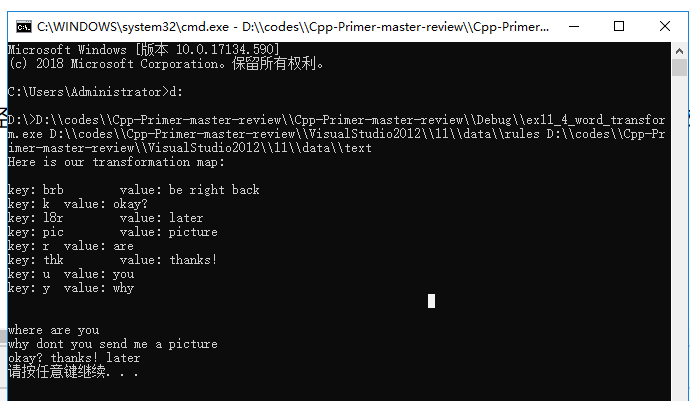
c++ prime 5 ex11_4
代码如下
// ex11_4_word_transform.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <map> #include <vector> #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <stdexcept> #include <sstream> using std::map; using std::string; using std::vector; using std::ifstream; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::getline; using std::runtime_error; using std::istringstream; map<string, string> buildMap(ifstream &map_file) { map<string, string> trans_map; // holds the transformations string key; // a word to transform string value; // phrase to use instead // read the first word into key and the rest of the line into value while (map_file >> key && getline(map_file, value)) if (value.size() > 1) // check that there is a transformation trans_map[key] = value.substr(1); // skip leading space else throw runtime_error("no rule for " + key); return trans_map; } const string & transform(const string &s, const map<string, string> &m) { // the actual map work; this part is the heart of the program auto map_it = m.find(s); // if this word is in the transformation map if (map_it != m.cend()) return map_it->second; // use the replacement word else return s; // otherwise return the original unchanged } // first argument is the transformations file; // second is file to transform void word_transform(ifstream &map_file, ifstream &input) { auto trans_map = buildMap(map_file); // store the transformations // for debugging purposes print the map after its built cout << "Here is our transformation map: "; for (auto entry : trans_map) cout << "key: " << entry.first << " value: " << entry.second << endl; cout << " "; // do the transformation of the given text string text; // hold each line from the input while (getline(input, text)) { // read a line of input istringstream stream(text); // read each word string word; bool firstword = true; // controls whether a space is printed while (stream >> word) { if (firstword) firstword = false; else cout << " "; // print a space between words // transform returns its first argument or its transformation cout << transform(word, trans_map); // print the output } cout << endl; // done with this line of input } } int main(int argc, char **argv) { // open and check both files //if (argc != 3) // throw runtime_error("wrong number of arguments"); argv[1] = "……"; argv[2] = "……"; ifstream map_file(argv[1]); // open transformation file if (!map_file) // check that open succeeded throw runtime_error("no transformation file"); ifstream input(argv[2]); // open file of text to transform if (!input) // check that open succeeded throw runtime_error("no input file"); word_transform(map_file, input); system("pause"); return 0; // exiting main will automatically close the files }
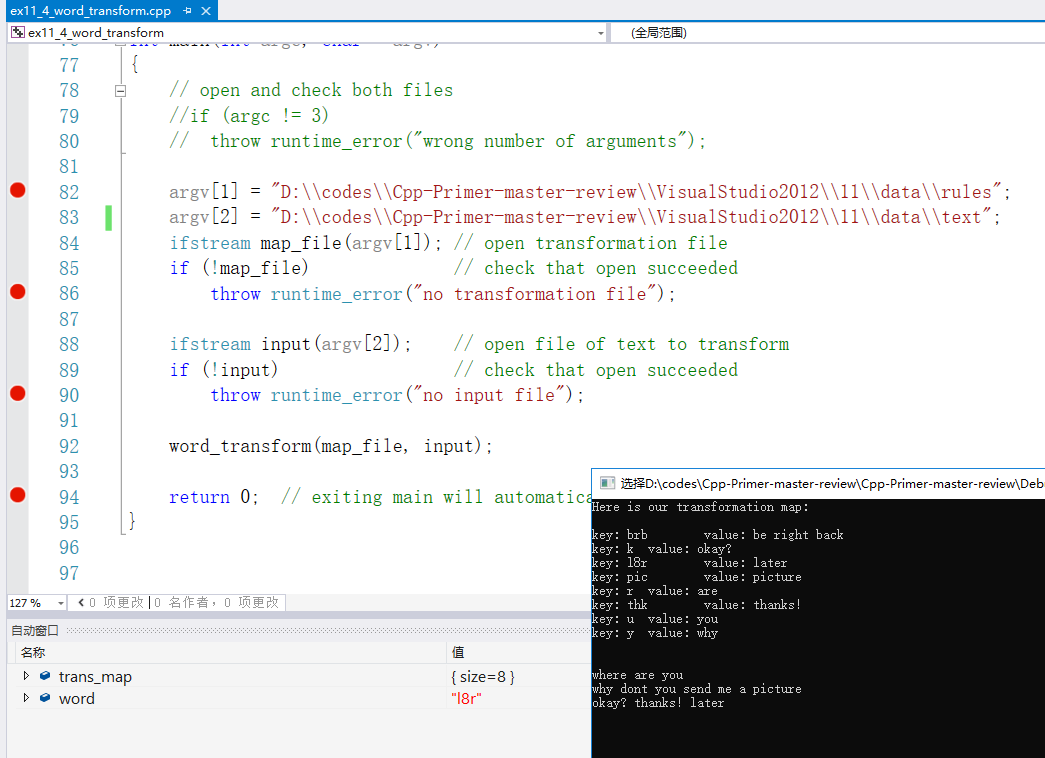
1.关于main函数中的三个参数 ,ref: int main(int argc,char* argv[])详解
char *argv[]是一个字符数组,其大小是int argc,主要用于命令行参数 argv[] 参数,数组里每个元素代表一个参数;
比如你输入
test a.c b.c t.c
则
argc = 4
argv[0] = "test"
argv[1] = "a.c"
argv[2] = "b.c"
argv[3] = "t.c"
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
argc记录了用户在运行程序的命令行中输入的参数的个数。
arg[]指向的数组中至少有一个字符指针,即arg[0].他通常指向程序中的可执行文件的文件名。在有些版本的编译器中还包括程序文件所在的路径。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
在调用一个可执行程序时,某些情况下需要向程序传递参数。如我们可以在控制台中键notepad.exe,
回车后将执行记事本程序。如果我们希望在打开notepad时同时打开一个文本文件,可以在notepad.exe 后面跟上文件的路径和名字,如notepad.exe example.txt(文件在当前路径)。
那么程序中如何能得到这些输入参数呢?这个工作是编译器帮我们完成的,编译器将输入参数的信息
放入main函数的参数列表中。
main函数的参数列表保存了输入参数的信息,第一个参数argc记录了输入参数的个数,第二个参数是字符串数组的,字符串数组的每个单元是char*类型的,指向一个c风格字符串。
以notepad.exe example.txt为例
argc是2,就是说argv数组中有两个有效单元
第一单元指向的字符串是"notepad.exe"
第二单元指向的字符串是"example.txt"
argv数组中的第一个单元指向的字符串总是可执行程序的名字,以后的单元指向的字符串依次是程序调用时的参数。
这个赋值过程是编译器完成的,我们只需要读出数据就可以了。
2.读写文件,ref:C++文件读写详解(ofstream,ifstream,fstream)
3. getline
ref:cin 输入空格符和 getline() 忽略开头换行符
C++中cin、cin.get()、cin.getline()、getline()、gets()等函数的用法
用cmd执行
argv[1]是exe的转义字符路径,argv[2]是 rules文件的转义字符路径,argv[3]是待转换文件的转义字符路径。