本章主要内容如下:
- 1)多行显示
- 2)居中显示
在上章3.数码相框-通过freetype库实现矢量显示里,我们使用矢量坐标时,该坐标仅仅在原点位置处,所以文字有可能会超出坐标,如下图所示:
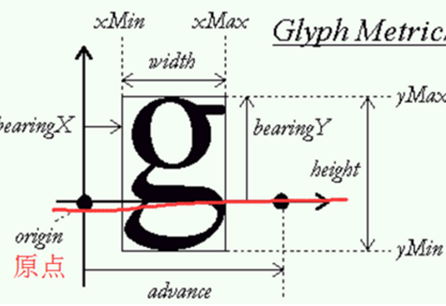
既然超出了坐标,会不会被下一行的文字覆盖掉?
答:对于几行同样大的文字而言,不会的.
以 24*24的韦字为例,让它显示在(0,40)处,所以文字的y范围在17~40,如下图所示,发现该文字超过了原点,而上方数据又会空出来一段,就不会覆盖到上一行数据.

对于几行规格大小不同的文字,则有可能会被覆盖.以20*20的韦字为例,如下图,可以发现空出的数据比24*24的少1行,若上一行的规格很大时(超出原点很大一部分), 那么这个20*20的韦字,就会覆盖掉上一行文字底部的数据.
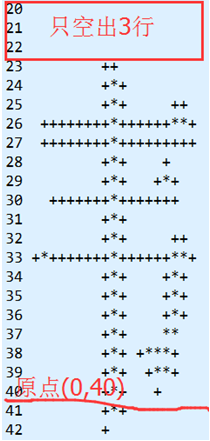
1.从左显示多行24*24文字
内容如下:
定义一个两个标志变量line_box_ymax和line_box_ymin.
通过FT_Glyph_Get_CBox()测量字形图像,获取一行文字的yMax,Min最大值,最小值.
显示第一行时:
pen.x = 0* 64; pen.y = ( fb_var.yres-24 ) * 64; // fb_var.yres:LCD总高度, 原点为(0,24)
显示第2~n行时:
pen.x = 0* 64; pen.y-= (line_box_ymax - line_box_ymin )* 64; //在上行的pen.y基础上,减去上行的边框高
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/mman.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <string.h> #include <linux/fb.h> #include <math.h> #include<wchar.h> #include <ft2build.h> #include FT_FREETYPE_H #include FT_GLYPH_H unsigned char *fbmem; unsigned char *hzkmem; struct fb_var_screeninfo fb_var; struct fb_fix_screeninfo fb_fix; unsigned int screensize; #define FONTDATAMAX 4096 /*rgb565*/ void pixel_show(int x,int y, unsigned int color) { unsigned int red,green,blue; switch(fb_var.bits_per_pixel) //rgb 像素 { case 32: { unsigned int *addr=(unsigned int *)fbmem+(fb_var.xres*y+x); *addr=color; break; } case 24: { unsigned int *addr=(unsigned int *)fbmem+(fb_var.xres*y+x); *addr=color; break; } case 16: //将RGB888 转为RGB565 { unsigned short *addr=(unsigned short *)fbmem+(fb_var.xres*y+x); red = (color >> 16) & 0xff; green = (color >> 8) & 0xff; blue = (color >> 0) & 0xff; color = ((red >> 3) << 11) | ((green >> 2) << 5) | (blue >> 3); *addr = color; break; } case 8: { unsigned char *addr=(unsigned char *)fbmem+(fb_var.xres*y+x); *addr = (unsigned char)color; break; } default: { printf("can't surport %dbpp ",fb_var.bits_per_pixel); break; } } } void draw_bitmap( FT_Bitmap* bitmap, FT_Int x, FT_Int y) { FT_Int i, j, p, q; FT_Int x_max = x + bitmap->width; //x:当前X位置, bitmap->该字宽度 FT_Int y_max = y + bitmap->rows; for ( i = x, p = 0; i < x_max; i++, p++ ) //i:lcd的x轴 { for ( j = y, q = 0; j < y_max; j++, q++ ) //j:lcd的y轴 { if ( i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= fb_var.xres || j >= fb_var.yres ) continue;
pixel_show( i, j, bitmap->buffer[q * bitmap->width + p]); } } } unsigned int line_box_ymax=0; unsigned int line_box_ymin=30000; void lcd_vector_show(char *argv,wchar_t *str[],unsigned int lines) { FT_Glyph glyph; FT_BBox acbox; FT_Library library; FT_Face face; FT_GlyphSlot slot; FT_Vector pen; /* untransformed origin */ unsigned char error; unsigned int line_nums=0; unsigned char n,font_size;
error = FT_Init_FreeType( &library ); /* initialize library */ if(error) { printf("FT_Init_FreeType ERROR "); return ; } error = FT_New_Face( library, argv, 0, &face ); /* create face object */ if(error) { printf("FT_New_Face ERROR "); return ; } slot = face->glyph; error = FT_Set_Pixel_Sizes( face, 0,24); /* set character size */ for(line_nums=0;line_nums<lines;line_nums++) { /*设置笔记落下位置*/ /*显示坐标(从LCD左上方显示3 行) *x=0 *y=fb_var.yres-24 (减24,是因为笛卡尔坐标以左下方开始计算坐标值的) */ if(line_nums==0) { pen.x = 0* 64; pen.y = ( fb_var.yres-24 ) * 64; } else { pen.x = 0* 64; pen.y-= (line_box_ymax - line_box_ymin )* 64; //在上行的Y值上减去边框高 /*清空标志位,因为上一行的ymin永远当前行小*/ line_box_ymax=0; line_box_ymin=30000; } for ( n = 0; n < wcslen(str[line_nums]); n++ ) { FT_Set_Transform( face, 0, &pen ); error = FT_Load_Char( face,str[line_nums][n], FT_LOAD_RENDER ); if ( error ) { printf("FT_Load_Char ERROR "); continue; } FT_Get_Glyph( face->glyph, &glyph ); //获取字形图像 的信息 FT_Glyph_Get_CBox( glyph,FT_GLYPH_BBOX_TRUNCATE,&acbox ); //获取此行文字的box if(acbox.yMax>acbox.yMin) { if(line_box_ymax<acbox.yMax) line_box_ymax=acbox.yMax; if(line_box_ymin>acbox.yMin) line_box_ymin=acbox.yMin; } draw_bitmap( &slot->bitmap, slot->bitmap_left, fb_var.yres- slot->bitmap_top ); pen.x += slot->advance.x; } } FT_Done_Face( face ); FT_Done_FreeType( library ); } int main(int argc,char **argv) { int fd_fb,fd_hzk; struct stat hzk_start; //HZK16文件信息 wchar_t *chinese_str[]={L"韦东山gh",L"abc 中国chinese",L"哈哈哈哈wqe"}; if ( argc != 2 ) { printf ("usage: %s font_file ", argv[0] ); return 0; } fd_fb=open("/dev/fb0", O_RDWR); if(fd_fb<0) { printf("can't open /dev/fb0 "); return 0; } if(ioctl(fd_fb,FBIOGET_VSCREENINFO,&fb_var)<0) { printf("can't get var "); return 0; } if(ioctl(fd_fb,FBIOGET_FSCREENINFO,&fb_fix)<0) { printf("can't get fix "); return 0; } screensize=fb_var.xres*fb_var.yres*(fb_var.bits_per_pixel/8); //显存大小 fbmem =(unsigned char *)mmap(NULL,screensize, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED, fd_fb, 0); //映射fb0 if(!fbmem) { printf("can't map /dev/fb0 "); return 0; } memset(fbmem, 0, screensize); //清屏黑色 /*显示3 行 矢量文字*/ lcd_vector_show(argv[1], chinese_str,3); munmap(fbmem,screensize); return 0; }
2.居中显示
参考第11页:https://wenku.baidu.com/view/060a0b44f12d2af90342e63a.html?from=search
1)首先定义一个用来存储一行文字的字形图像数组
#define MAX_GLYPHS 100 //最多存储一行100个字 TGlyph glyphs[MAX_GLYPHS]; /* glyphs table */
2)首先以坐标(0,0)为基值,获取每个文字的字形图像和坐标值,存到glyphs[]里
/*初始化库,获取face,设置字体*/ error = FT_Init_FreeType( &library ); /* initialize library */ if(error) { //... ...} error = FT_New_Face( library, argv[1], 0, &face ); /* create face object */ if(error) {//... ...} FT_Set_Pixel_Sizes(face, 24, 0); ... ...
int num_glyphs = 0; PGlyph glyph = glyphs; // Pglyph在库里被定义为Tglyph *, glyph指向glyphs int pen_x = 0; int pen_y = 0; for (n = 0; n < wcslen(wstr); n++) // wstr: wchar_t类型的文字数组 { glyph->index = FT_Get_Char_Index( face, wstr[n]); //存储每个文字的索引值 glyph->pos.x = pen_x; //记录每个文字的坐标值,后面会用来设置字形图像的位置信息 glyph->pos.y = pen_y; error=FT_Load_Glyph(face, glyph->index, FT_LOAD_DEFAULT); //通过索引值,找到face(字体文件)里的字形图像,并放到face->glyph字符槽里. if ( error ) continue; FT_Get_Glyph(face->glyph, &glyph->image );//然后存储每个文字的字形图像 if ( error ) continue; FT_Glyph_Transform(glyph->image, 0, &glyph->pos ); //使用FT_Glyph_Transform(),使glyph->image包含位置信息 pen_x += face->glyph->advance.x; // 以1/64像素点为单位 glyph++; } num_glyphs= glyph- glyphs; //获取转换成功的文字个数
3)通过glyphs[]存的一行字形图像,计算出边界框
FT_BBox bbox; bbox.xMin = bbox.yMin = 32000; bbox.xMax = bbox.yMax = -32000; /*判断一行文字的边界框范围*/ for ( n = 0; n < num_glyphs; n++ ) { FT_BBox glyph_bbox; FT_Glyph_Get_CBox(glyphs[n].image, FT_GLYPH_BBOX_TRUNCATE, &glyph_bbox ); // FT_GLYPH_BBOX_TRUNCATE:获取的坐标信息以像素坐标为单位 if (glyph_bbox.xMin < bbox.xMin) bbox.xMin = glyph_bbox.xMin; if (glyph_bbox.yMin < bbox.yMin) bbox.yMin = glyph_bbox.yMin; if (glyph_bbox.xMax > bbox.xMax) bbox.xMax = glyph_bbox.xMax; if (glyph_bbox.yMax > bbox.yMax) bbox.yMax = glyph_bbox.yMax; }
4)通过边界框,找到居中显示的坐标信息
int line_box_width; int line_box_height; line_box_width = bbox.xMax - bbox.xMin; //一行文字的宽度 line_box_height = bbox.yMax - bbox.yMin; //一行文字的高度 pen.x = (var.xres - line_box_width)/2 * 64; // var.xres:LCD总宽度 pen.y = (var.yres - line_box_height)/2 * 64;
5)通过坐标信息,将glyphs[]存的一行字形图像显示出来
for (n = 0; n < num_glyphs; n++) { //再次使用FT_Glyph_Transform(),更新glyphs[n].image里的坐标值 FT_Glyph_Transform(glyphs[n].image, 0, &pen); error = FT_Glyph_To_Bitmap(&glyphs[n].image, FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL, 0,1); //转化为位图,1:转换后并摧毁glyphs[n].image的内容 if( !error ) { FT_BitmapGlyph bit = (FT_BitmapGlyph)glyphs[n].image; draw_bitmap(&glyphs[n].image->bitmap, bit->left, var.yres - bit->top); //打印位图 FT_Done_Glyph(glyphs[n].image ); //注销一个Glyph } }