秒级随机值-常用方法:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(void)
{
int buf[10],i,j;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
buf[i]=rand()%100;
printf("%d ",buf[i]);
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}
上面的srand((unsigned)time(NULL));表示给rand()产生随机值的种子.
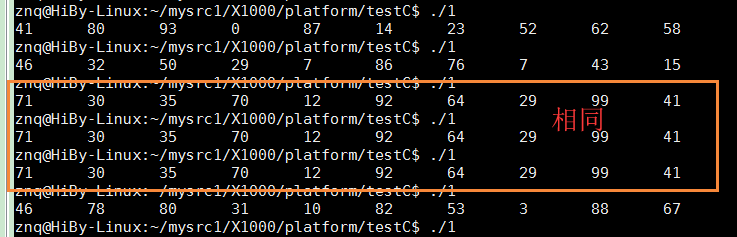
其中(unsigned)time(NULL)则将当前时间转为一个正整数,也就是说,如果我们如果在小于1秒之内多次运行该代码,则随机值都是相同的.
编译运行-如下图所示,可以看到如果运行时间小于1秒时,则随机值都是相同的:
毫秒级实现
- 可以通过ftime()函数来获取timeb结构体,既可实现毫秒级随机数变化了
其中ftime()函数如下:
int ftime(struct timeb *tp);
其中timeb结构体定义如下:
struct?? timeb{ time_t time; /* 为1970-01-01至今的秒数*/ unsigned short millitm; /* 毫秒值 */ short timezonel; /* 为目前时区和Greenwich相差的时间,单位为分钟 */ short dstflag; /* 为日光节约时间的修正状态,如果为非0代表启用日光节约时间修正 */ };
代码如下所示:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
int main(void)
{
int buf[10],i,j;
struct timeb timer;
ftime(&timer);
srand(timer.time * 1000 + timer.millitm);
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
buf[i]=rand()%100;
printf("%d ",buf[i]);
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}