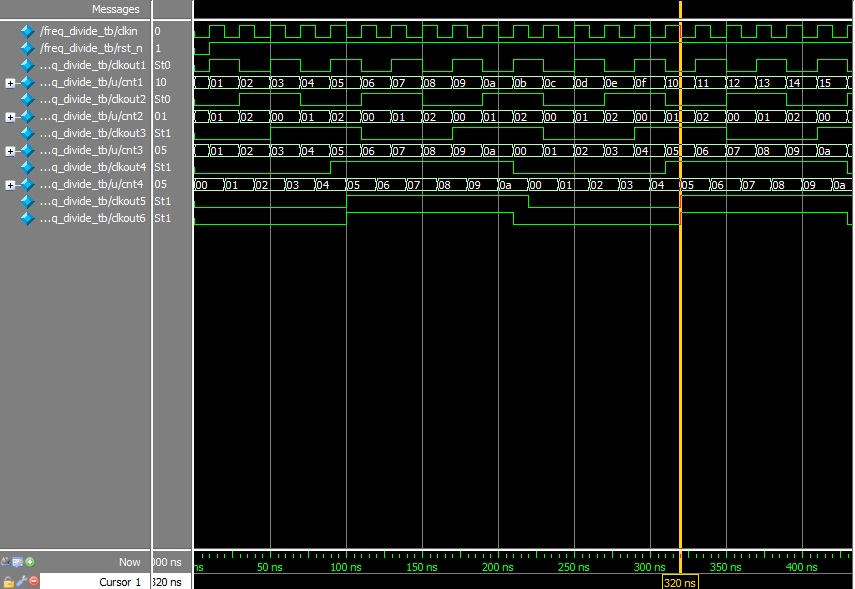
仿真图如下