collections
https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/collections.html
实现一些特殊的容器数据类型。
是对通用内置容器的替代, 例如 词典、列表、集合、元组。
特殊的含义是通用数据类型,在某些常用场景上,不满足,需要手动实现的一些特殊的编程模式。
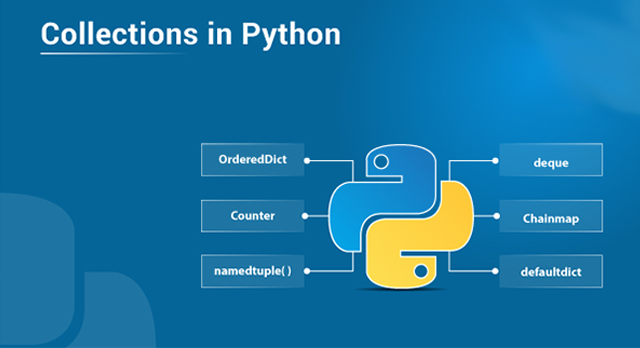
This module implements specialized container datatypes providing alternatives to Python’s general purpose built-in containers,
dict,list,set, andtuple.
namedtuple()factory function for creating tuple subclasses with named fields dequelist-like container with fast appends and pops on either end ChainMapdict-like class for creating a single view of multiple mappings Counterdict subclass for counting hashable objects OrderedDictdict subclass that remembers the order entries were added defaultdictdict subclass that calls a factory function to supply missing values UserDictwrapper around dictionary objects for easier dict subclassing UserListwrapper around list objects for easier list subclassing UserStringwrapper around string objects for easier string subclassing
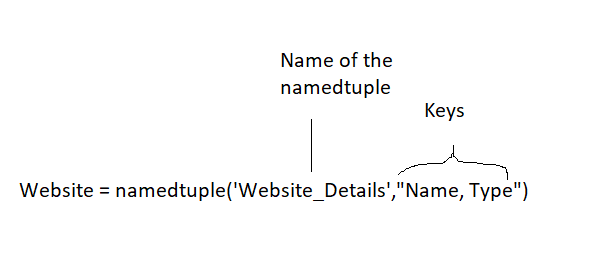
命名元组- namedtuple
对于元组,只能采用index方式索引元组。
对于结构化数据,例如数据库中的表,表头可能是数十个,这样采用元组的index方式索引,很容易误用索引。
命名元组集成了元组的索引方式,同时引入类似dict的命名方式作为索引。
Python supports a type of container like dictionaries called “namedtuple()” present in module, “collections“. Like dictionaries they contain keys that are hashed to a particular value. But on contrary, it supports both access from key value and iteration, the functionality that dictionaries lack.
# Python code to demonstrate namedtuple() from collections import namedtuple # Declaring namedtuple() Student = namedtuple('Student',['name','age','DOB']) # Adding values S = Student('Nandini','19','2541997') # Access using index print ("The Student age using index is : ",end ="") print (S[1]) # Access using name print ("The Student name using keyname is : ",end ="") print (S.name)
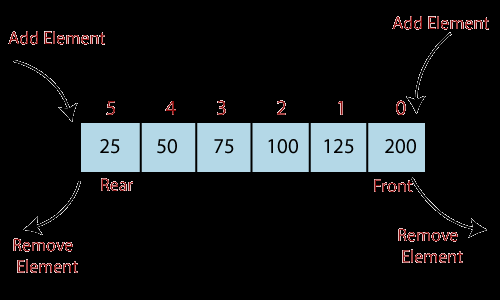
双边队列 - deque(Doubly Ended Queue)
双边队列是泛华的栈和队列。两边都可以添加和删除元素。
你可以把他当成栈用,也可以当成队列使用。
相对于list方式存储,其对于添加和删除元素具有线性时间花费。
https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/collections.html#collections.deque
Deques are a generalization of stacks and queues (the name is pronounced “deck” and is short for “double-ended queue”). Deques support thread-safe, memory efficient appends and pops from either side of the deque with approximately the same O(1) performance in either direction.
Though
listobjects support similar operations, they are optimized for fast fixed-length operations and incur O(n) memory movement costs forpop(0)andinsert(0, v)operations which change both the size and position of the underlying data representation.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/deque-in-python/?ref=lbp
Deque (Doubly Ended Queue) in Python is implemented using the module “collections“. Deque is preferred over list in the cases where we need quicker append and pop operations from both the ends of container, as deque provides an O(1) time complexity for append and pop operations as compared to list which provides O(n) time complexity.
# Python code to demonstrate working of # append(), appendleft(), pop(), and popleft() # importing "collections" for deque operations import collections # initializing deque de = collections.deque([1,2,3]) # using append() to insert element at right end # inserts 4 at the end of deque de.append(4) # printing modified deque print ("The deque after appending at right is : ") print (de) # using appendleft() to insert element at right end # inserts 6 at the beginning of deque de.appendleft(6) # printing modified deque print ("The deque after appending at left is : ") print (de) # using pop() to delete element from right end # deletes 4 from the right end of deque de.pop() # printing modified deque print ("The deque after deleting from right is : ") print (de) # using popleft() to delete element from left end # deletes 6 from the left end of deque de.popleft() # printing modified deque print ("The deque after deleting from left is : ") print (de)
ChainMap
https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/collections.html#collections.ChainMap
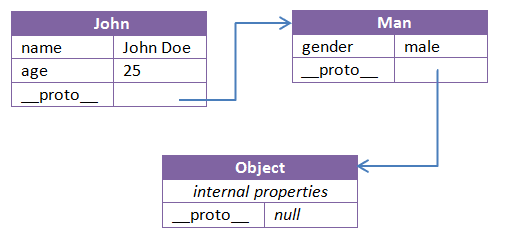
将多个字典和其它类型的映射组直接来,创建一个单一的、可更新的视图。
类似Js对象的原型链,从实际对象出发寻找指定属性名的值,一直找到其顶部祖先。
写也是修改第一个找到属性的节点。
A
ChainMapgroups multiple dicts or other mappings together to create a single, updateable view. If no maps are specified, a single empty dictionary is provided so that a new chain always has at least one mapping.The underlying mappings are stored in a list. That list is public and can be accessed or updated using the maps attribute. There is no other state.
Lookups search the underlying mappings successively until a key is found. In contrast, writes, updates, and deletions only operate on the first mapping.
A
ChainMapincorporates the underlying mappings by reference. So, if one of the underlying mappings gets updated, those changes will be reflected inChainMap.All of the usual dictionary methods are supported. In addition, there is a maps attribute, a method for creating new subcontexts, and a property for accessing all but the first mapping:
例如下面的例子, 先找命令行参数,没找到,再找系统环境,还是没有找到,使用默认值。
import os, argparse defaults = {'color': 'red', 'user': 'guest'} parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument('-u', '--user') parser.add_argument('-c', '--color') namespace = parser.parse_args() command_line_args = {k:v for k, v in vars(namespace).items() if v} combined = ChainMap(command_line_args, os.environ, defaults) print(combined['color']) print(combined['user'])
Counter
本身是dict类型的子类,用于计数。
https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/collections.html#collections.Counter
A
Counteris adictsubclass for counting hashable objects.It is an unordered collection where elements are stored as dictionary keys and their counts are stored as dictionary values.
Counts are allowed to be any integer value including zero or negative counts.
The
Counterclass is similar to bags or multisets in other languages.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/counters-in-python-set-1/?ref=lbp
Counter is a container included in the collections module. Now you all must be wondering what is a container. Don’t worry first let’s discuss about the container.
What is Container?
Containers are objects that hold objects. They provide a way to access the contained objects and iterate over them. Examples of built in containers are Tuple, list, and dictionary. Others are included in Collections module.
A Counter is a subclass of dict. Therefore it is an unordered collection where elements and their respective count are stored as a dictionary. This is equivalent to a bag or multiset of other languages.
Syntax :
class collections.Counter([iterable-or-mapping])Initialization :
The constructor of counter can be called in any one of the following ways :
- With sequence of items
- With dictionary containing keys and counts
- With keyword arguments mapping string names to counts
# A Python program to show different ways to create # Counter from collections import Counter # With sequence of items print(Counter(['B','B','A','B','C','A','B','B','A','C'])) # with dictionary print(Counter({'A':3, 'B':5, 'C':2})) # with keyword arguments print(Counter(A=3, B=5, C=2))
更新
# A Python program to demonstrate update() from collections import Counter coun = Counter() coun.update([1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2]) print(coun) coun.update([1, 2, 4]) print(coun)
OrderedDict
词典的key是无序的,无论插入的先后。
此类型,首先其继承了dict,拥有dict方法。
其次,dict中元组(key, value)按照插入的先后次序排列。
解析器内部使用 一个链表来管理 key插入的先后次序。

而dict采用hash table实现, 所以决定了插入顺序不能被保存。
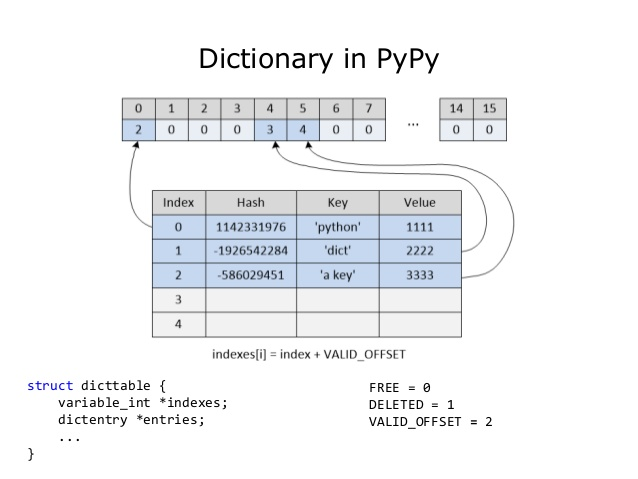
详细的dict实现介绍。
https://www.slideshare.net/delimitry/python-dictionary-past-present-future
https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/collections.html#collections.OrderedDict
Return an instance of a dict subclass, supporting the usual
dictmethods. An OrderedDict is a dict that remembers the order that keys were first inserted. If a new entry overwrites an existing entry, the original insertion position is left unchanged. Deleting an entry and reinserting it will move it to the end.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/ordereddict-in-python/?ref=lbp
An OrderedDict is a dictionary subclass that remembers the order that keys were first inserted. The only difference between dict() and OrderedDict() is that:
OrderedDict preserves the order in which the keys are inserted. A regular dict doesn’t track the insertion order, and iterating it gives the values in an arbitrary order. By contrast, the order the items are inserted is remembered by OrderedDict.
# A Python program to demonstrate working of OrderedDict from collections import OrderedDict print("This is a Dict: ") d = {} d['a'] = 1 d['b'] = 2 d['c'] = 3 d['d'] = 4 for key, value in d.items(): print(key, value) print(" This is an Ordered Dict: ") od = OrderedDict() od['a'] = 1 od['b'] = 2 od['c'] = 3 od['d'] = 4 for key, value in od.items(): print(key, value)
defaultdict
其继承了dict。
不同于dict,其还拥有在索引不存在的key时候,不报错的优点。
实现上是返回一个预定的数据类型。
https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/collections.html#collections.defaultdict
Returns a new dictionary-like object.
defaultdictis a subclass of the built-indictclass. It overrides one method and adds one writable instance variable. The remaining functionality is the same as for thedictclass and is not documented here.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/defaultdict-in-python/?ref=lbp
Defaultdict is a container like dictionaries present in the module collections. Defaultdict is a sub-class of the
dictclass that returns a dictionary-like object. The functionality of both dictionaries and defualtdict are almost same except for the fact that defualtdict never raises aKeyError. It provides a default value for the key that does not exists.Syntax: defaultdict(default_factory)
Parameters:
- default_factory: A function returning the default value for the dictionary defined. If this argument is absent then the dictionary raises a
KeyError.
# Python program to demonstrate # defaultdict from collections import defaultdict # Function to return a default # values for keys that is not # present def def_value(): return "Not Present" # Defining the dict d = defaultdict(def_value) d["a"] = 1 d["b"] = 2 print(d["a"]) print(d["b"]) print(d["c"])
UserDict
用户可以自定义一些dict行为
代理真正的dict。
https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/collections.html#collections.UserDict
The class,
UserDictacts as a wrapper around dictionary objects. The need for this class has been partially supplanted by the ability to subclass directly fromdict; however, this class can be easier to work with because the underlying dictionary is accessible as an attribute.
- class
collections.UserDict([initialdata])Class that simulates a dictionary. The instance’s contents are kept in a regular dictionary, which is accessible via the
dataattribute ofUserDictinstances. If initialdata is provided,datais initialized with its contents; note that a reference to initialdata will not be kept, allowing it be used for other purposes.In addition to supporting the methods and operations of mappings,
UserDictinstances provide the following attribute:
dataA real dictionary used to store the contents of the
UserDictclass.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/collections-userdict-in-python/?ref=lbp
# Python program to demonstrate # userdict from collections import UserDict # Creating a Dictionary where # deletion is not allowed class MyDict(UserDict): # Function to stop deleltion # from dictionary def __del__(self): raise RuntimeError("Deletion not allowed") # Function to stop pop from # dictionary def pop(self, s = None): raise RuntimeError("Deletion not allowed") # Function to stop popitem # from Dictionary def popitem(self, s = None): raise RuntimeError("Deletion not allowed") # Driver's code d = MyDict({'a':1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}) print("Original Dictionary") print(d) d.pop(1)
UserList
同上。
UserString
同上。