使用RESTful风格的接口有如下优势:
语言无关
开发效率高、调试方便
接口的语义明确 然而缺点也显而易见:基于HTTP的RPC在效率上不如传统的RPC。
在ModelService中,我们使用SpringMVC框架来实现RESTful接口。但是,在最近一次对ModelService的更新中我们发现SpringMVC的RESTful接口性能存在问题。
RESTful风格的uri:
@RequestMapping(path = "/list/cityId/{cityId}", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String getJsonByCityId(@PathVariable Integer cityId){
}
客户端请求: GET /list/cityId/1
非RESTful:
@RequestMapping(path = "/list/cityId", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getJsonByCityId(@RequestParam Integer cityId)
使用Apache JMeter对SpringMVC RESTful接口与非RESTful接口进行了性能测试:
*并发量为200
*测试在同一台机器上进行,执行业务逻辑相同,仅接口不同。
*为了证明的确是SpringMVC造成的问题,我们使用了最简单的业务逻辑,直接返回字符串。
由结果可见,非RESTful接口的性能是RESTful接口的两倍,且请求的最大响应时间是35毫秒,有99%的请求在20毫秒内完成。相比之下,RESTful接口的最大响应时间是436毫秒。
由于ModelService是一个对并发性能要求极高的系统,且被多个上层业务系统所依赖,所有请求需在50ms内返回,若超时则会引起上层系统的read timeout,进而导致502。所以需要对这一情况进行优化。
方案一:将所有的url修改为非RESTful风格(不使用@PathVariable)
这是最直接的方式,也是最能保证效果的方式。但是这么做需要修改的是ModelService中已有的全部100+个接口,同时也要修改客户端相应的调用。修改量太大,而且极有可能由于写错URL导致404。更令人不爽的是这种修改会导致接口没有了RESTful风格。故该方案只能作为备选。
方案二:对SpringMVC进行改造
根据实际现象以及测试的结果,几乎可以确定的是问题出在SpringMVC的RESTful路径查找中。所以我们对SpringMVC中的相关代码进行了调查。
SpringMVC的请求处理过程中的路径匹配过程:
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#lookupHandlerMethod (spring-webmvc-4.2.3.RELEASE)
匹配部分源码:
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
public RequestMappingInfo getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (methods == null || params == null || headers == null || consumes == null || produces == null) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
methods = getAccessControlRequestMethodCondition(request);
if (methods == null || params == null) {
return null;
}
}
else {
return null;
}
}
PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (patterns == null) {
return null;
}
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (custom == null) {
return null;
}
return new RequestMappingInfo(this.name, patterns,
methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom.getCondition());
}
SpringMVC首先对HTTP请求中的path与已注册的RequestMappingInfo(经解析的@RequestMapping)中的path进行一个完全匹配来查找对应的HandlerMethod,即处理该请求的方法,
这个匹配就是一个Map#get方法。若找不到则会遍历所有的RequestMappingInfo进行查找。这个查找是不会提前停止的,直到遍历完全部的RequestMappingInfo。
在遍历过程中,SpringMVC首先会根据@RequestMapping中的headers, params, produces, consumes, methods与实际的HttpServletRequest中的信息对比,剔除掉一些明显不合格的RequestMapping。
如果以上信息都能够匹配上,那么SpringMVC会对RequestMapping中的path进行正则匹配,剔除不合格的。
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request)); Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
接下来会对所有留下来的候选@RequestMapping进行评分并排序。最后选择分数最高的那个作为结果。
评分的优先级为:path pattern > params > headers > consumes > produces > methods
所以使用非RESTful风格的URL时,SpringMVC可以立刻找到对应的HandlerMethod来处理请求。但是当在URL中存在变量时,即使用了@PathVariable时,SpringMVC就会进行上述的复杂流程。
值得注意的是SpringMVC在匹配@RequestMapping中的path时是通过AntPathMatcher进行的,这段path匹配逻辑是从Ant中借鉴过来的。
String[] pattDirs = tokenizePattern(pattern); String[] pathDirs = tokenizePath(path); int pattIdxStart = 0; int pattIdxEnd = pattDirs.length - 1; int pathIdxStart = 0; int pathIdxEnd = pathDirs.length - 1; // Match all elements up to the first ** while (pattIdxStart <= pattIdxEnd && pathIdxStart <= pathIdxEnd) { String pattDir = pattDirs[pattIdxStart]; if ("**".equals(pattDir)) { break; } if (!matchStrings(pattDir, pathDirs[pathIdxStart], uriTemplateVariables)) { return false; } pattIdxStart++; pathIdxStart++; }
path的匹配首先会把url按照“/”分割,然后对于每一部分都会使用到正则表达式,即使该字符串是定长的静态的。所以该匹配逻辑的性能可能会很差。
在大多数情况下,我们在写@RequestMapping时不会去写除了path以外的值,至多会指定一个produces,这会让SpringMVC难以快速剔除不合格的候选者。我们首先试图让SpringMVC在进行path匹配前就可以产生匹配结果,
从而不去执行path匹配的逻辑,以提高效率。然而实际情况是我们无法做到让每个方法都有独特的params, produces, consumes, methods,所以我们尝试让每个方法有一个独特的headers,然后进行了一次性能测试。
性能的确得到了一定的提升(约20%),但这个结果并不令我们满意,我们需要的是能够达到与非RESTful接口一样的性能。
我们对匹配逻辑的性能进行了进一步的测试
| RESTful URL数量 | QPS |
|---|---|
| 1 | 16116.0 |
| 10 | 13342.2 |
| 20 | 10615.7 |
| 40 | 7800.3 |
| 100 | 4056.8 |
| 1000 | 505.6 |
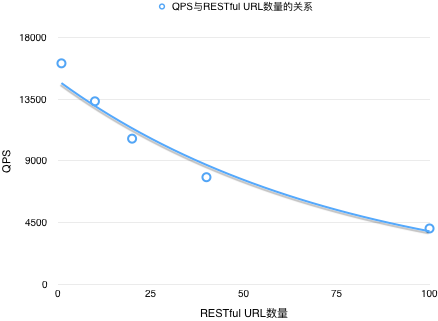
从结果可见,这段匹配逻辑对性能的影响很大,URL数量越多,SpringMVC的性能越差,初步验证了我们从源码中得出的结论。在最近一次ModelService的更新中,接口数量翻了一倍,导致性能下降了一半,这也符合我们的结论。考虑到未来ModelService的接口必定会持续增加,我们肯定不能容忍在请求压力不断增加的情况下ModelService的性能反而不断下降的情况。所以现在我们要做的就是防止SpringMVC执行这种复杂的匹配逻辑,找到一种方式可以绕过它。
通过继承
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
我们可以实现自己的匹配逻辑。由于ModelService已经服务化,所以每个接口都有一个服务名,通过这个服务名即可直接找到对应的方法,并不需要通过@RequestMapping匹配的方式。而在服务消费端,由于服务消费端是通过服务名进行的方法调用,所以在服务消费端可以很直接地获取到服务名,把服务名加到HTTP请求的header中并不需要对代码进行大量的修改。
最终方案:
服务端:
- 在每个@RequestMapping中添加接口对应服务名的信息。
- 实现自己定义的HandlerMethod查询逻辑,在HandlerMethod注册时记录与之对应的服务名,在查询时通过HTTP请求头中的服务名查表获得HandlerMethod。
客户端:
- 调用服务时将服务名加入到HTTP请求头中
分析:
- 这样的查询时间复杂度是O(1)的,典型的空间换时间。理论上使用这样的查找逻辑的效率和非RESTful接口的效率是一样的。
- 由于HandlerMethod的注册是在服务启动阶段完成的,且在运行时不会发生改变,所以不用考虑注册的效率以及并发问题。
- SpringMVC提供了一系列的方法可以让我们替换它的组件,所以该方案的可行性很高。
实现步奏源码:
第一步:服务端源码,调整requestMapping的匹配逻辑
package cc.zeelan.framework.interceptor.mapping;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;
/**
* 原理:
* 1、在每个@RequestMapping中添加接口对应服务名的信息。
* 2、实现自己定义的HandlerMethod查询逻辑,在HandlerMethod注册时记录与之对应的服务名,
* 在查询时通过HTTP请求头中的服务名查表获得HandlerMethod。
*
* @author witts
* @project core-auth
* @package cc.zeelan.framework.optimize
* @version 1.0
* @param <T>
* @message 林花谢了春红,太匆匆。无奈朝来寒雨,晚来风
*/
public class RestfulRequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingHandlerMapping {
private static Map<String, HandlerMethod> nameLookup = new LinkedHashMap<String, HandlerMethod>();
private static Map<HandlerMethod, RequestMappingInfo> mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap<HandlerMethod, RequestMappingInfo>();
@Override
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, RequestMappingInfo mapping) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
RequestMapping requestAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class);
nameLookup.put(requestAnnotation.name(), handlerMethod);//根据传入的名字映射方法
mappingLookup.put(handlerMethod, mapping); //验证规则
super.registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mapping);
}
@Override
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 自己的查找逻辑,如果找不到,再执行原有的逻辑,以免出现错误情况
String serviceName = request.getHeader("serviceName");
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = nameLookup.get(serviceName);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(serviceName) && handlerMethod != null) {
handleMatch(mappingLookup.get(handlerMethod), lookupPath, request); //根据名字映射规则
return handlerMethod;
}
return super.lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); //调用默认的spring路由匹配原则
}
}
第二步:实现WebMvcConfigurationSupport
@Configuration public class CustomHandlerMethodMapping extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport { @Override protected RequestMappingHandlerMapping createRequestMappingHandlerMapping() { return new RestfulRequestMappingHandlerMapping(); } }
第三步:spring管理自定义的CustomHandlerMethodMapping对象
<bean name="handlerMapping" class="cc.zeelan.framework.interceptor.mapping.CustomHandlerMethodMapping"/>
第四步:然后在控制器类上加上@Configuration注解就可以使用了。
@RequestMapping(value="user/login/")
@Configuration
@ResponseBody
public class userLoginController {
@RequestMapping(name="user_login",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public void login(){
} }
第五步:客户端在Header里面传入serviceName参数就能自动快速匹配到RequestMapping对应的方法上面
request.setHeader("serviceName","user_login");
uri>>>>>> user/login/
实现细节:
我们要建立一个HandlerMethod与服务名的映射,保存在一个Map中。注意到在@RequestMapping中有一个name属性,这个属性并没有被SpringMVC用在匹配逻辑中。该属性是用来在JSP中直接生成接口对应的URL的,但是在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry中已经提供了一个name与Handler Method的映射,直接拿来用即可。所以我们只需要在每个接口的@RequestMapping中添加name属性,值为接口的服务名。在SpringMVC启动时会自动帮我们建立起一个服务名与Handler Method的映射。我们只要在匹配时从HTTP请求头中获取请求的服务名,然后从该Map中查询到对应的HandlerMethod返回。如果没有查询到则调用父类中的原匹配逻辑,这样可以保证不会对现有的系统造成问题。
*小细节:
因为RESTful接口存在@PathVariable,我们还需要调用handleMatch方法来将HTTP请求的path解析成参数。然而这个方法需要的参数是RequestMappingInfo,并不是HandlerMethod,SpringMVC也没有提供任何映射,所以我们还是要自己实现一个HandlerMethod => RequestMappingInfo的反向查询表。重写AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#registerMapping方法即可在@RequestMapping的注册阶段完成映射的建立。
最后我们有两种方式可以把自己实现的RequestMappingHandlerMapping替换掉SpringMVC中的默认组件。
方法一:配置文件
删除注解,添加如下配置:
<bean name="handlerAdapter" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"> <property name="webBindingInitializer"> <bean class="org.springframework.web.bind.support.ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer"> <property name="conversionService" ref="conversionService"/> </bean> </property> <property name="messageConverters"> <list> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter"/> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter"/> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.ResourceHttpMessageConverter"/> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"/> </list> </property> </bean> <bean name="conversionService" class="org.springframework.format.support.DefaultFormattingConversionService"/> <bean name="handlerMapping" class="path.to.your.request.mapping.handler.mapping"/>
这样做其实就是展开了注解,然后替换了其中的handlerMapping组件。
方法二:Java类+注解
继承 org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport
重写createRequestMappingHandlerMapping方法,在方法中返回自己实现的RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象。然后在类上加上@Configuration注解。
如果配置文件中有,且该类在base-package中,则到此已完成了全部工作。如果没有,则需要在配置文件中添加这个类作为bean(bean的名称可以不用指定)。
本地性能测试:

*该测试与之前的测试在同一台机器上进行,执行业务逻辑相同。
性能与非RESTful接口相当,比之前提高了一倍。


